- Production-based CO2 emissions is the amount of CO2 emitted in a particular country.
- Consumption-based CO2 emissions are adjusted for trade and reflect CO2 emissions related to goods and services consumed in a particular country.
Explanation of production vs Consumption-based CO2 emissions
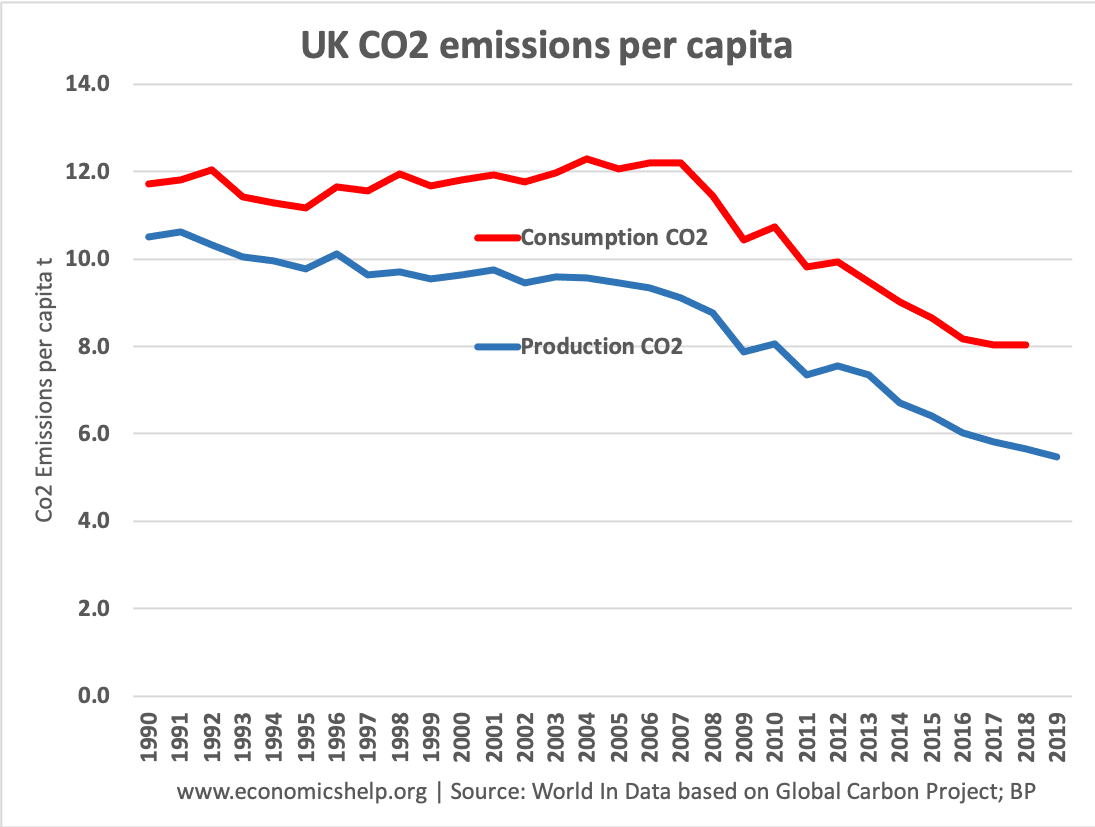
Suppose the UK used to produce its own steel, the production process would cause CO2 emissions reflected in UK stats. However, suppose the UK steel industry closes down and the UK now imports steel from China. Closing the UK steel industry would see a fall in UK CO2 emissions and a rise in Chinese CO2 emissions.
However, although the UK shows less production of CO2, the CO2 emissions still relate to UK based consumption.
