The learning effect can mean one of two things
- How education leads to increased productivity and higher wages
- How production processes can learn from past production to increase productivity over time.
The learning effect can lead to a learning curve – which represents how average costs of production change over time.
Learning effect – Education
When there is spending on education, people will gain more skills such as literacy, numeracy and problem-solving skills. With this greater education, the general productivity (output per worker) of the economy will increase, leading to higher economic growth and firms will be able to increase wages.
Generally, economies with higher levels of education have higher real wages. An improvement in education should lead to higher productivity, though it may take considerable time.
Learning effect – production
Usually, when a product is first produced, the average cost of production is high because the first firm needs to learn by trial and error the best way to make the product. However, the more that the product is produced, firms will find more efficient ways to produce, and so they will learn how to make the good more efficiently. There are many different ways that firms can learn how to make goods cheaper.
- Finding the most efficient combination of capital and labour
- Making small improvements in the production process to reduce inefficiencies.
- Finding better materials, which can do the job more cheaply.
- Economies of scale from increasing production.
- External economies of scale as the industry increases in size. As the product develops, firms will benefit from improved supply chains and access to raw materials.
- As price falls and demand rises, it will stimulate more research and development leading to more productivity gains.
- As the market expands, the market is likely to attract new entrants and become more competitive, keeping prices down.
Example of learning effect – Solar modules
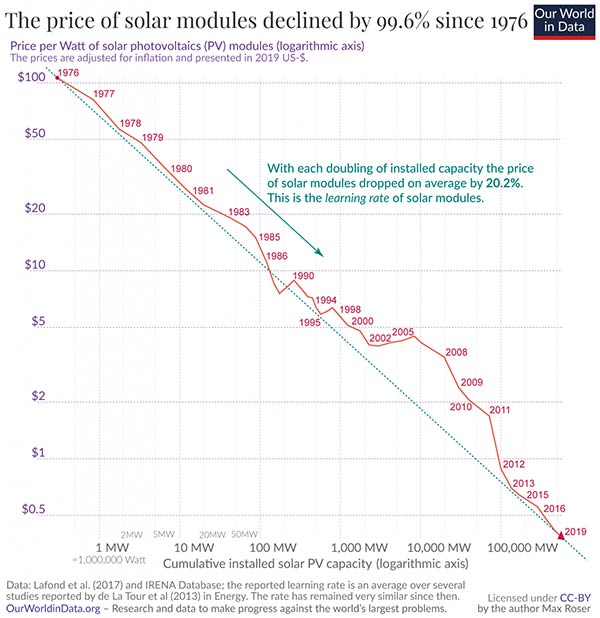
Price of electricity – learning curves
This graph shows the learning effect of new renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power
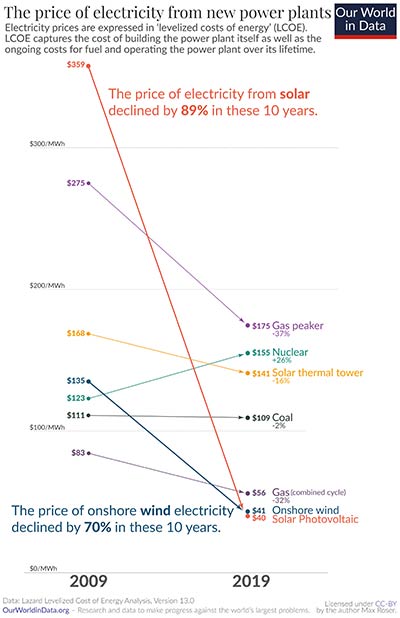
This shows that wind and solar power have steep learning curves suggesting that their prices will continue to fall.
Why no learning effect for coal and nuclear power?
Coal powered energy is an established industry that has been around for many years, so its learning curve will have been stronger in the industry’s birth. These days, the biggest cost is the raw material coal. Productivity improvements cannot reduce the price of raw materials and so there is limited scope for reducing costs when raw material costs are fixed. Solar energy is not limited by raw material costs (the sun is free) Technology has the biggest impact on output.
Nuclear power has seen increased costs, which might reflect limited increase in capacity (countries are wary of massively increasing nuclear power). But, also as time progresses, countries may want to spend more on safety features which increases unit cost.
