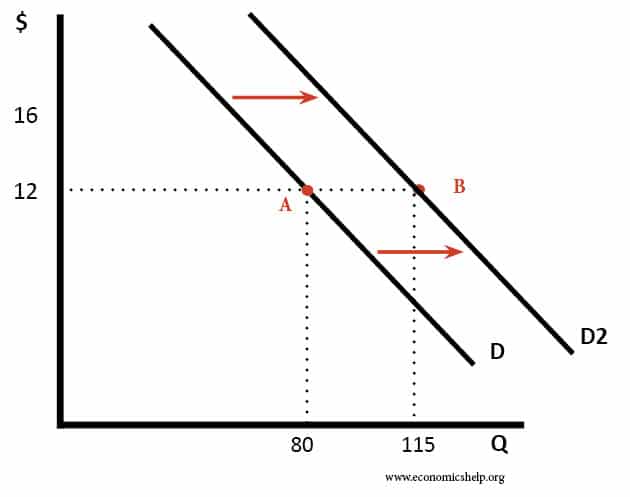
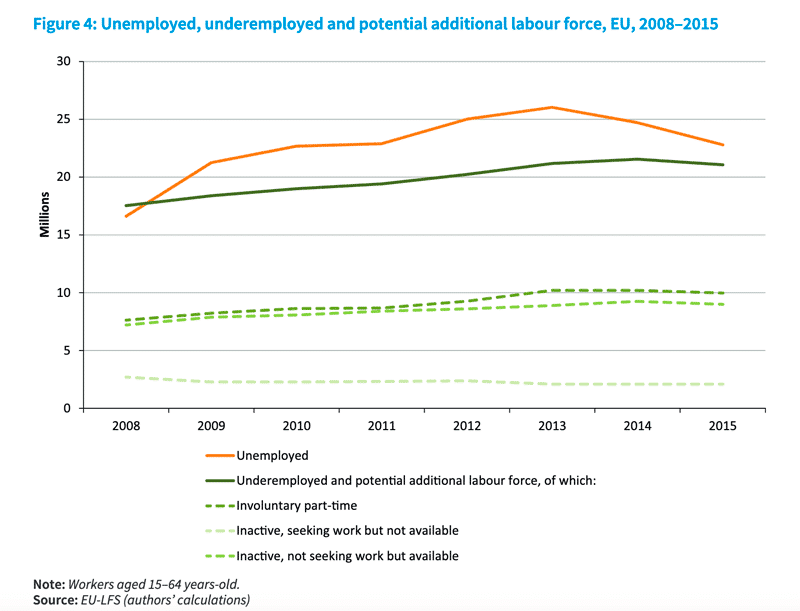
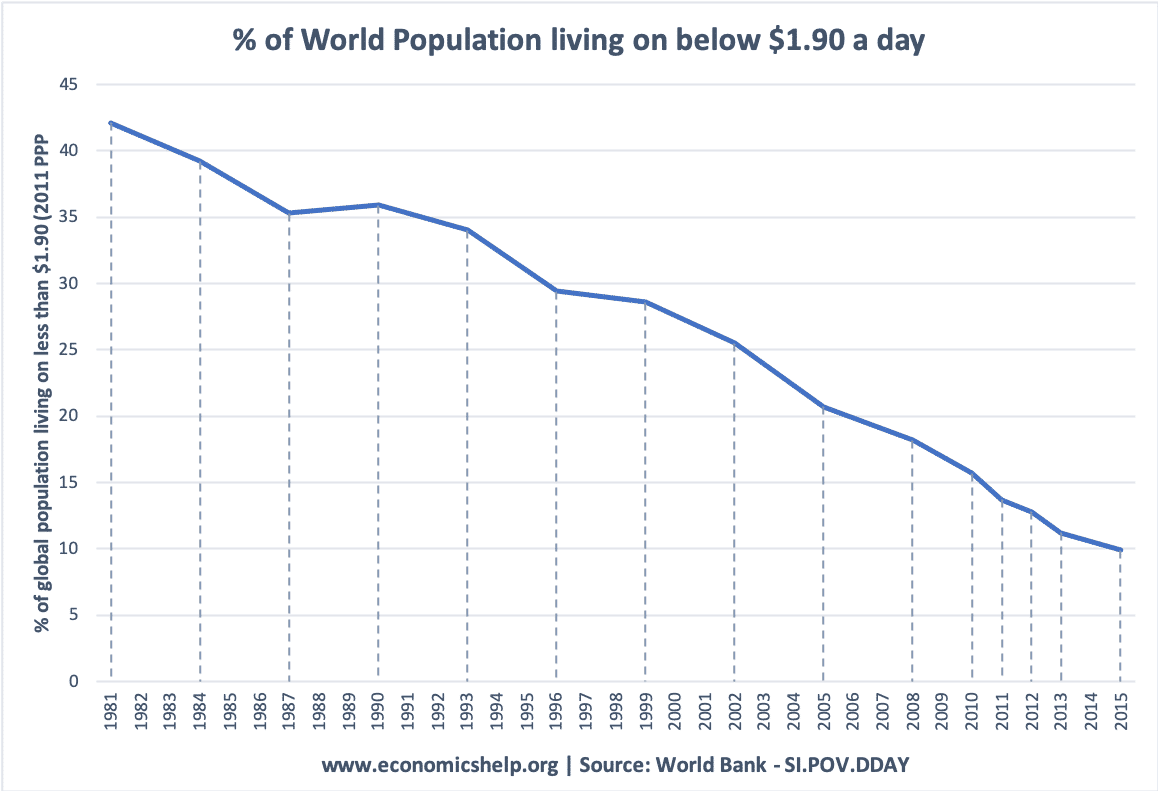
Asymmetric information problem
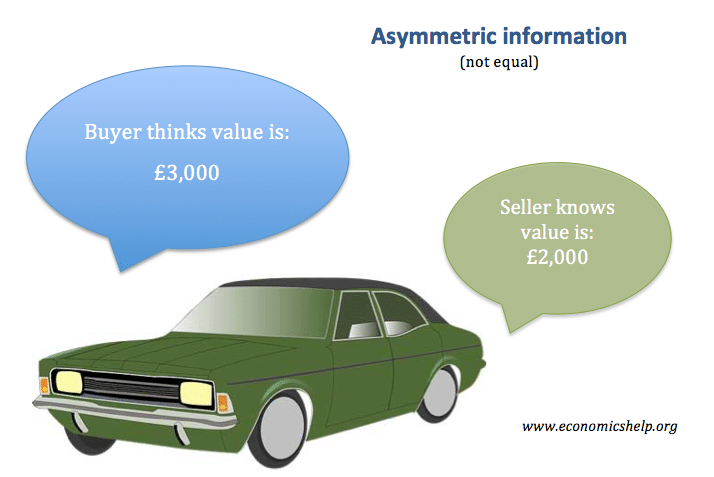
Definition of asymmetric information: This is a situation where there is imperfect knowledge. In particular, it occurs where one party has different information to another. A good example is when selling a car, the owner is likely to have full knowledge about its service history and its likelihood to break-down. The potential buyer, by contrast, …