The elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of a change in quantity supplied to a change in price.
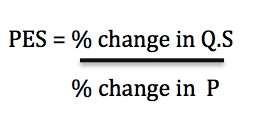
If price increases – firms generally find it more profitable to supply a good. So an increase in price leads to higher supply.
- However, if it is difficult to increase supply (e.g. shortage of capacity, difficulty to hire extra workers), then supply will be inelastic – an increase in price will lead to a smaller percentage change in supply.
- If firms find it easy to increase supply, then supply will be elastic, and an increase in price will lead to a bigger percentage change in supply.
Diagram showing the effect of elasticity of supply
![]()
- If supply is price elastic, an increase in demand will cause only a small rise in price, but a significant increase in demand.
- If supply is inelastic, an increase in demand will cause a large rise in price but only a small increase in demand.
Therefore, the elasticity of supply has important implications for markets.
Housing and inelastic supply
For example, the UK housing market has been particularly affected by inelastic supply. Despite rising demand, supply has struggled to keep up. It is profitable to build new houses, the difficulty is getting planning permission to build on a limited supply of land. Therefore, the inelastic supply of UK housing leads to higher prices than many European countries who have more elastic supply.
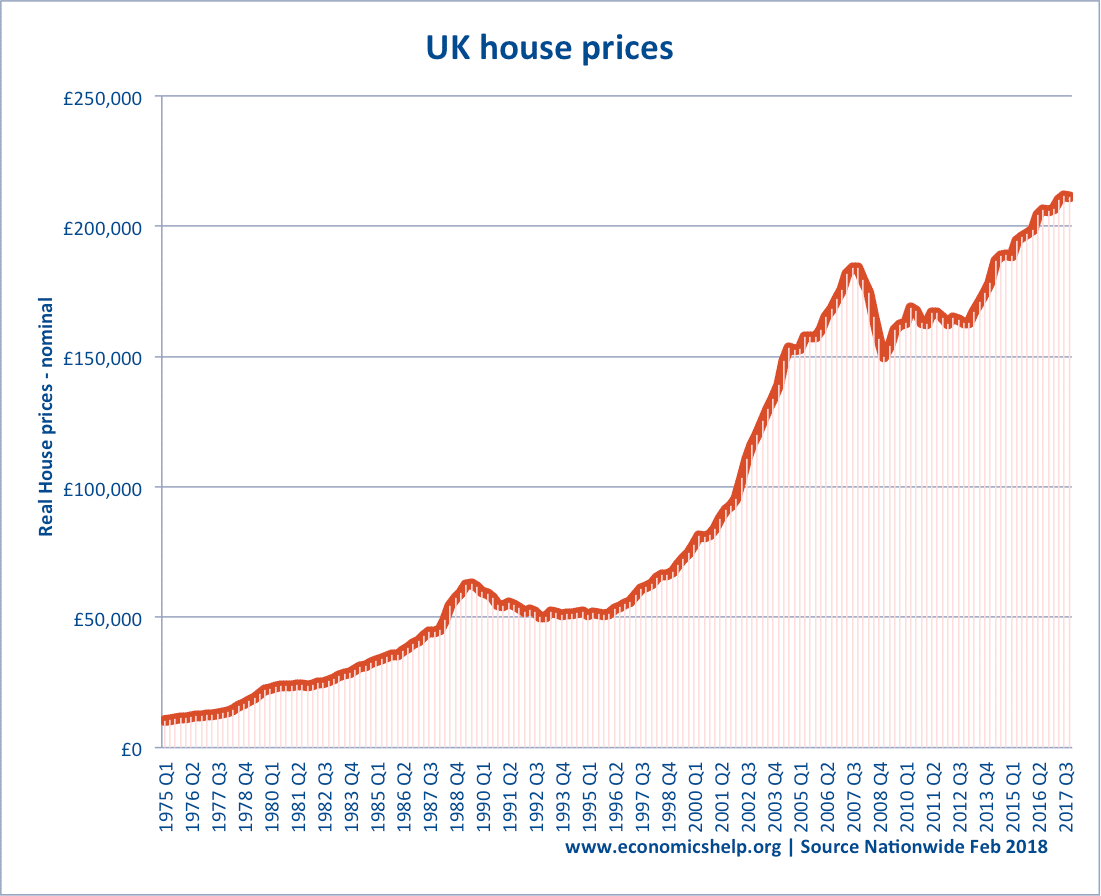
This shows a persistent increase in real house prices in the UK, which is partly due to inelastic supply.
Volatility of prices
If supply is inelastic, it invariably causes prices to be more volatile.
