International trade between different countries is an important factor in raising living standards, providing employment and enabling consumers to enjoy a greater variety of goods.
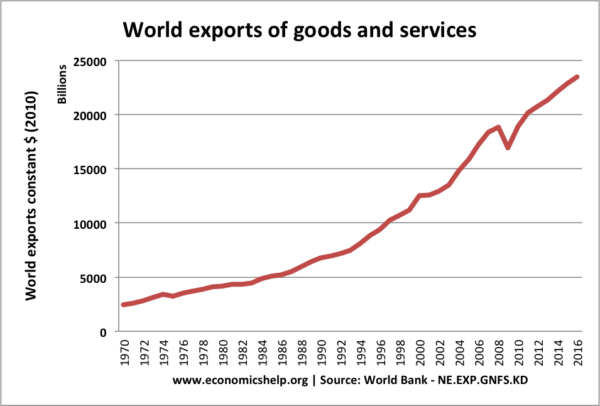
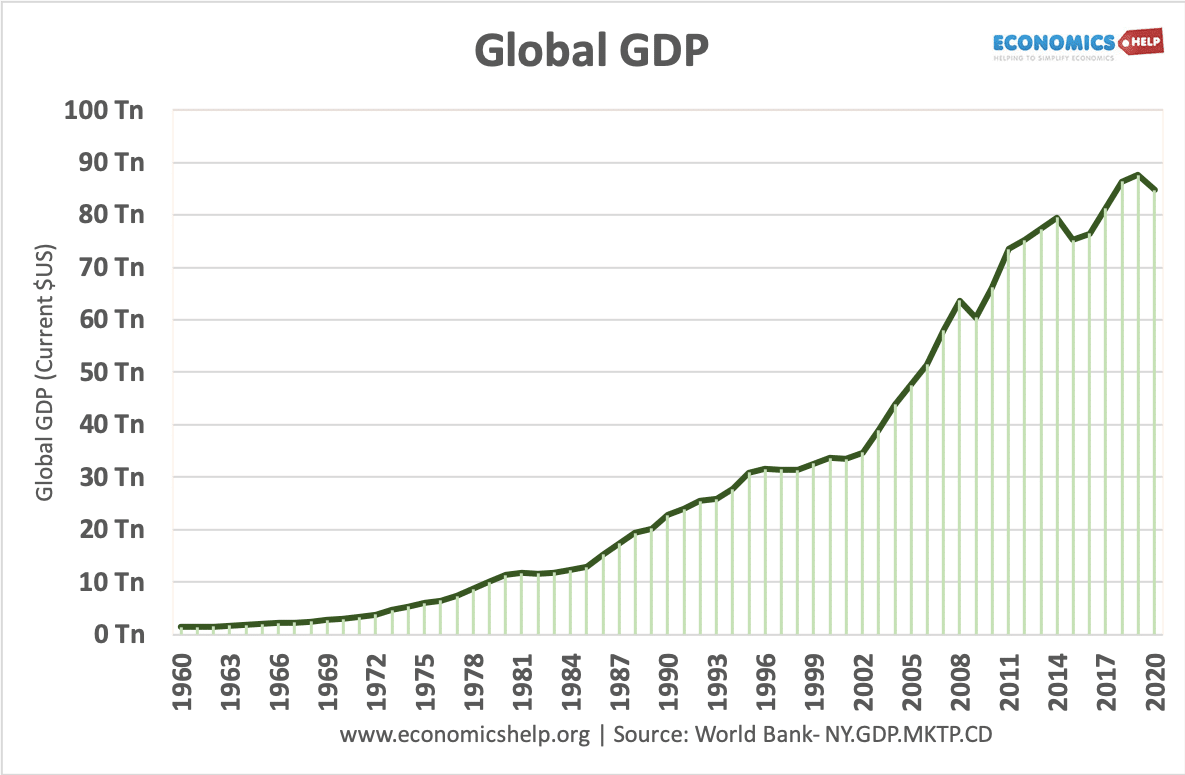
International trade has occurred since the earliest civilisations began trading, but in recent years international trade has become increasingly important with a larger share of GDP devoted to exports and imports.
