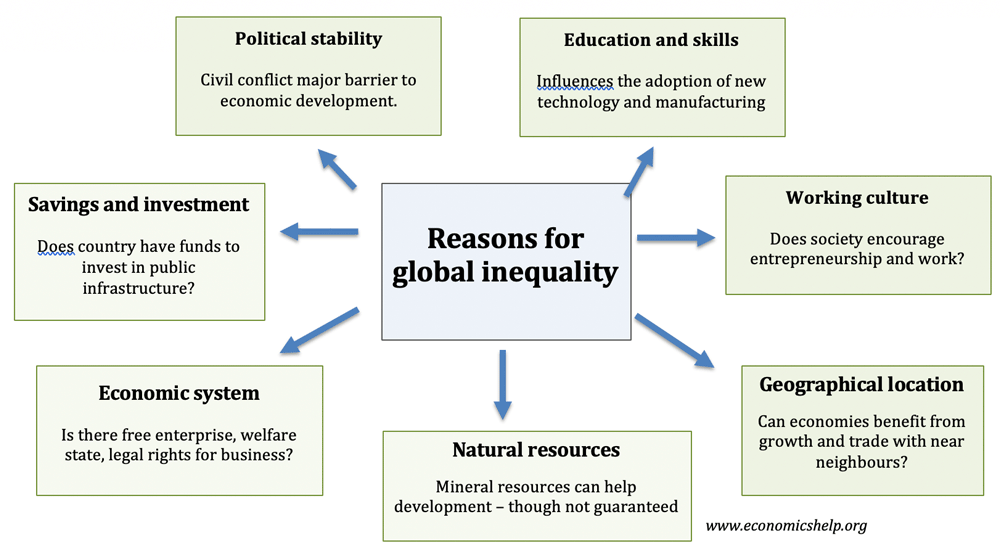
Why is there so much global inequality?
Living standards vary significantly across the globe. Wealthy economies, such as the US have an average GDP per head (at PPP) of $59,495 in the US (IMF 2017) This compares to an average annual income as low as $808 Burundi. (IMF 2017) There are many reasons for these divergences in income including – historical trends, …