The Neo-Classical Theory of Firms makes the following assumptions
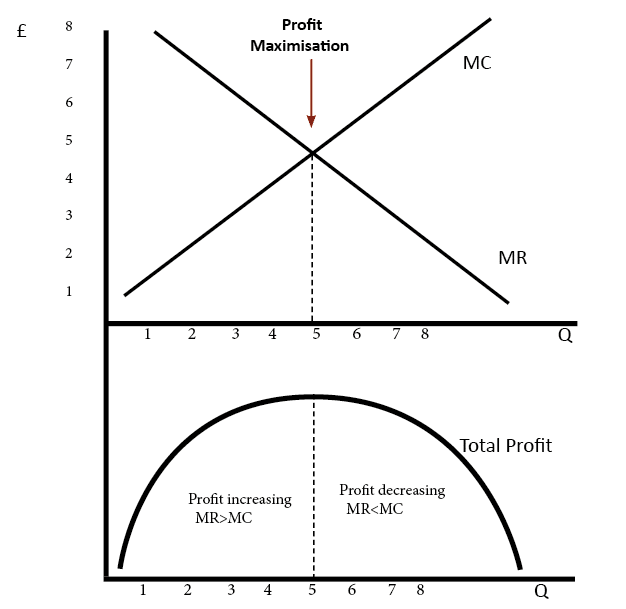
- Firms are profit maximisers. Firms will maximise profits where MR=MC
- In the short run, firms are subject to diminishing returns. In the short run, capital is fixed, therefore MC is upwardly sloping after diminishing returns sets in.
- Prices are flexible. If there is a shortage of the good, the price mechanism will lead to higher prices.
- There is an assumption that many markets are competitive and close to the model of perfect competition, therefore, prices will be determined by competitive pressures.
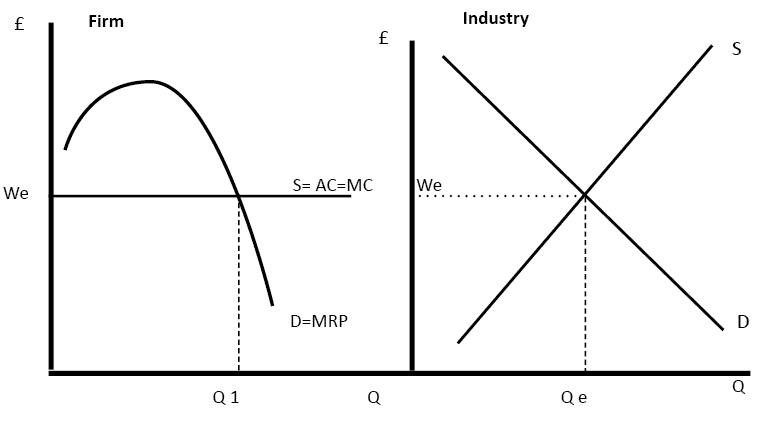
- Firms employ labour like any other factor of production. Therefore wages and quantity of labour are determined by marginal revenue product theory (MRP)
- Neo-classical economics also assumes wages are flexible. For example, if there is a fall in demand for workers, this will lead to a fall in wages to maintain equilibrium
Wage determination in neo-classical theory.
Criticism of Neo-Classical Theory of Firms
- Firms often seek to maximise the size of the firm and market share, rather than profit.
- Profit satisficing. Firms have a principle-agent problem. The owners may wish to maximise profits, but the workers don’t. Therefore, the workers do enough to keep the owners happy, but then pursue other objectives such as enjoying themselves at work. This is also known as a problem of separation of ownership and control
- Other objectives such as environmental, cultural and social objectives. Humans are not just profit maximisers but consider other non-financial objectives.
- Wages may not be flexible. For example, unions may resist nominal wage cuts.
- Labour cannot always be treated like a commodity like say capital. This ignores the human psychology of workers getting frustrated or de-motivated.
- Behavioural economics suggests there is a range of factors that determine business and consumer behaviour other than utility maximisation theory. Firms may wish to become more prestigious. They may take risks for non-economic reasons or they may want to avoid losing what they already have.
The Value of Neo-Classical Theory
It could be argued that when firms pursue other objectives, they have in the back of their mind profit maximisation. E.g. a firm may engage in a price war to maximise market share. However, the reason is that in the long run, the firm hopes that this increased market share enables higher monopoly power and therefore higher profits in the future. The same could be said of environmental objectives, these give a better corporate image and therefore boost long-run profitability
Profit satisficing can be overcome through share deals and performance-related pay. Therefore the neoclassical theory is useful because it shows how and why firms should make sure workers have sufficient incentives to maximise profits like the owners.
Related
See also: Objectives of firms

How do you relate ‘Ricardian Equalance’ with ‘Rational Expectation’?