Definition of the trend rate of economic growth
The trend rate of economic growth is the average sustainable rate of economic growth over a period of time. For example, in the UK, the trend rate has tended to be about 2.5%.
The trend rate of growth is the rate of economic growth that can be maintained without inflationary pressures. It is also known as the ‘underlying trend rate of growth’.
Fluctuations from the Trend Rate
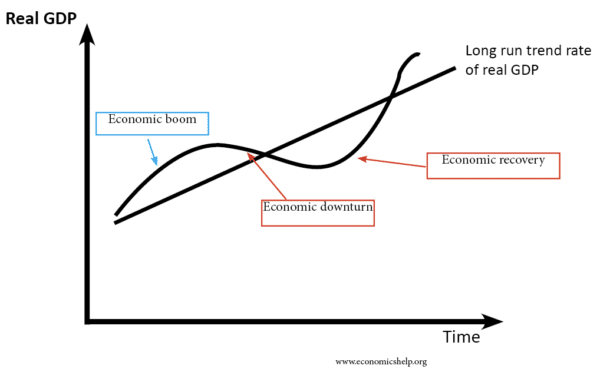
- The real GDP growth rate can diverge from this average trend. For example, in a boom, growth may be higher than the trend rate. However, sustained economic growth above the trend rate is likely to cause inflation and be unsustainable.
- When economic growth is below the trend rate, it will cause an increase in spare capacity, higher unemployment and usually a lower inflation rate.
Factors affecting the trend rate of economic growth
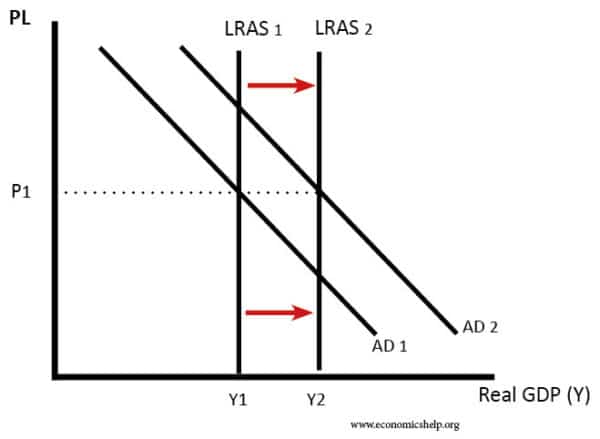
The trend rate of growth is determined by the growth of productivity and the growth of Long Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS). Therefore, the long-run trend rate will be determined by
- Investment in capital – higher levels of investment enable higher productive capacity
- Technological development. Improved technological progress can enable higher productivity of capital.
- Labour productivity – output per worker, will be determined by education, qualifications, skills and motivation of the labour force.
- Flexibility – are factors of production mobile and flexible?
- Public sector investment. Investment in public transport, education, healthcare will all affect the productive capacity of the economy
Fluctuations in demand can cause fluctuations in the actual growth rate.
Typically aggregate supply in the UK will increase by about 2.5% a year.
The trend rate of growth in China could be 8-9% a year. In China, there is more spare capacity and scope for efficiency gains – old state industries can easily cut costs and benefit from an elastic supply of labour.
AD / AS Diagram showing Trend Rate of Economic Growth
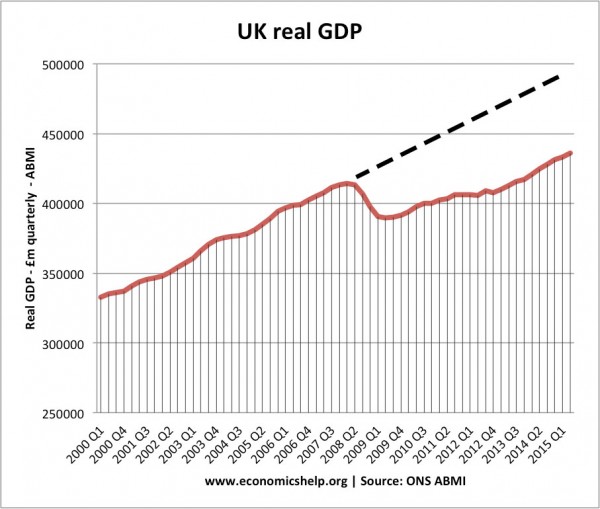
Trend Rate of Growth in UK
Between 2002 and 2007, the actual growth of real GDP is close to the trend rate. But, following the great recession of 2008, output fails to grow at the trend rate and stagnates.
Example of Trend Rate and Actual Growth in Mexico
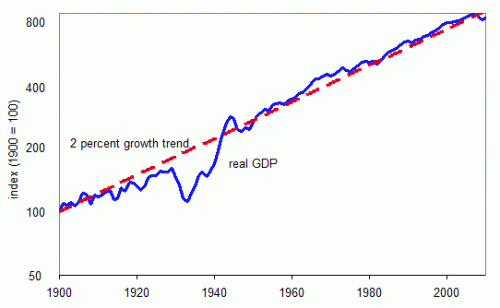 The red line indicates the trend rate of economic growth (averaging 2% a year.) (source image Vox)
The red line indicates the trend rate of economic growth (averaging 2% a year.) (source image Vox)
The blue line indicates actual Real GDP. In the 1930s (the great depression) output fell significantly, and it took over a decade to catch up.
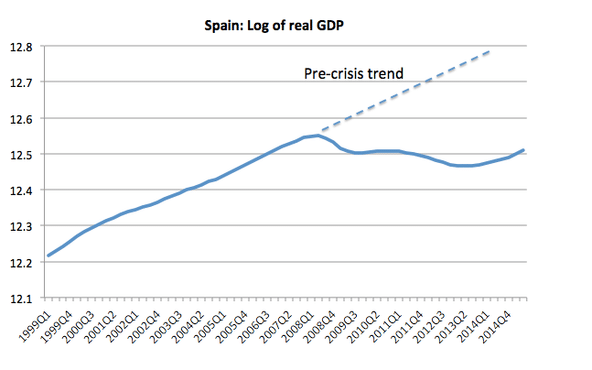
Spain’s trend rate of economic growth also hit by the great recession.
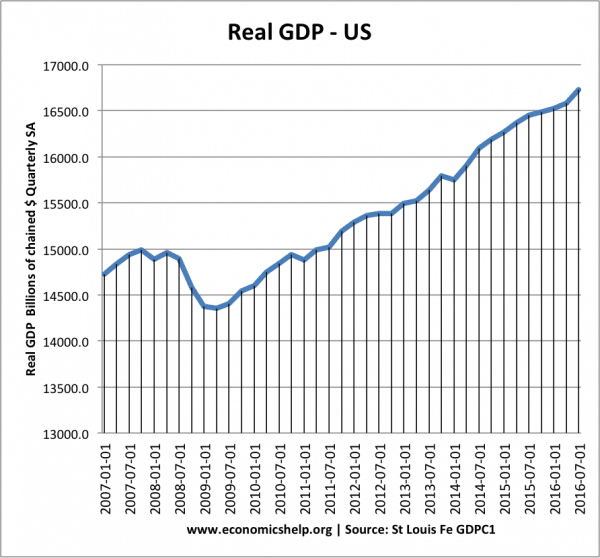
The US GDP
Related

how can we calculate trend growth rate?