Benefits of Price Discrimination
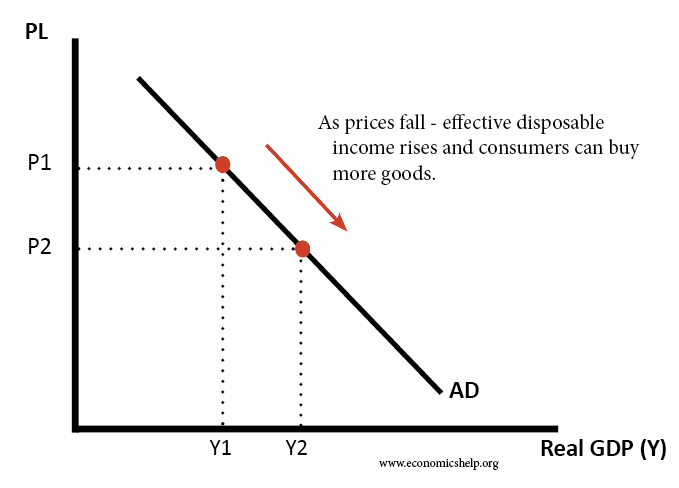
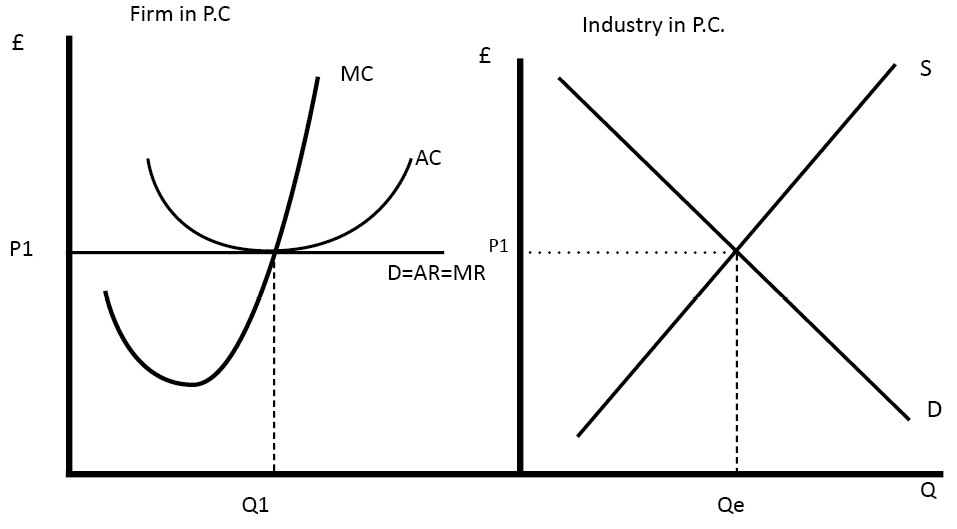
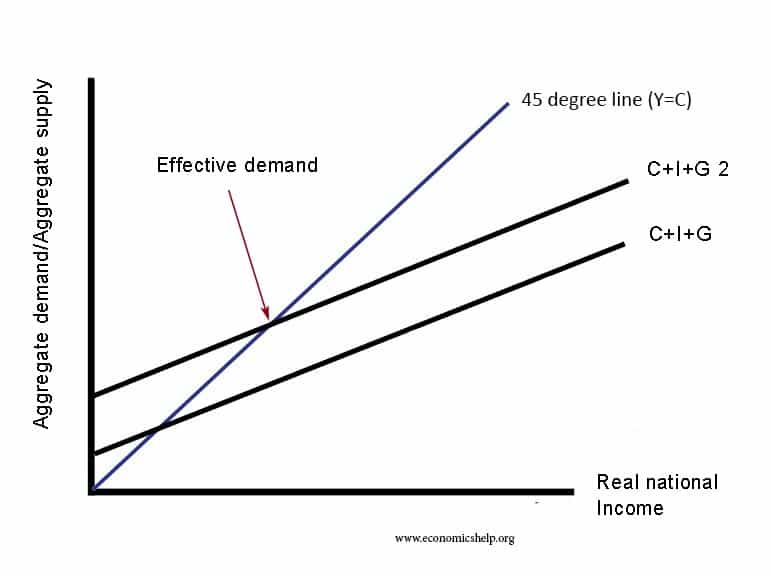
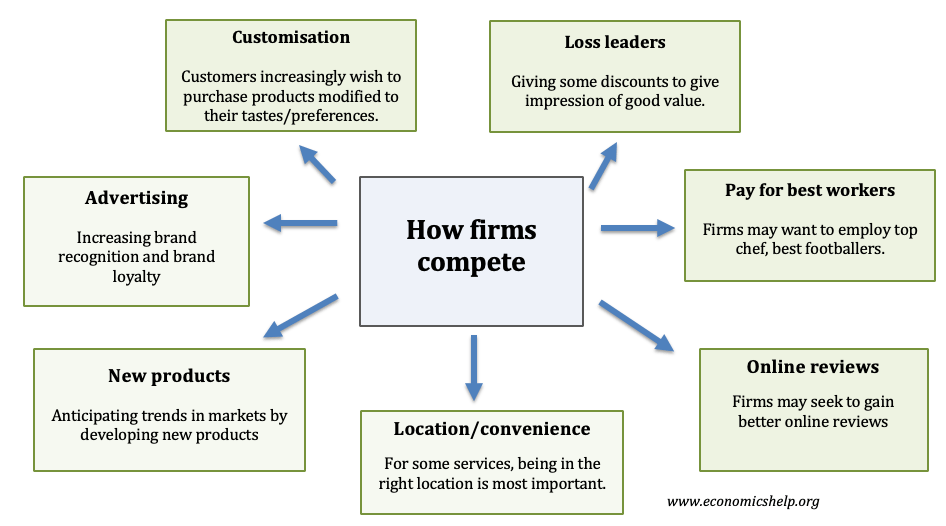
Readers Question: Can price discrimination be of benefit to consumers? Price Discrimination involves charging a different price to different groups of consumers for the same good. Price discrimination can provide benefits to consumers, such as potentially lower prices, rewards for choosing less popular services and helps the firm stay profitable and in business. The advantages …