Economic growth is an increase in national output/income (higher real GDP).
There are two main aspects of economic growth:
- Aggregate demand (AD) (consumer spending, investment levels, government spending, exports-imports)
- Aggregate supply (AS) (Productive capacity, the efficiency of economy, labour productivity)
To increase economic growth
We need to see a rise in demand and/or an increase in productive capacity:
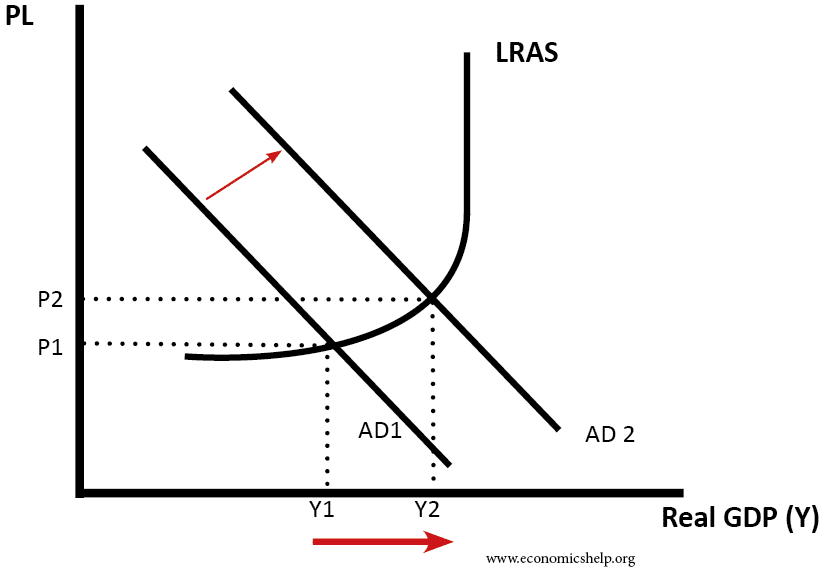
1. A rise in aggregate demand
Aggregated demand can increase for various reasons.
- Lower interest rates – reduce the cost of borrowing and increase consumer spending and investment.
- Increased real wages – if nominal wages grow above inflation then consumers have more disposable to spend.
- Higher global growth – leading to increased export spending.
- Devaluation, making exports cheaper and imports more expensive, increasing domestic demand.
- Rising wealth, e.g. rising house prices cause consumers to spend more (they feel more confident and can remortgage their house.
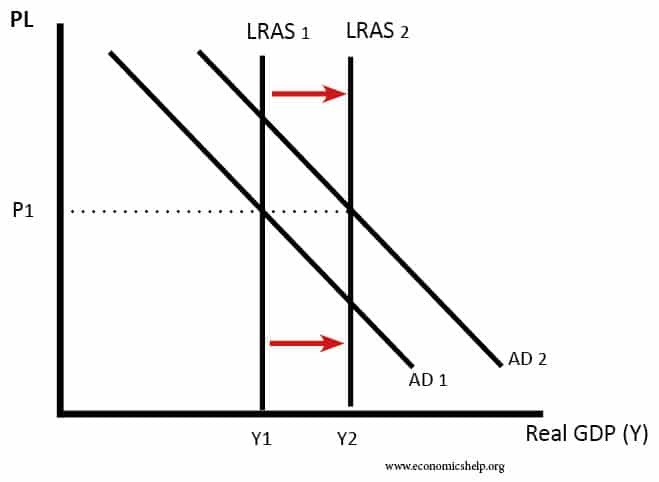
Growth in productivity
This is growth in aggregate supply (productive capacity). This can occur due to:
- Development of new technology, e.g. steam power and telegrams helped productivity in the nineteenth century. Internet, AI and computers are helping to increase productivity in the twenty-first century.
- Introduction of new management techniques, e.g. Better industrial relations helps workers become more productive.
- Improved skills and qualification.
- More flexible working practices – working from home, self-employment.
