Inflation Targeting Pros and Cons
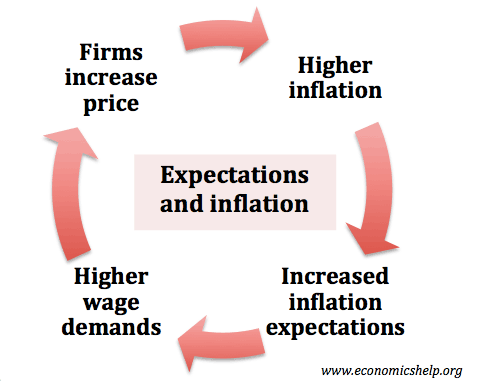
Inflation targeting means Central Banks are responsible for using monetary policy to keep inflation close to the agreed target (usually around 2%). Since the mid-1990s, inflation targeting has become widely adopted by developed economies, such as UK, US, and the Eurozone. Inflation targets were introduced to help reduce inflation expectations and help avoid the periods …