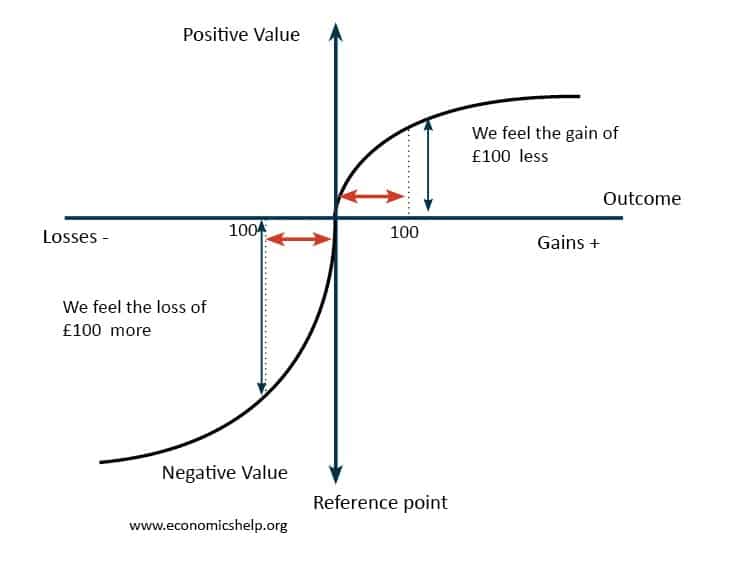
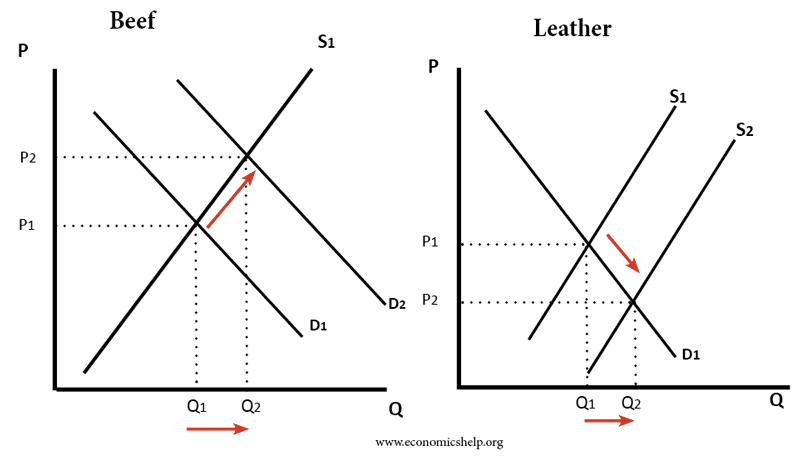
Definition of comparative advantage
Comparative advantage occurs when one country can produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than another. This means a country can produce a good relatively cheaper than other countries The theory of comparative advantage states that if countries specialise in producing goods where they have a lower opportunity cost – then there …