- Increased net migration – especially encouraging workers with the skills that are in short supply (e.g. builders, fruit pickers)
- Raise retirement age and therefore increasing the supply of labour.
- Public sector investment – e.g. improved infrastructure, increased spending on education and
To what extent can the government increase economic growth?
A government can try to influence the rate of economic growth through demand-side and supply-side policies,
- Expansionary fiscal policy – cutting taxes to increase disposable income and encourage spending. However, lower taxes will increase the budget deficit and will lead to higher borrowing. The expansionary fiscal policy is most appropriate in a recession when there is a fall in consumer spending.
- Expansionary monetary policy (now usually set by independent Central Bank) – cutting interest rates can boost domestic demand.
- Stability. A key function of the government is to provide economic and political stability which enables the usual economic activity to take place. Uncertainty and political tension can discourage investment and economic growth.
Government supply-side policies
- Investment in infrastructure, e.g. new roads, railways lines and broadband internet – increases productive capacity and reduces congestion.
- Privatisation and deregulation – increase efficiency and productivity.
Factors beyond the government’s influence
- The rate of technological innovation tends to come from the private sector and it is hard for the government to influence this.
- Industrial relations and workers motivation are driven by the private sector. The government’s influence on worker morale and motivation is limited at best.
- Entrepreneurs who set up a business are largely self-motivated. Though government regulations and tax rates can influence the willingness of an entrepreneur’s willingness to take risks.
- Level of savings can influence growth (e.g. see Harrod-Domar model) Higher savings enable higher investment, but it can be hard for the government to influence savings.
- Willingness to work. In the post-war period, the defeated countries Germany and Japan saw rapid rates of economic growth – reflecting a determination to rebuild after the war. UK economy had less dynamism – this could reflect different attitudes to work and willingness to introduced new ideas.
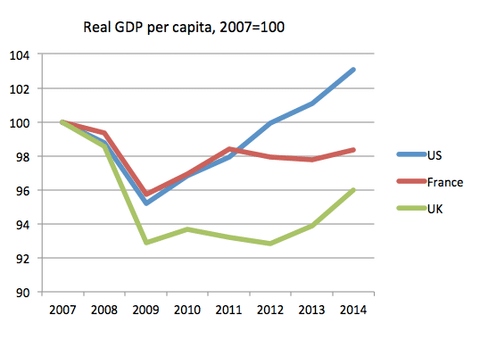
- Global growth exerts a strong influence on any economy. If the world enters a global recession, it is very hard for an individual economy to avoid the costs. For example, the credit crunch of 2009 negatively affected economic growth in OECD economies.
US, France and the UK all entered the recession in 2009. However, the better recovery in the US could be due to different policy responses. Expansionary fiscal policy of 2009/10 and a looser monetary policy.
Governments often over-estimate how much they are able to increase productivity growth. Most of the technological progress comes from private sector without government intervention. Supply-side policies can help increase efficiency to some extent, but it is debatable how much they can actually increase growth rates.
For example, after supply-side policies of the 1980s, the government hoped there had been a supply-side miracle which enables a much faster rate of economic growth. However, the Lawson boom of the 80s proved to be unsustainable and the UK growth rate remained pretty much the same at around 2.5% At the very least supply-side policies will take substantial time, e.g. increasing labour productivity through education and training will take several years.
For developing economies with substantial infrastructure failures and lack of basic amenities, there is much greater scope for the government increasing growth rates. By providing basic levels of education and infrastructure the scope for higher growth rates is much higher.
Most productivity growth is determined by the private sector. With a few exceptions, most technological improvements come from private firms. It is the private sector which develops new technology which enables the vast majority of productivity growth we see in the UK. I’m sceptical of the government’s ability to invest in new technology which would boost this rate of productivity growth. (though it can happen – especially in war)
Economic growth in the UK
Since 1945, the UK economy has grown by an average of 2.5% a year. Most economists would argue that, on average, the UK’s productive capacity can increase by around 2.5% a year. This is known as the ‘trend rate of growth’ or ‘underlying trend rate’.
