Quantitative easing: risks vs benefits
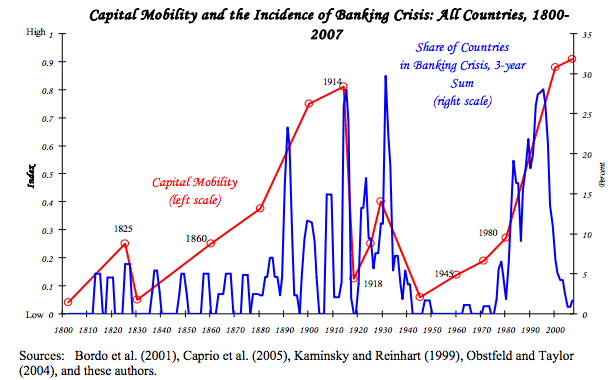
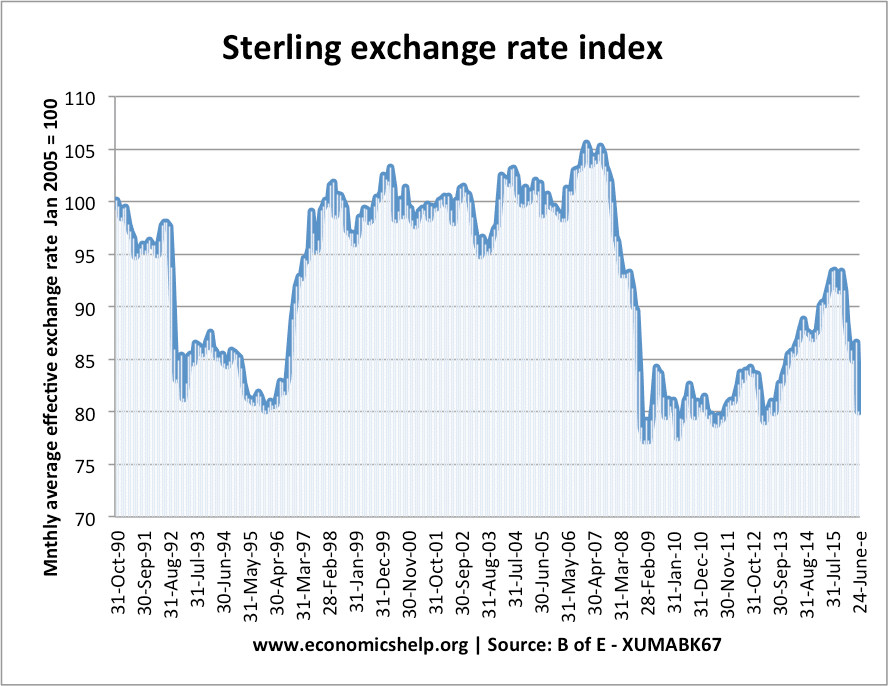
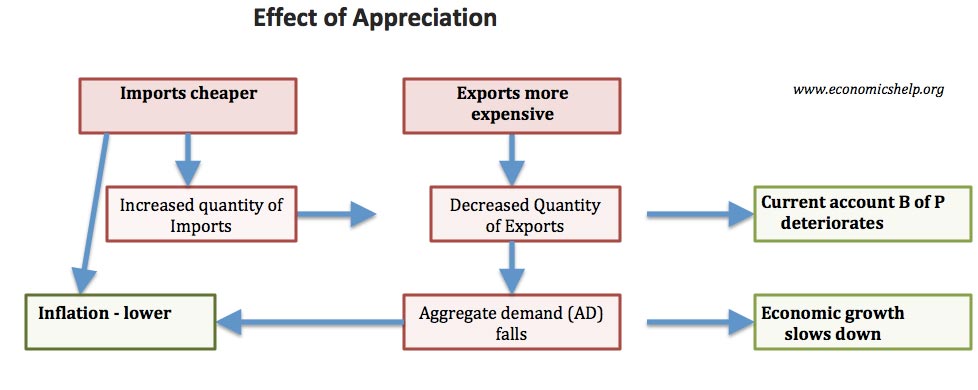
Readers Question: Could you comment on This BBC programme on Q.E. The programme highlights several criticisms of Quantitative Easing, especially the Q.E. adopted by the Bank of England. Since 2009, the Bank of England’s balance sheet has quadrupled, and now a third of all government bonds are now held by Bank of England. The programme …