Perfect competition
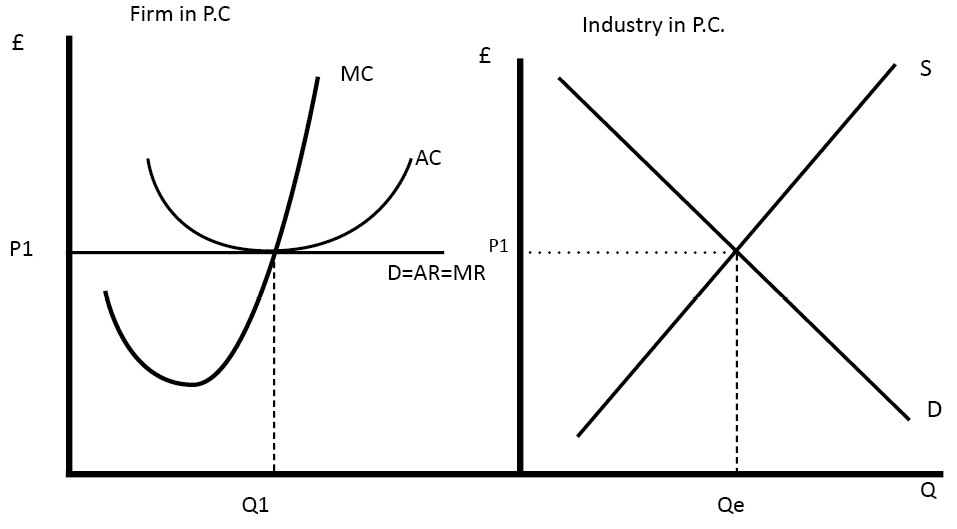
Perfect competition is a market structure where many firms offer a homogeneous product. Because there is freedom of entry and exit and perfect information, firms will make normal profits and prices will be kept low by competitive pressures. Features of perfect competition Many firms. Freedom of entry and exit; this will require low sunk costs. …