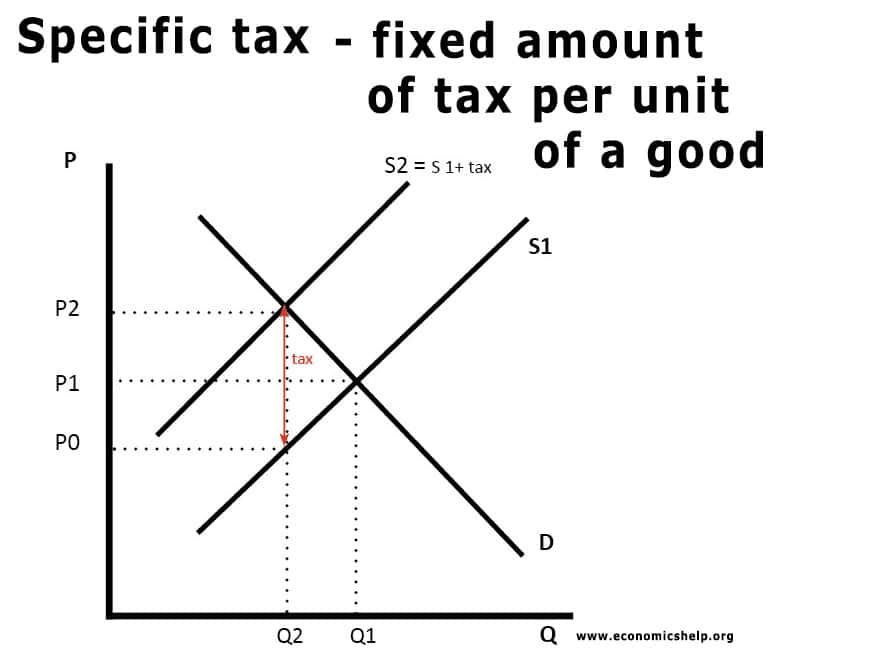
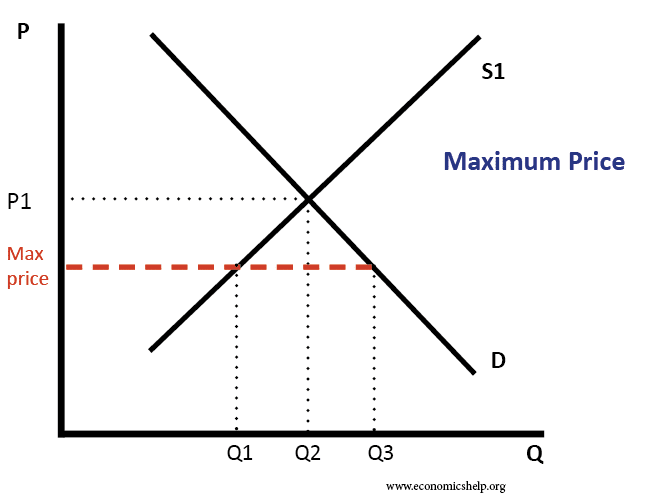
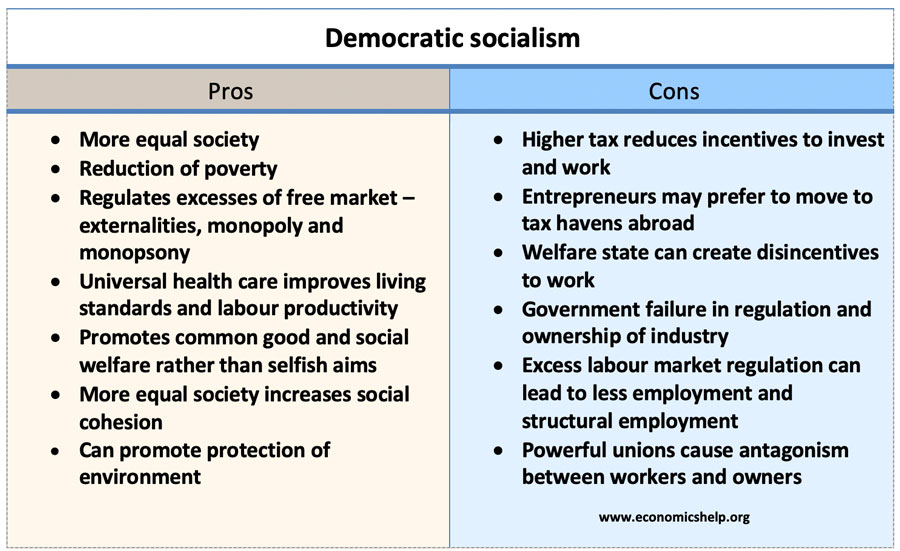
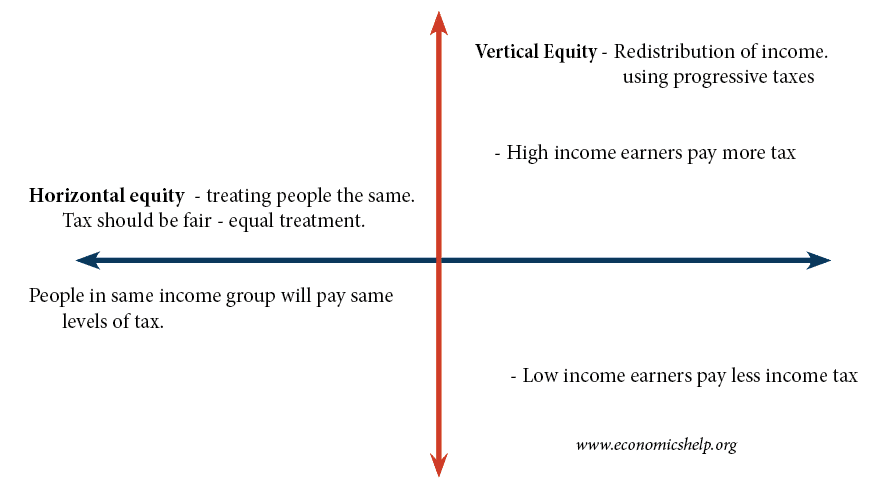
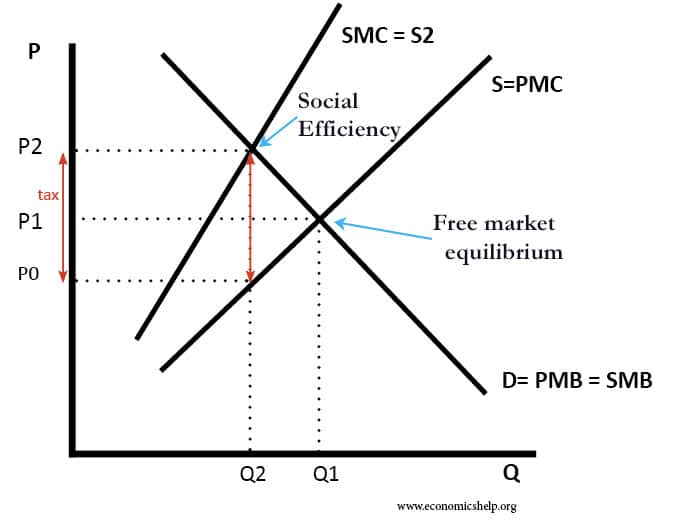
Efficiency vs Equity
A big issue in economics is the tradeoff between efficiency and equity. Efficiency is concerned with the optimal production and allocation of resources given existing factors of production. For example, producing at the lowest cost. See: Different types of efficiency Equity is concerned with how resources are distributed throughout society. Vertical equity is concerned with …