Reasons for persistent US Current Account Deficit
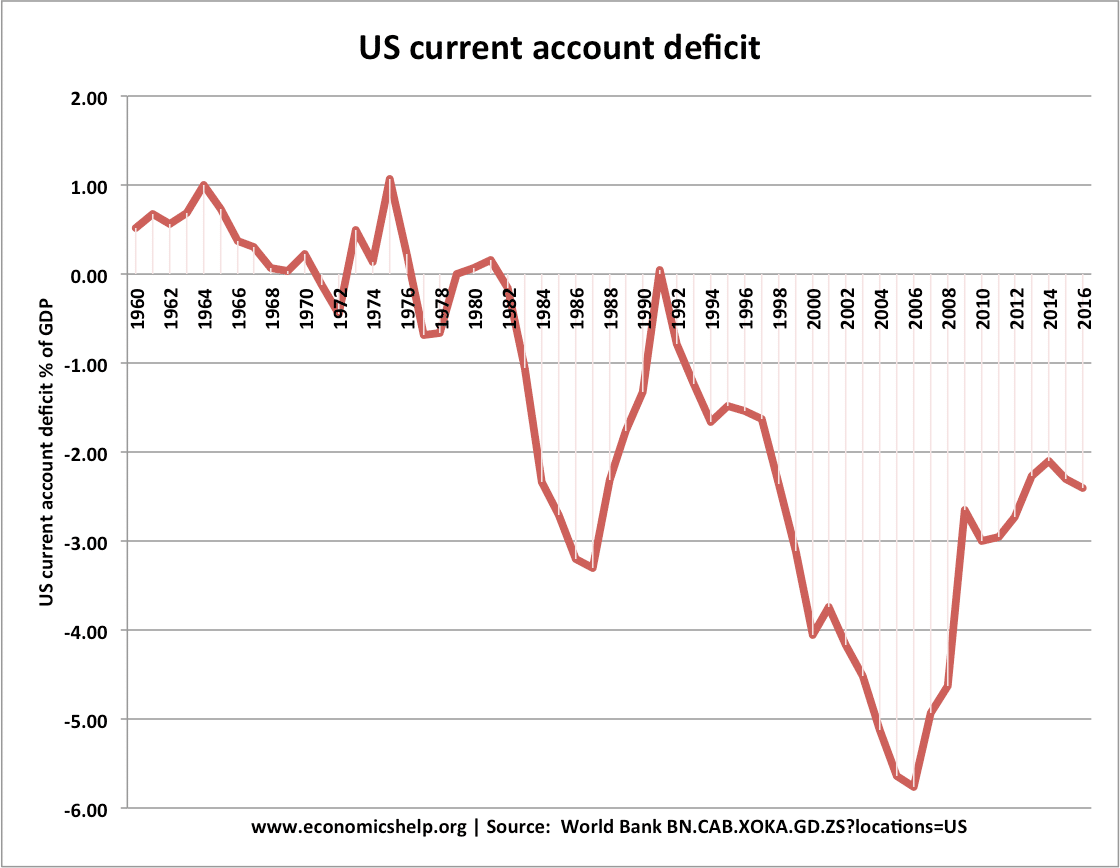
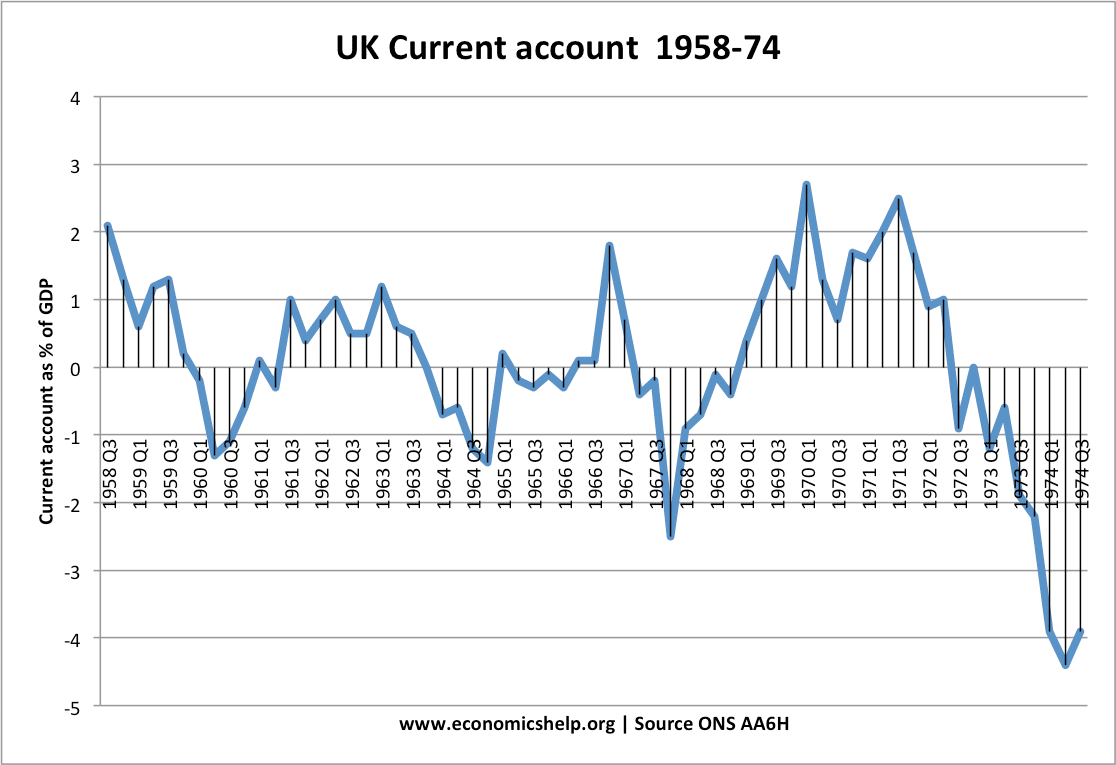
Readers Question: How much are US economic policies are responsible for its current account deficit? At one stage, the US current account deficit reached 6.5% of GDP, which was one of the highest in the industrialised world. Since the early 1980s, the US has been running a persistent current account deficit. Reasons for the US …