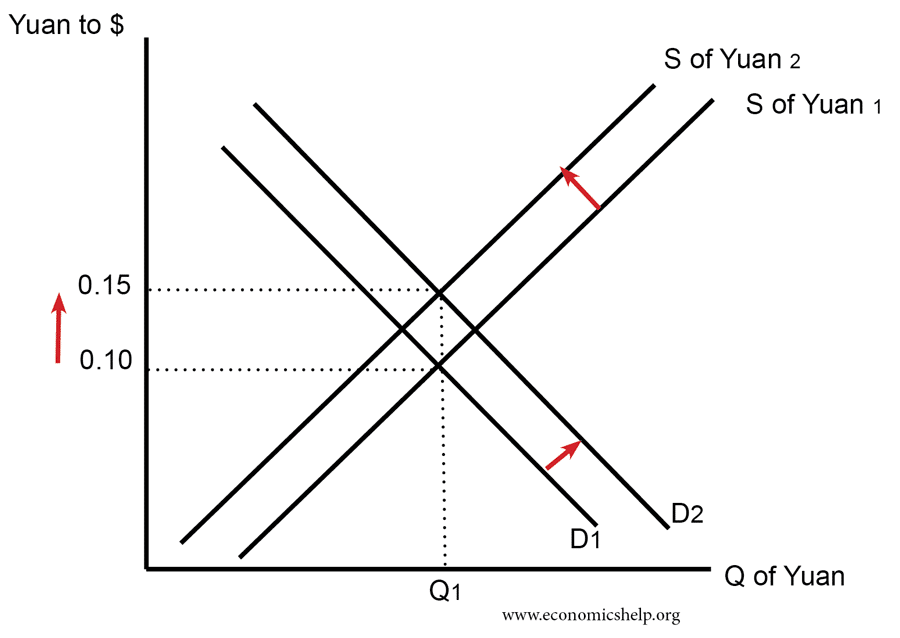
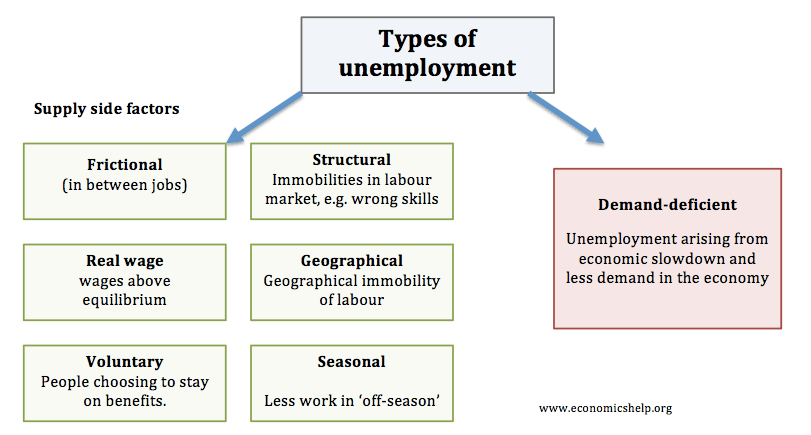
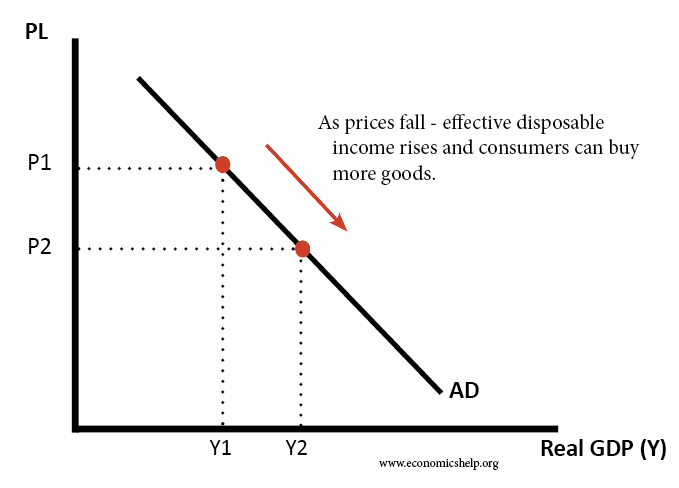
How firms grow in size
What factors enable a firm to grow in size? Internal expansion When a firm increases size through increasing production and sales. External expansion – When the firm grows through a merger with another firm. Internal expansion can involve Cutting price to increase sales and gain more market share. This may make the firm less profitable …