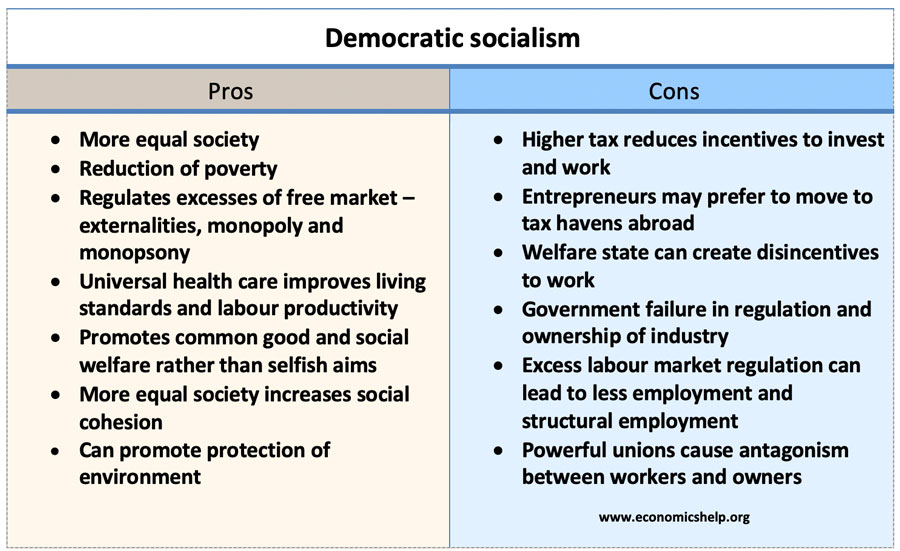
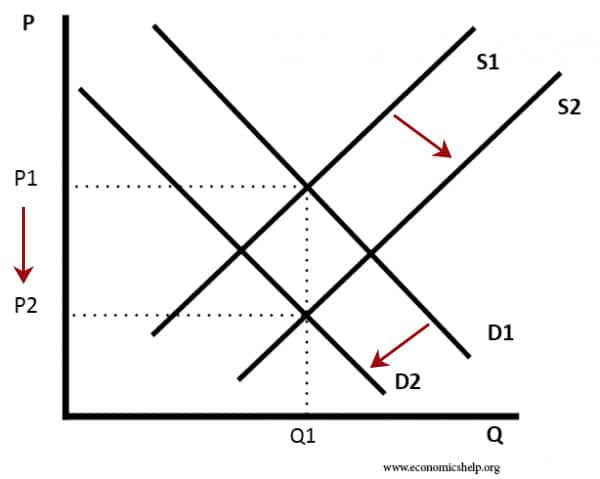
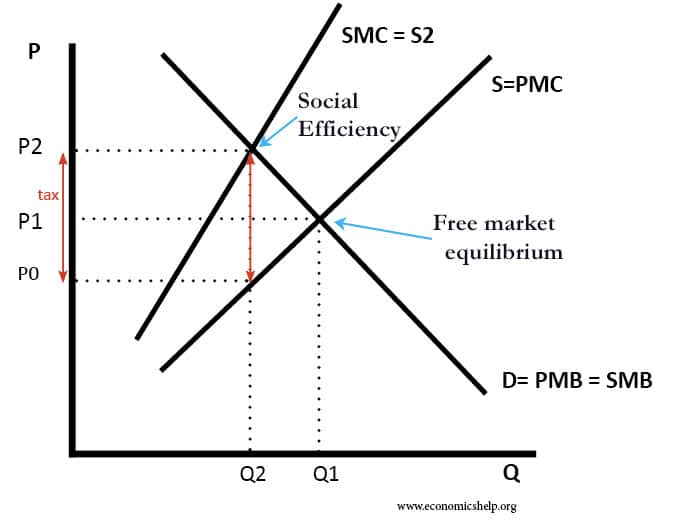
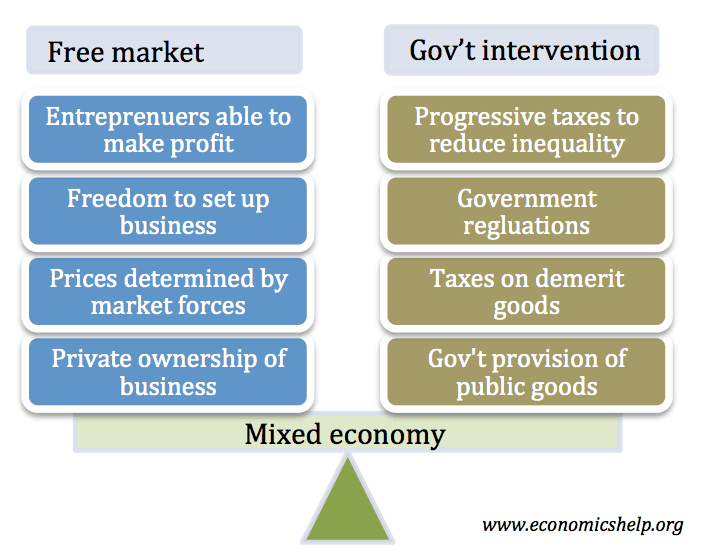
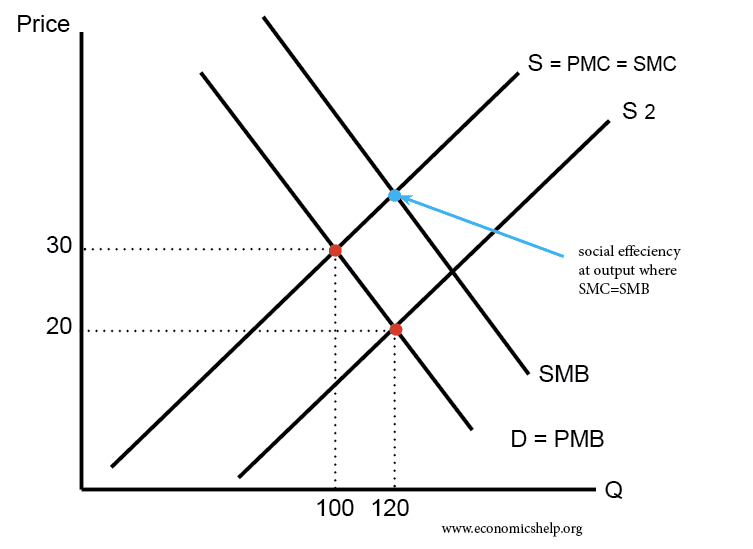
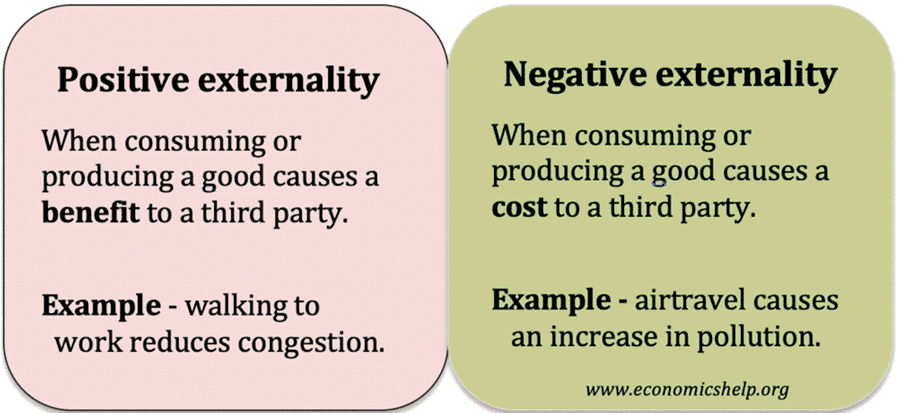
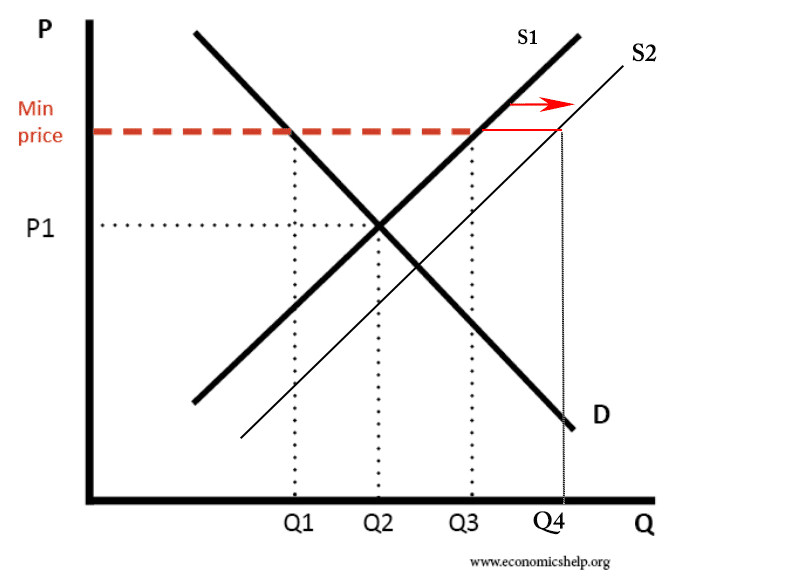
Pros and cons of socialism
There are different forms of socialism but for this blog will use the form of democratic socialism advocated by Socialist parties in Western Europe. For example, Nordic countries where government spending is between 40-50% of GDP. This brand of socialism believes in: Redistribution of income and wealth through a progressive tax system and welfare state. …