Economic development implies an improvement in economic welfare through higher real incomes and other welfare indices such as improved literacy, better infrastructure, reduced poverty and better health care.
Economic development requires a degree of political stability, investment and mixture of public and private initiatives to increase economic potential.
The main factors affecting economic development include
- Levels of infrastructure – e.g. transport and communication. In recent years, economic development in Central Africa has been improved due to increased investment in roads, railways and seaports. Part of this investment has come from Chinese companies who have a vested interest in transporting raw materials from Africa to China.
- Education. Levels and standards of education have a significant influence on labour productivity. Without basic literacy and numeracy, it is difficult for an economy to develop from manual labour to new higher tech industries in the service sector. For example, good levels of education in India have given opportunities for growth in service industries, such as IT and call centres.
- Levels of inward investment. Developing countries that can attract inward investment can see significant growth in development due to higher levels of capital and benefits of attracting multinational companies into their economy. For newly industrialised countries (NICs), inward investment has played a significant role in increasing economic development. For example in 2011, inward investment in Brazil stood at $101bn.
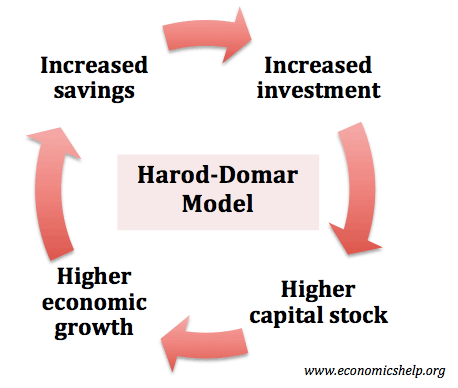
- Levels of savings/capital In growth models, such as Harod Domar, levels of savings and capital are seen as a key factor in determining economic growth. Higher savings enables a virtuous circle of increased investment, higher growth, and therefore, higher savings.
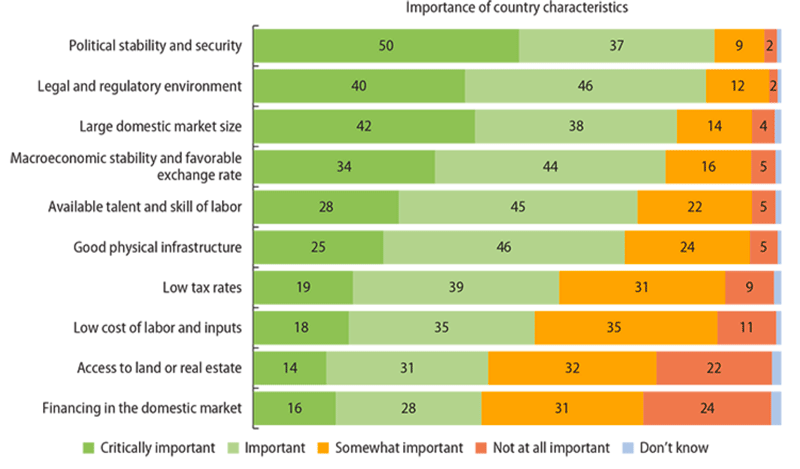
- Political stability / Law and order. Political stability and the protection of private property was ranked as the most important factors for encouraging firms to invest in developing economies. Any sign of instability increases the economic and personal risk of investing in developing countries.
The biggest block to development is prolonged civil unrest/military conflict as this causes investment to dry up and resources to be wasted in unproductive means.
- Macroeconomic stability. Similar to political stability, macroeconomic stability encourages investment and development. This involves low rates of inflation and exchange rate stability. Rapid devaluation can cause capital flight and a decline in growth.
- Labour mobility. Is labour able to move from relatively unproductive agriculture to more productive manufacturing?
- Foreign aid. Targeted aid, can help improve infrastructure and living standards. It can be important for developing economies with low levels of savings and capital investment. Aid depends on how it is used – whether it is tied to trade deals or used to overcome market failure in areas such as education and health care. There is also some criticism of foreign aid that it can influence incentives and
- Regional effects. Economic development is strongly influenced by the development of an economies neighbours. For example, in the 1980s and 1990s, south east Asia showed strong levels of economic growth and development. However, Sub-Saharan African countries experienced very slow growth. This is partly due to the gravity effect – the theory that trade is most profitable and efficient with near neighbours. If a neighbour does well, there tends to be spill over effects, such as increased trade and increased investment.
