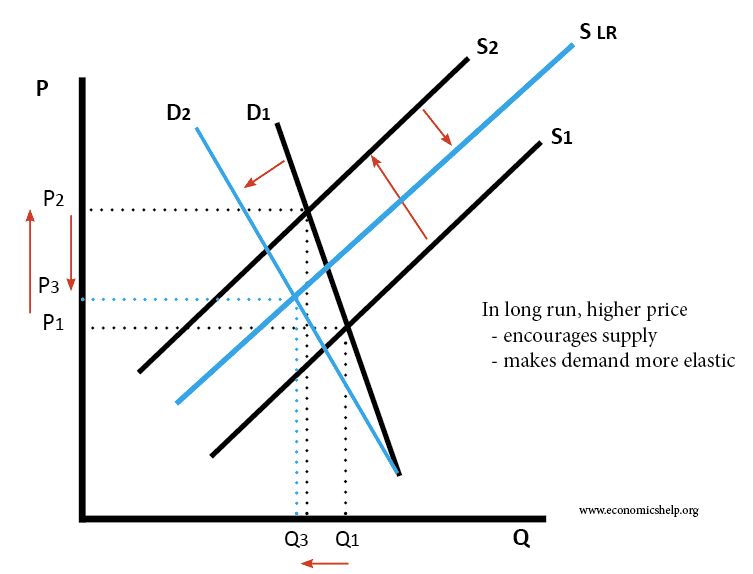
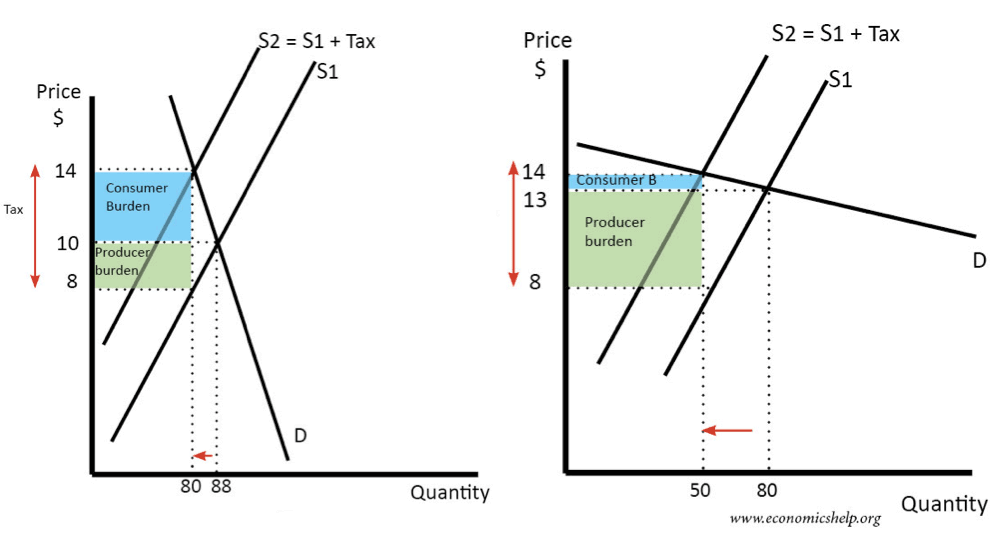
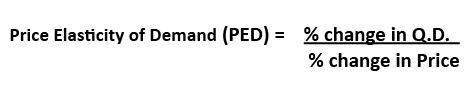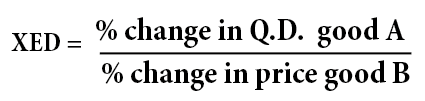Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
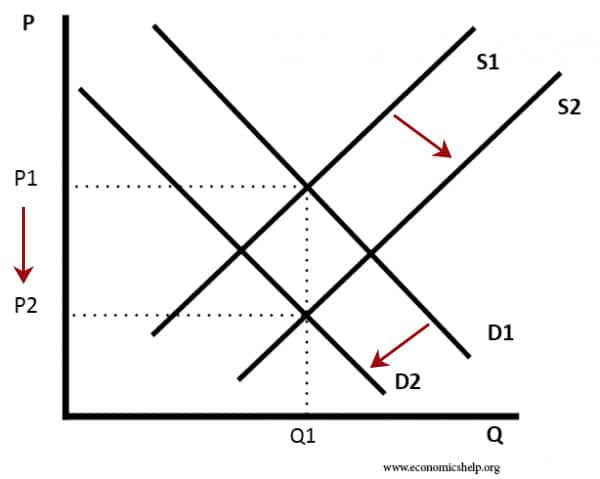
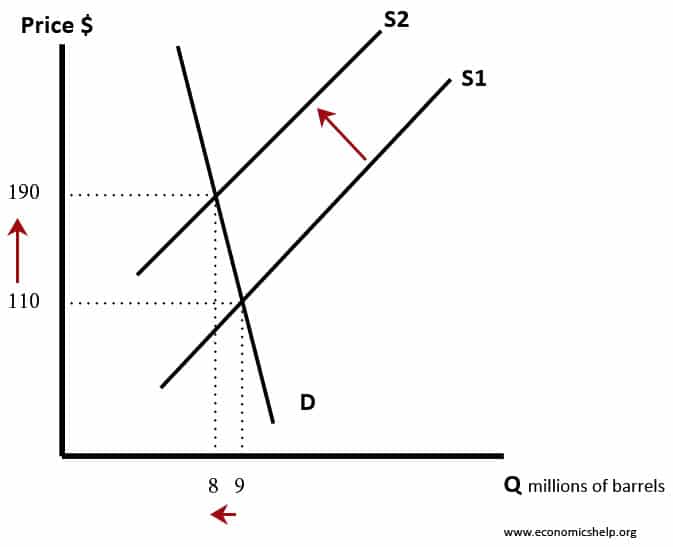
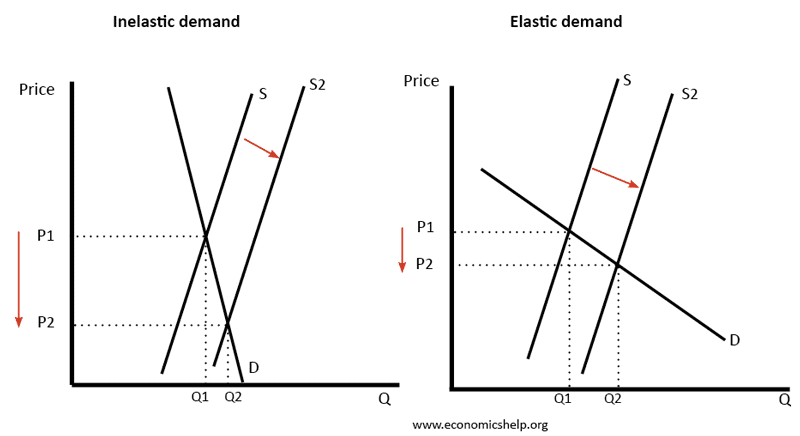
Definition: Price elasticity of demand (PED) measures the responsiveness of demand after a change in price. Example of PED If price increases by 10% and demand for CDs fell by 20% Then PED = -20/10 = -2.0 If the price of petrol increased from 130p to 140p and demand fell from 10,000 units to 9,900 …