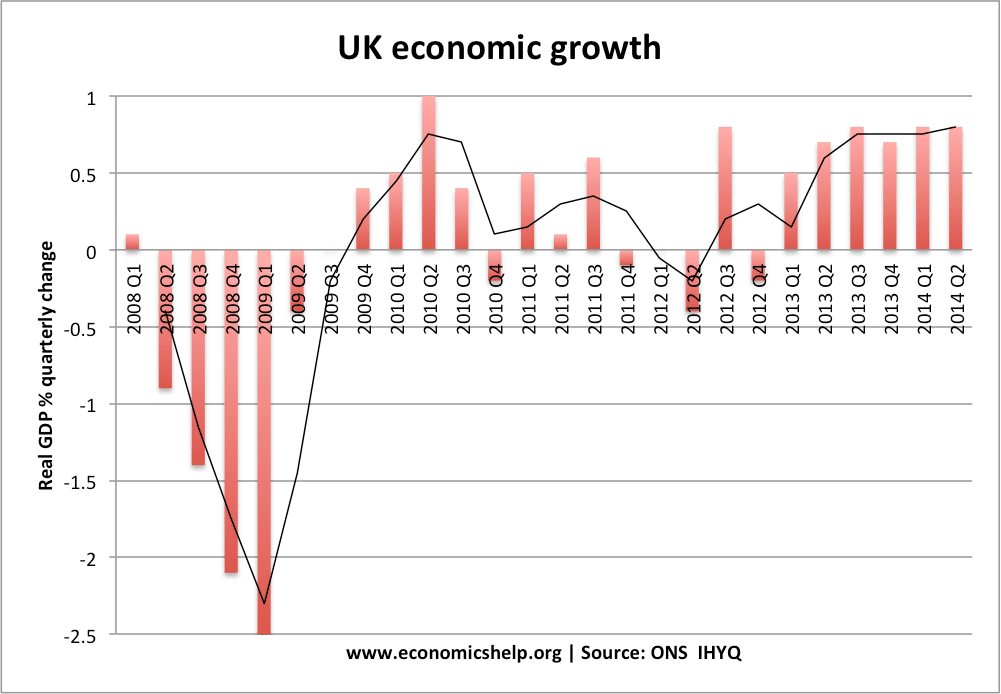
UK Monetary Policy
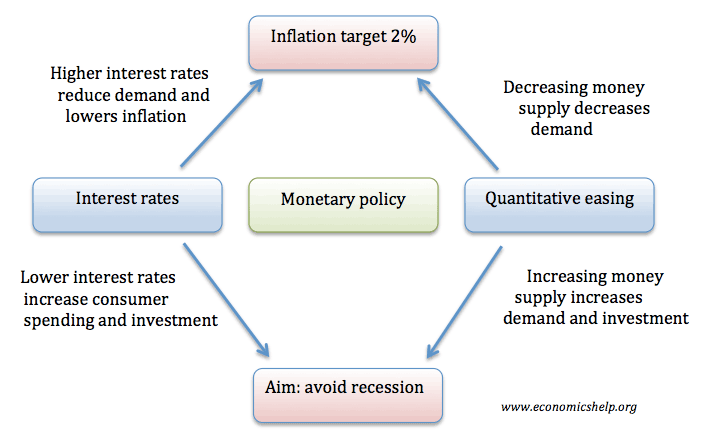
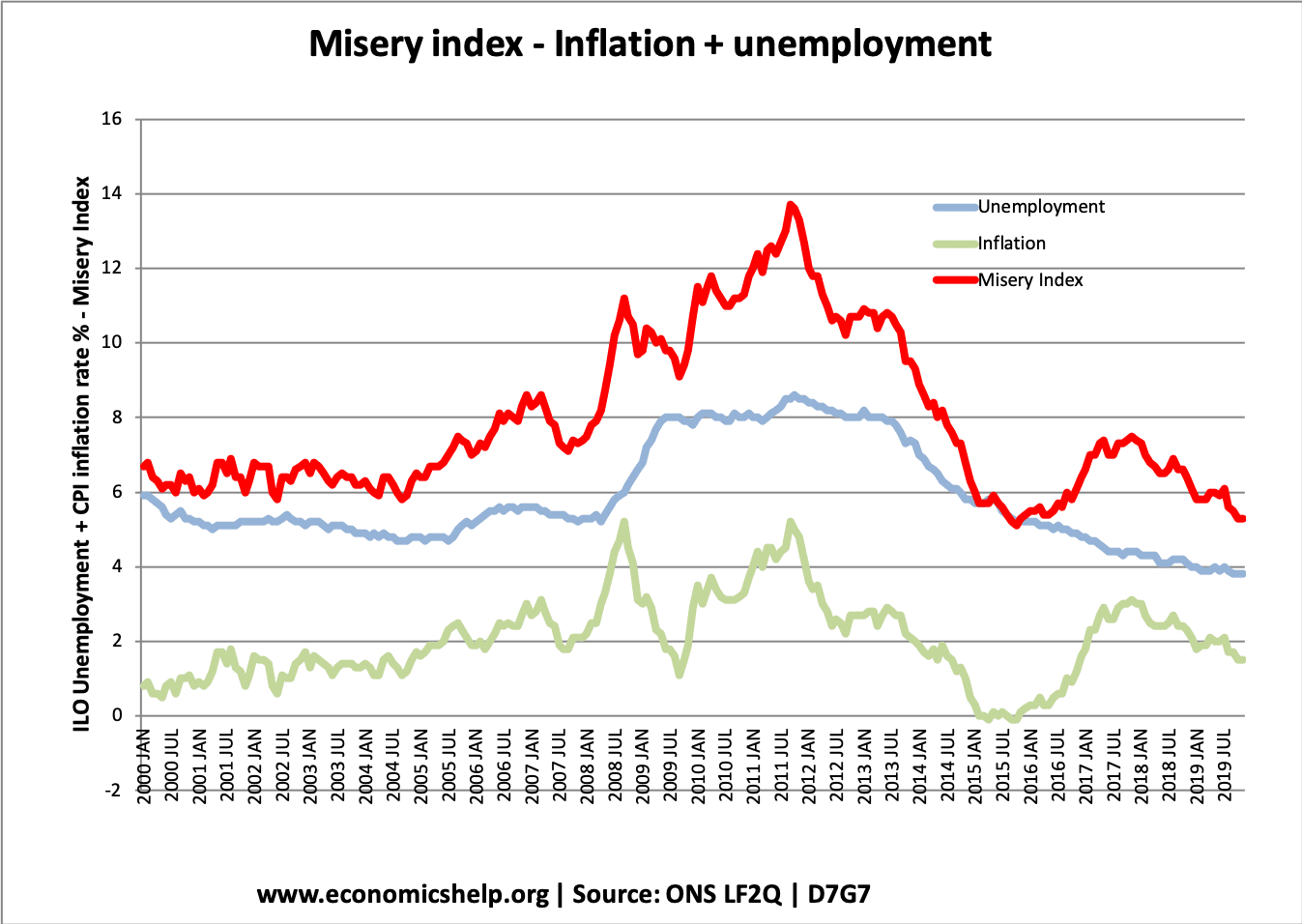
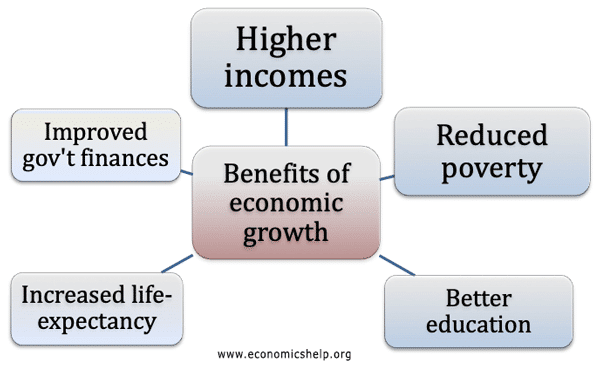
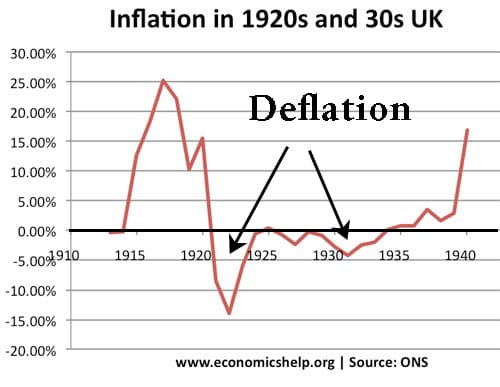
Monetary policy involves using interest rates and other monetary tools to influence the levels of consumer spending and aggregate demand (AD). In particular monetary policy aims to stabilise the economic cycle – keep inflation low and avoid recessions. Aim of monetary policy Low inflation. UK target is CPI 2% +/-1. Low inflation is considered an important …