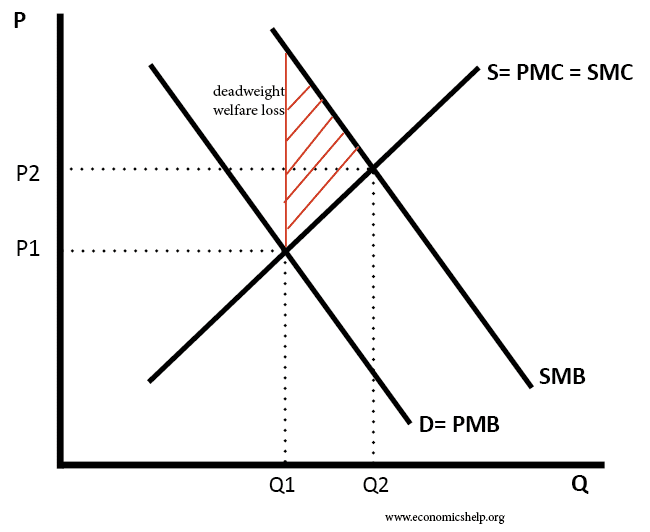
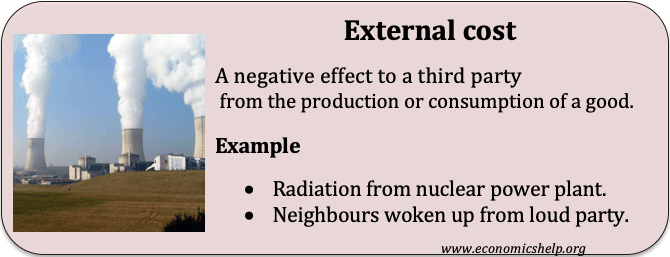
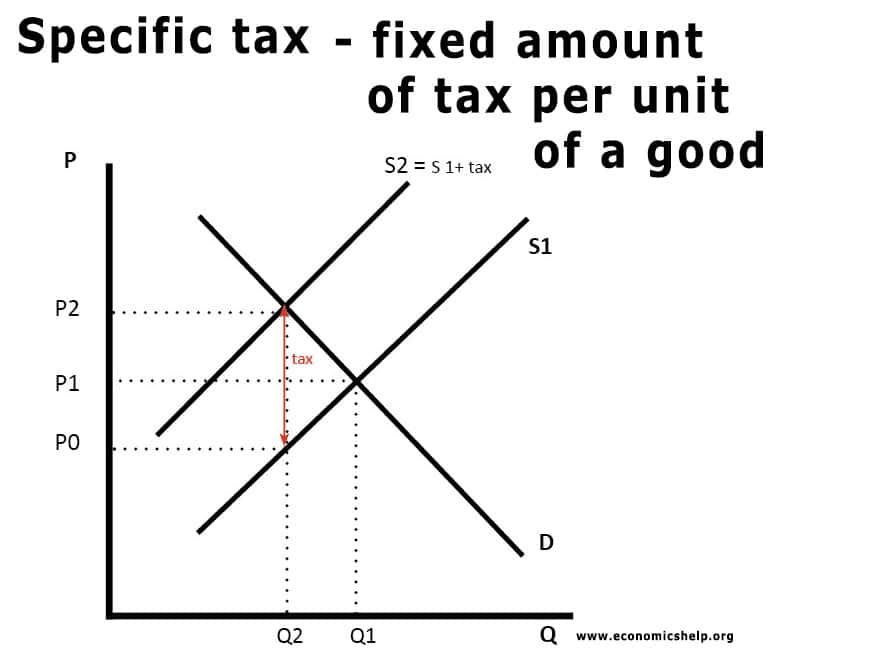
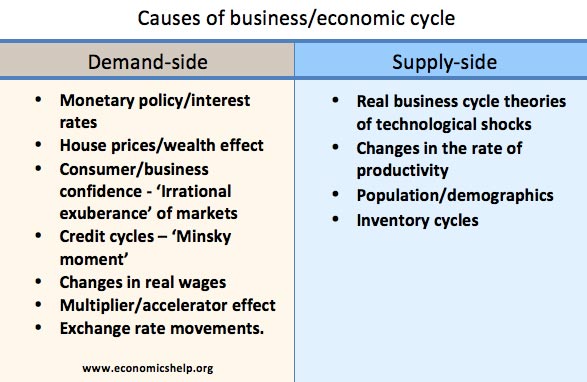
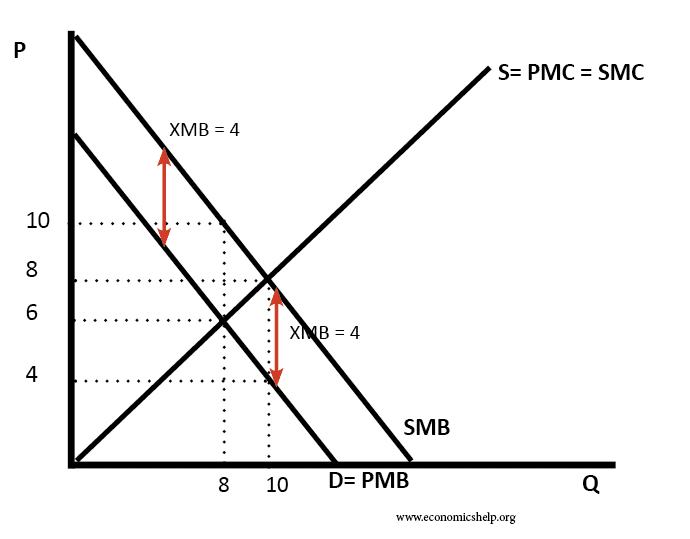
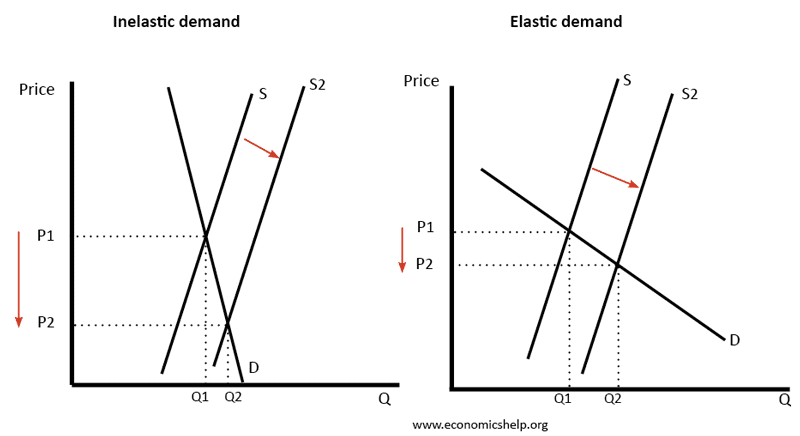
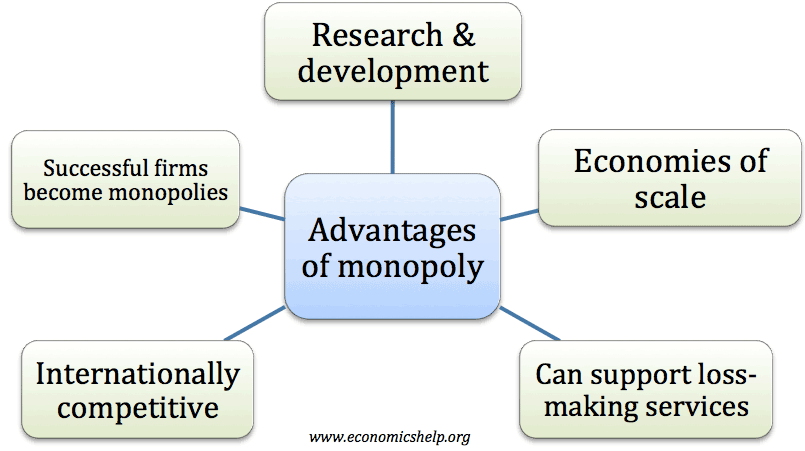
Theory of Comparative Advantage
Comparative Advantage. A country has a comparative advantage if it can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another country. A lower opportunity cost means it has to forego less of other goods in order to produce it. Example of Output of two goods Textiles Books UK 1 4 India 2 3 Total …