Countries with a large trade deficit, (exports less than imports of goods) usually have lower production CO2 emissions than consumption
Example of UK consumption and production
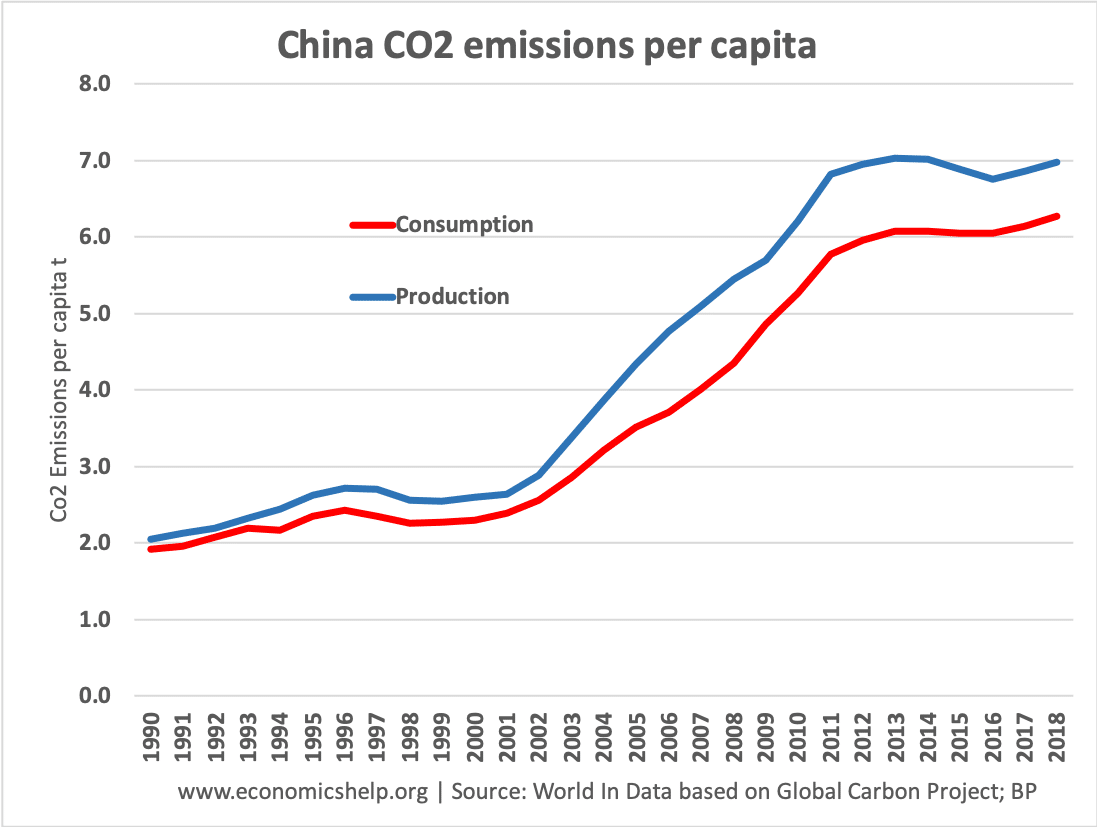
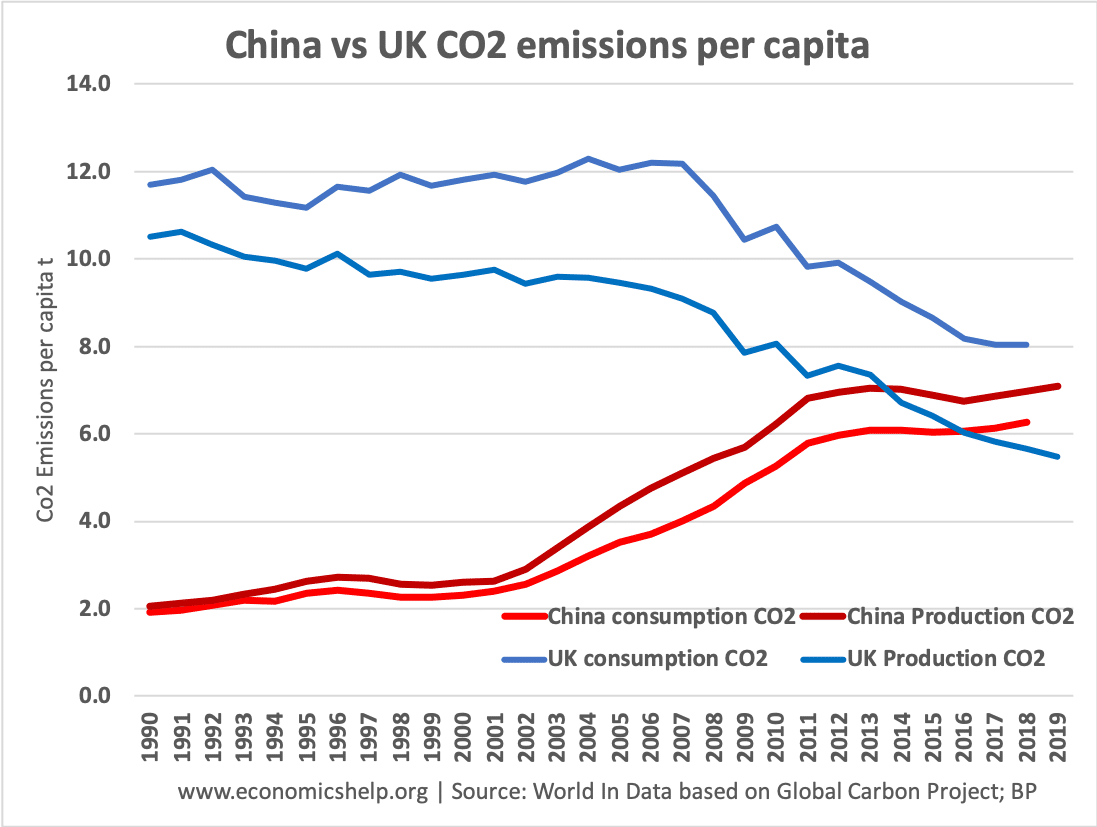
China CO2 emissions per capita – Production and consumption
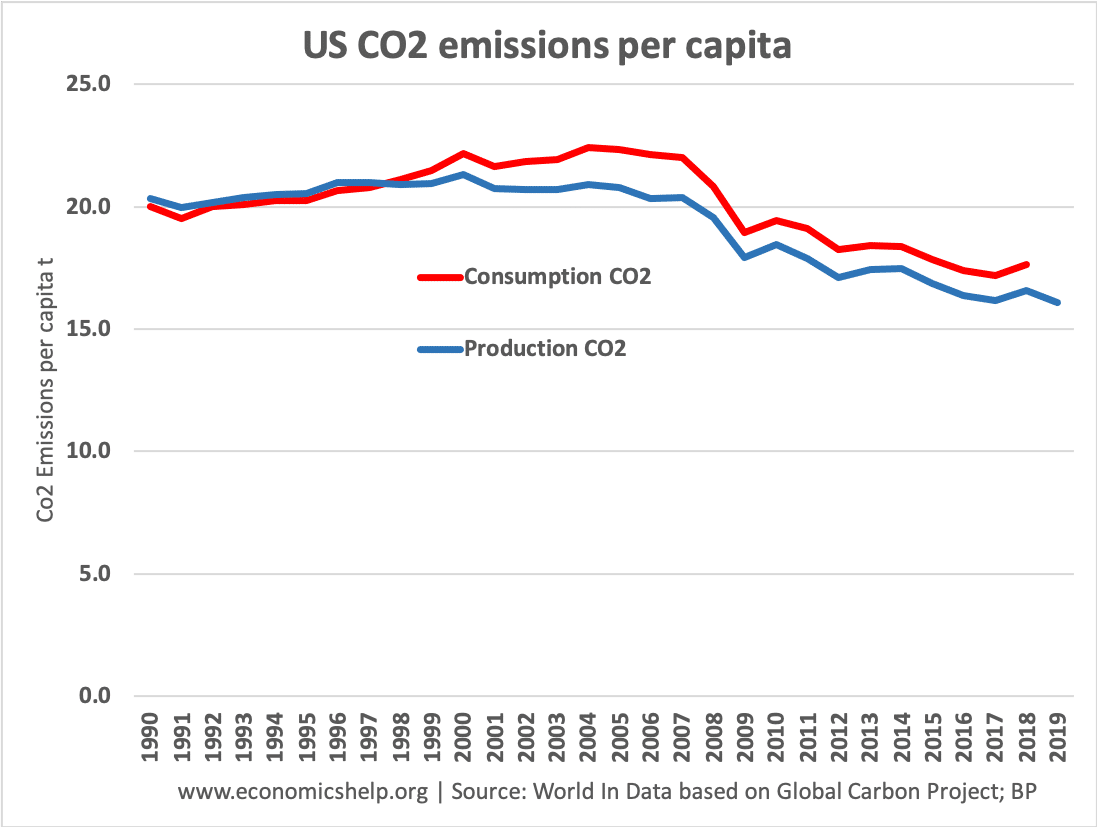
US CO2 emissions
In the 1990s, consumption and production levels of CO2 were very similar. A reflection of the US oil industry and relatively smaller share of trade. However, since 2000, consumption levels of CO2 have been marginally higher than production levels.
Qatar
Qatar has the highest level of CO2 emissions per capita, due to its energy-based economy – natural gas and oil. However, consumption-based CO2 emissions reduce this level.
China vs UK CO2 Emissions.
Related


Thank you for your explanation. Where can I obtain the historical data for the consumption and production of CO2 by country?
Kind regards