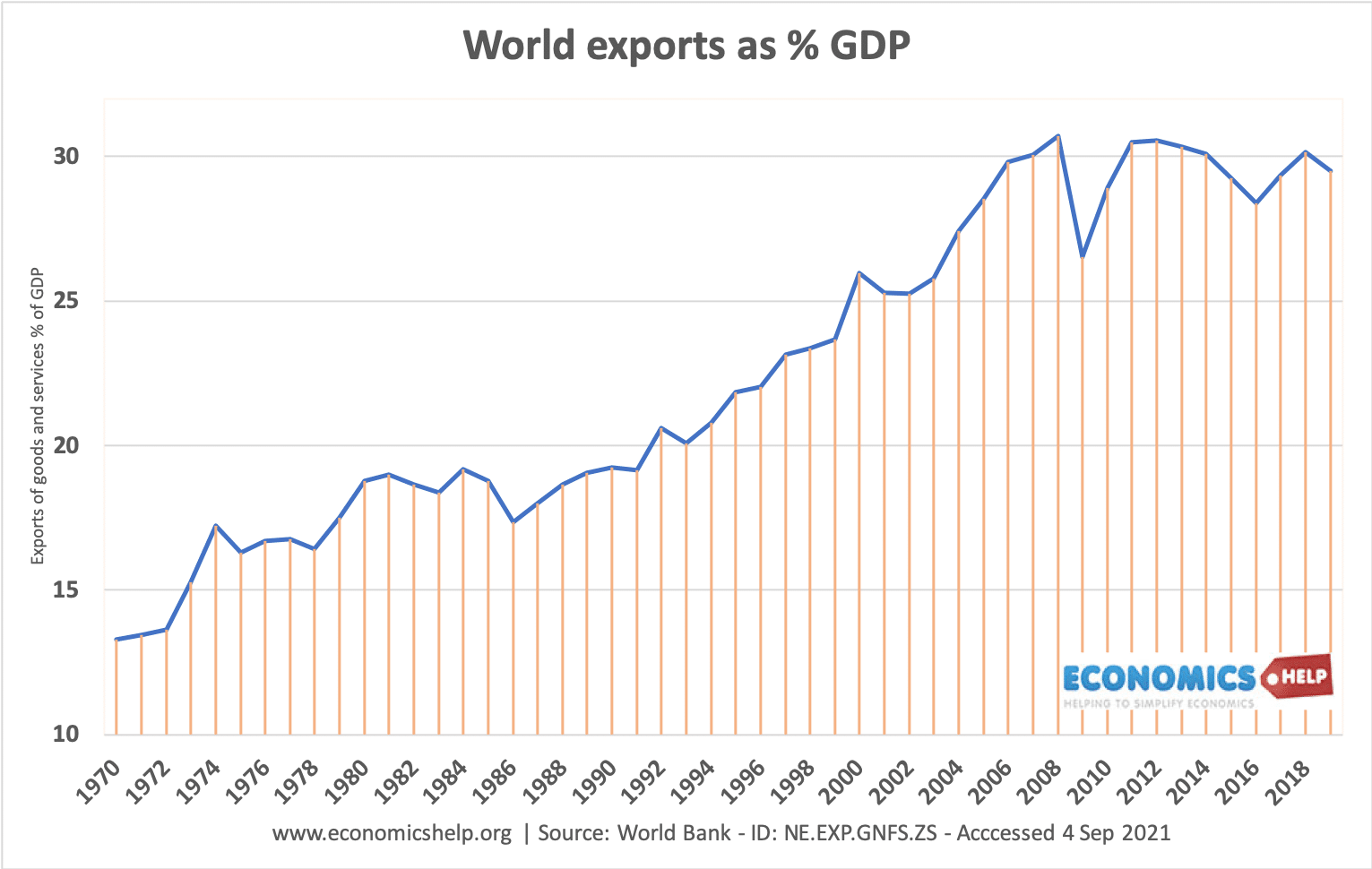
World Bank stats show how world exports as a % of GDP have increased from 13% in 1970 to 30% just before the financial crisis of 2008.
In the past decade, world exports as a share of GDP have flatlined, with no rise since the peak of 2008.
Pros and cons of international trade
International trade plays an important role in improving living standards and reducing poverty levels. But, there are also concerns about the unequal distribution effects and the environmental costs of trade.