Note, even when the government tried supply-side policies, they usually failed to shift this long-run trend rate. (e.g. supply-side policies of the 1980s, did little to alter the long-run trend rate)
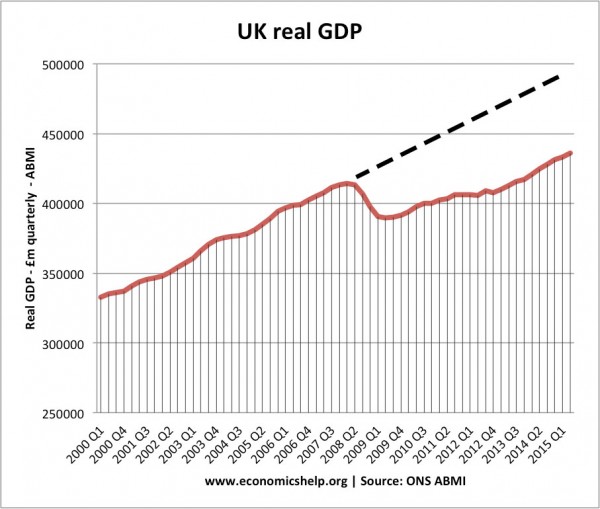
The graph below shows how actual GDP fell below the trend rate from 2008. This was due to the recession and a significant fall in Aggregate Demand.
Growth in productive capacity (AS) occurs because of:
- Improved technology developed by the private sector which enables higher labour productivity (e.g. development of computers enables greater productivity)
- Improved management techniques which enable a more skilled workforce.
- Improved education and training by both private sector and public sector
- Investment in infrastructure, e.g. building new roads and train lines. This is mainly the responsibility of the government.
The Problem of Demand
Since 2007, UK growth has fallen way below the trend rate. Between 2009-11, the problem was the precipitous fall in AD that occurred in 2009, and second, set back in 2011.
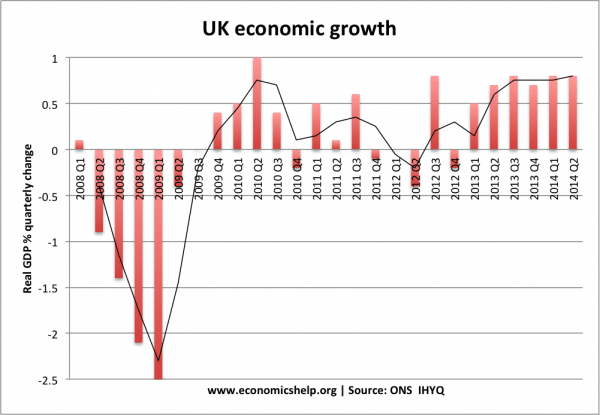
Demand fell in 2009 because
- Credit crunch – banks stopped lending. Firms couldn’t borrow to invest
- Fall in consumer confidence from financial concerns
- Rise in unemployment created negative multiplier effect
- Fall in house prices led to negative wealth effect and fall in confidence.
Demand in 2011 was weak because:
- Government spending cuts
- Fear of unemployment
- Low wage growth; real wages are falling because inflation is higher than nominal wage growth.
- Continuation of credit crunch
Unsurprisingly, this fall in economic output led to a sharp rise in unemployment.