- Natural resources. Ceteris paribus countries with higher levels of natural resources can use this for economic development. For example, the revenues gained from oil have enabled the Gulf states to develop rapidly gaining high levels of real GDP. For African and Asian countries, raw materials are an important source of revenue and export earnings which enables higher development.
- However, the link between natural resources and development is not straightforward. One theory suggests raw materials can lead to a ‘resource curse‘ where an economy is stuck in producing primary products with no incentive to diversify the economy. It can also depend on whether natural resources are owned by developing economy and actually filter through to different sections of society.
- Tax rates and levels of corruption – e.g what percentage of tax rates are actually collected and spent on public services. For foreign multinationals, a low tax rate may be important to encourage investment. However, there needs to be a balance as the government need to collect tax to fund public services and public infrastructure.
- Free trade vs protectionism. An important debate in economic development is between the benefits of free trade versus protectionism. Removal of tariff barries can lead to a rise in exports, which contribute towards economic development. Asian countries, such as Korea, Taiwan and China have all benefitted from removal in tariffs. However, for developing economies stuck in producing primary products (where they have static comparative advantage) there is a strong case for temporary tariffs to enable new infant industries to develop.
- Tourism. For developing economies with an attractive climate and environment, tourism can be an important source of foreign earnings and incentive to develop infrastructure and new hotels.
Evaluation – other possible factors that influence economic development
- Culture of entrepreneurship. For example, in the past 20 years, India has seen a shift from a conservative religious society to a more secular society with a greater focus on material improvement.
- Political system. Some argue a Command economy can lead to economic stagnation, e.g. Cuba. China has successfully managed a partial economic shift to free-market based economy (with still political control of Communist Party)
- Regulation/free market system. Free market economists, such as Milton Friedman argue the openeness of an economy is important. For example, privatisation and deregulation, reduces barriers to invesment and economic growth.
Low income trap
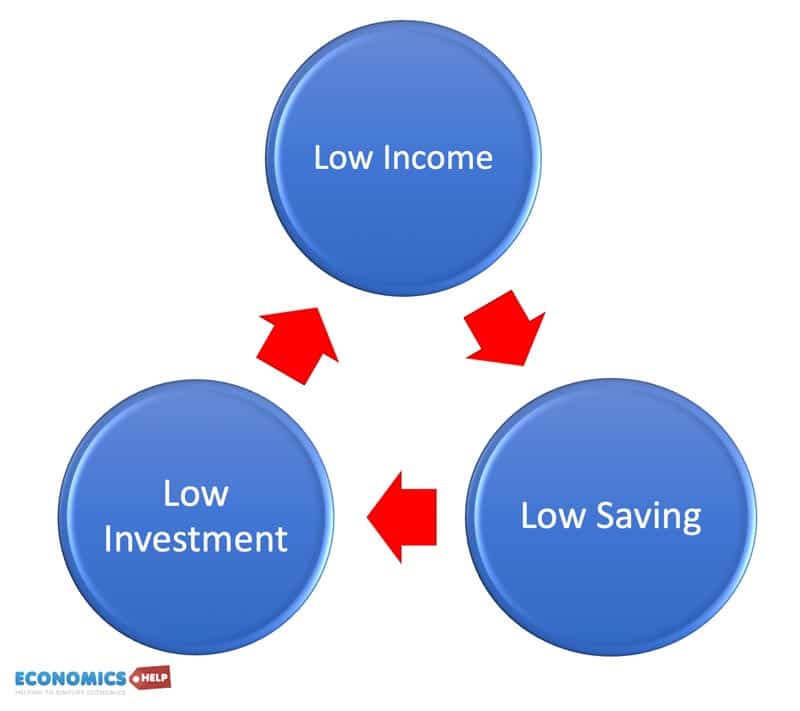
A low-income trap is when an economy gets caught in low growth and struggles to ‘break out’. With low income, savings will be low, leading to low investment and low growth. The economy will focus on commodity exports
Related

I read this, I want to economic development related economic sector for example primary sector, secondary sector—–ect
Why is development preferred over underdevelopment??
Why is subsaharan africa yet to attain development?
Poor education, poor nutrition and health care, corruption
great,…help here, explain five issues that economists consider to be central to the process of economic development
Why Tanzania sees as a one poor country