![]()
In the short-term, the supply of agricultural goods is inelastic. It takes time for a farmer to grow more crops. If there is a rise in demand for a particular vegetable. (e.g. organic celery), then we are likely to see a significant rise in price.
Demand for agricultural products may also be more price inelastic which contributes to price volatility.
If it was a manufactured good, such as chocolate bars, it is generally easier for a manufacturer to respond by increasing supply
Shortage of toys at Christmas
Sometimes, manufacturers can get caught out by unprecedented demand for a particular toy at Christmas. There may be a ‘craze’ or fashion for a particular toy. But, in the short-term, even manufacturers struggle to respond to an increase in demand, and in short-term – supply is inelastic. Demand outstrips supply.
Examples
- Teletubbies mania (1997)
- Buzz Light Year (1996)
- Hatchimals (2016)
In this case, the manufacturers may decide not to increase prices for fear of adverse publicity and appearing to be unfair and profit from their own shortage. In this case, demand will outstrip supply and there will be queuing for the limited stock of presents. In extreme cases, there are reports of ‘fighting’ by customers for the limited toy available.
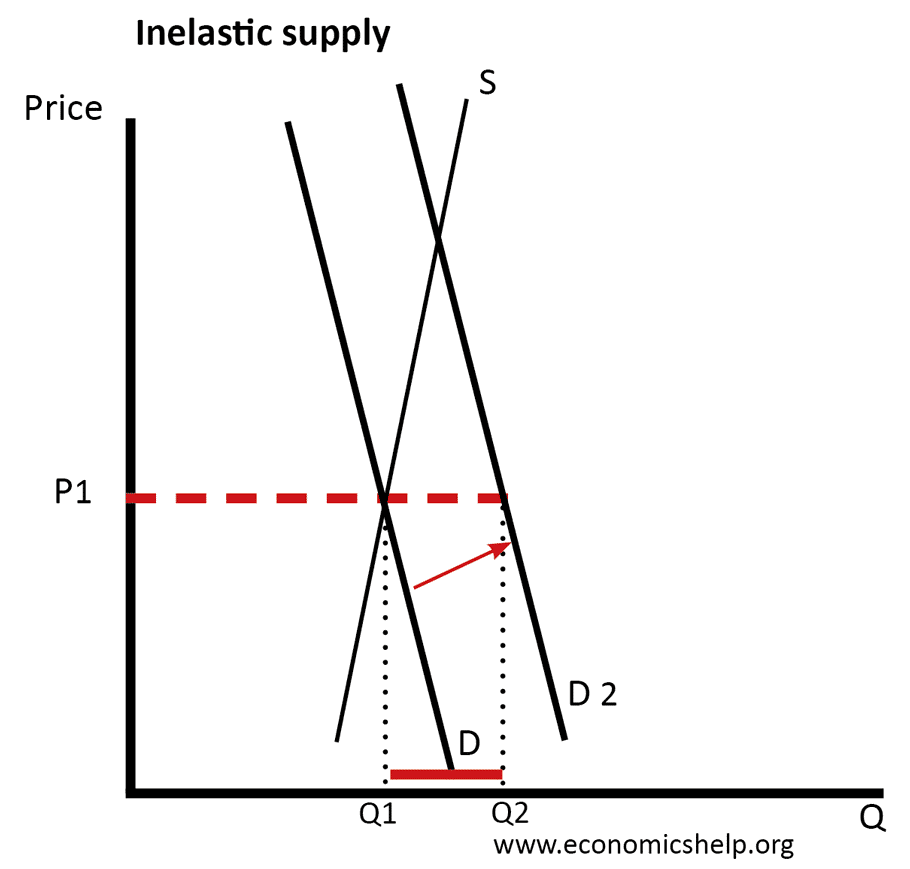
In this case, inelastic supply leads to a shortage of the good because the price is fixed at P1.
This shortage could lead to a black market as those who are willing to pay a higher price but can’t get the limited good.
Importance to firms of elasticity
Firms will wish to try and make supply more elastic so they can respond to increased demand. Firms will consider
- Invest in spare capacity which can be used if demand rises.
- Paying workers overtime to increase production
- Using agencies to hire more workers at busy times.
- To outsource production to other firms who can meet supply
- Improve efficiency and just in time management techniques to increase supply.
However, all these measures will have a cost. Therefore, a firm has to weigh the benefits of more flexible supply against the costs.
Related

good explanation
Well explained
Please I have not still found my answer, to the importance of elasticity of supply.
Pls explain more I did not get my answer to the importance of elasticity of supply