Shortages
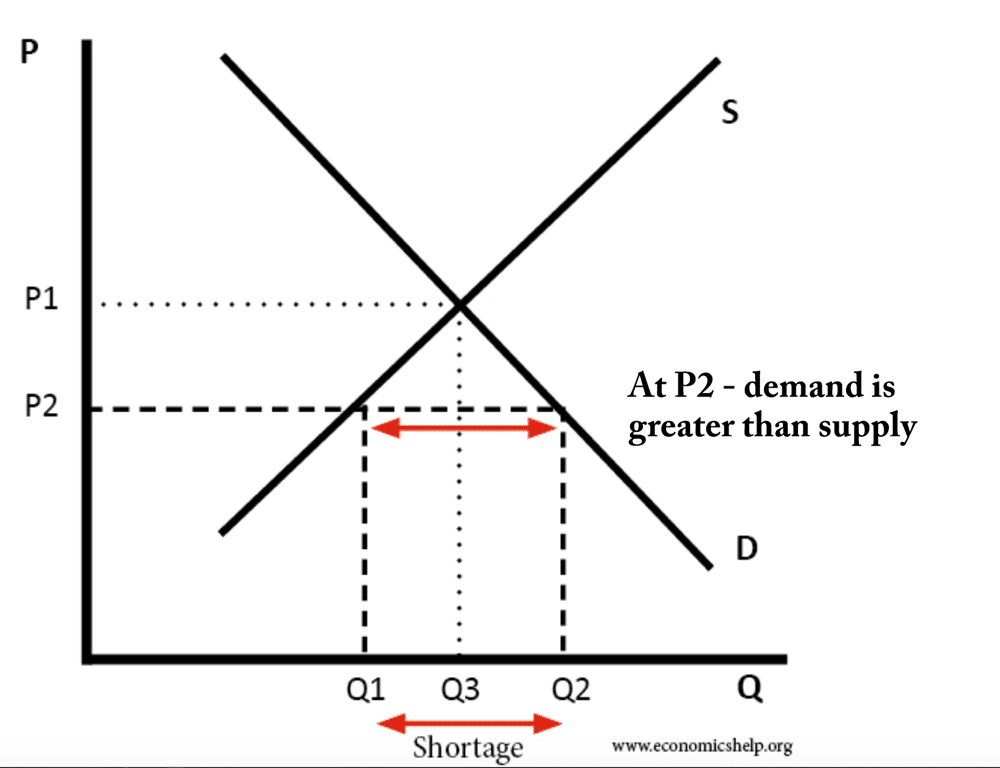
In economics a shortage occurs when demand is greater than supply, causing unfulfilled demand. A shortage can occur due to Temporary supply constraints, e.g. supply disruption due to weather or accident at a factory. Fixed prices – and unexpected surge in demand, e.g. demand for fuel in cold winter. Government price controls, such as maximum …