Measuring unemployment
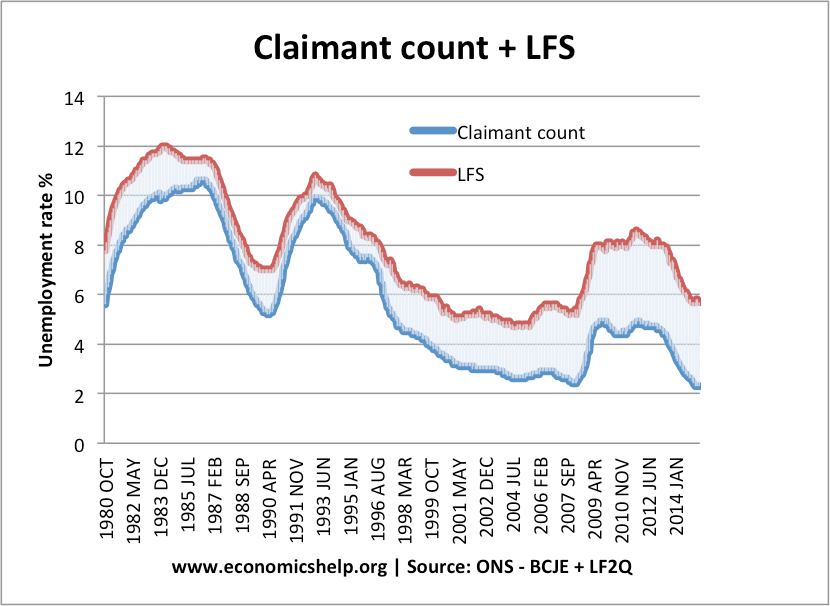
In the UK there are two main measures of unemployment – The claimant count (number receiving unemployment benefits) ILO – Labour Force Survey (A survey which asks – are you unemployed and actively seeking work?) Graph showing unemployment levels UK Unemployment In recent years, the gap between the labour force survey and the claimant count …