The fundamental problem in the UK was insufficient aggregate demand. However, there is also a productivity problem
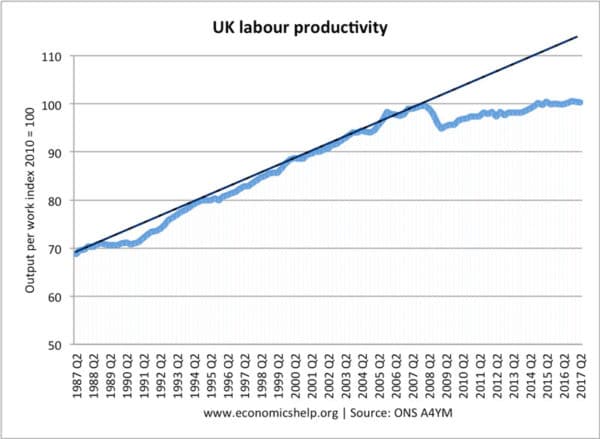
Since 2008 labour productivity has tailed off – only marginally growing and falling well behind the long-run trend rate. This is due to several factors
Fall in global productivity growth – (lower rate of technological improvement)
- Relatively low levels of investment and the adoption of new technology in the UK.
- UK specific shocks – fiscal austerity of 2010 onwards.
- Uncertainty over Brexit causing a delay in investment decisions
- More flexible labour markets leading to growth in low-wage jobs encouraging firms to employ cheap labour rather than investing in higher productivity.
Related

“The first is clearly impossible as we would bust at the seams.” Where is the evidence for this, what does it actually mean?
The UK population is already so large, that in order to grow economically the population would have to grow beyond the UK’s ability to support.
Another important factor impacting the economic growth of a nation is its Human Resource. You mentioned that “willingness to work” serves as a key factor in determining economic growth. The point seems very valid. However, only when a person is well-equipped with required skills and training, will his willingness to work bear desired fruit. Food for thought.
A country like Nigeria is endowed with natural resources making used of it in appropriate way hasn’t out in place….
These recommendations though grounded in academic principles fall short of understanding the underlying systemic deficiencies ib the South African economy. They fall even shorter in terms of the streaghths/opportunities to make the economy more efficient through better circulation of wealth and lowering the cost of living.
Increasing real wages is a lacklustre strategy which could only be the thought of an infant which has spent little to no time trying to come to grips with the problem.
What would you recommend for the growth of weaker economies
A weaker economy will have to industrialize and manufacture
Far away from the complicated ecnomic terms i think when you produce you realise self sufficiency and export
These economic policies requires in-depth understanding for application. However, sometimes I wonder whether economists in Liberia understand the basics of these concepts. At least just by reading them.
Some key factors to consider for an economy to grow are as follows:
Key Factors
1. Identify usual demand and usual supply.
2. Identify or create/compel new tastes to foster(encourage) new demand and new supply.
3. Take advantage of an enabling environment to foster economic growth.
4. Create an enabling environment for economic growth.
Explanation of key factors
1. If there’s demand for goods and services. If meet the demand and supply, the economy will grow.
2. New things, new ideas and innovations leads to new demand and new supply of goods and services that are important for economic growth.
3. Taking advantage means investing in businesses, producing/supplying goods and services in relation to demand. The surplus goods and services would even be exported.
The shortfall can sometimes be imported. However, there’s need to encourage more exports than imports.
4. An enabling environment is ensuring social, economic, political stability in a nation. Where there is social, economic and political stability; an economy can grow substantially.
I would like to learn more about growing a country’s GDP and per capita. So more information is very needed.
Economics is a very difficult concept as a science and achievable as an art as long as we play the right roll and overcome once responsibility factually on the ground Applying effectively and efficiently the recommended policies in solving the causes would allow a national economic growth’ In the Ethiopian context the current inflation and economic crises is automatically the result of answering the questions such as tax cut , wage raise , improving employee productivity minimizing imports and increasing exports un properly—
What if the aggregate demand is high
thanks for sharing this great information
We are chosen Noida’s best truck transport services providers. We have low-cost transport facilities for you. We provide nationwide services. It is very easy to book our trucks online with few steps. We have also a dedicated team who will assist you 24/7.
I think the tecnic is good but why african faces low GDP ?
Thanks For Giving Me Information It Really Helped Me Since I’m Making A Project On Economic Growth!
Sincerely: Gal Zuck 🙂
Thanks for providing this valuable knowledge on how to increase economic growth. It helps me with my projects.