Importance of trade
1. Make use of abundant raw materials
Some countries are naturally abundant in raw materials – oil (Qatar), metals, fish (Iceland), Congo (diamonds) Butter (New Zealand). Without trade, these countries would not benefit from the natural endowments of raw materials.
A theoretical model for this was developed by Eli Heckscher and Bertil Ohlin. Known as the Heckscher–Ohlin model (H–O model) it states countries will specialise in producing and exports goods which use abundant local factor endowments. Countries will import those goods, where resources are scarce.
2. Comparative advantage
The theory of comparative advantage states that countries should specialise in those goods where they have a relatively lower opportunity cost. Even if one country can produce two goods at a lower absolute cost – doesn’t mean they should produce everything. India, with lower labour costs, may have a comparative advantage in labour-intensive production (e.g. call centres, clothing manufacture). Therefore, it would be efficient for India to export these services and goods. While an economy like the UK may have a comparative advantage in education and video game production. Trade allows countries to specialise. More details on how comparative advantage can increase economic welfare. The theory of comparative advantage has limitations, but it explains at least some aspects of international trade.
3. Greater choice for consumers
New trade theory places less emphasis on comparative advantage and relative input costs. New trade theory states that in the real world, a driving factor behind the trade is giving consumers greater choice of differentiated products. We import BMW cars from Germany, not because they are the cheapest but because of the quality and brand image. Regarding music and film, trade enables the widest choice of music and film to appeal to different tastes. When the Beatles went on tour to the US in the 1960s, it was exporting British music – relative labour costs were unimportant.
Perhaps the best example is with goods like clothing. Some clothing (e.g. value clothes from Primark – price is very important and they are likely to be imported from low-labour cost countries like Bangladesh. However, we also import fashion labels Gucci (Italy) Chanel (France). Here consumers are benefitting from choice, rather than the lowest price. Economists argue that international trade often fits the model of monopolistic competition. In this model, the important aspect is brand differentiation. For many goods, we want to buy goods with strong brands and reputations. e.g. the popularity of Coca-Cola, Nike, Addidas, McDonalds e.t.c.
4. Specialisation and economies of scale – greater efficiency
Another aspect of new trade theory is that it doesn’t really matter what countries specialise in, the important thing is to pursue specialisation and this enables companies to benefit from economies of scale which outweigh most other factors. Sometimes, countries may specialise in particular industries for no over-riding reason – it may just be a historical accident. But, that specialisation enables improved efficiency. For high value-added products, multinationals often split the production process into a global production system. For example, Apple designs their computers in the US but contract the production to Asian factories. Trade enables a product to have multiple country sources. With car production, the productive process is often even more global with engines, tyres, design and marketing all potentially coming from different countries.
5. Service sector trade
Trade tends to conjure images of physical goods import bananas, export cars. But, increasingly the service sector economy means more trade is of invisibles – services, such as insurance, IT services and banking. Even in making this website, I sometimes outsource IT services to developers in other countries. It may be for jobs as small as $50. Furthermore, I may export a revision guide for £7.49 to countries all around the world. A global economy with modern communications enables many micro trades, which wouldn’t have been as possible in a pre-internet age.
6. Global growth and economic development
International trade has been an important factor in promopting economic growth. This growth has led to a reduction in absolute poverty levels – especially in south east Asia which has seen high rates of growth since the 1980s.
Problems arising from free trade
Given the importance of free trade to an economy, it is unsurprising that people are concerned about the potential negative impacts.
- Infant industry argument. The fear is that ‘free trade’ can cause countries to specialise in primary products – goods which have volatile prices and low-income elasticity of demand. To develop, economies may need to restrict imports and diversify the economy. This isn’t an argument against trade per se, but an awareness trade may need to be ‘managed’ rather than just rely on free markets. See more at Infant Industry Argument.
- Trade can lead to cultural homogenisation. Some fear trade gives an advantage to multinational brands and this can negatively impact local produce and traditions. Supporters argue that if local products are good, they should be able to create a niche than global brands cannot.
- Displacement effects. Free trade can cause uncompetitive domestic industries to close down, leading to structural unemployment. The problem with free trade is that there are many winners, but the losers do not gain any compensation. However, free-market economists may counter that some degree of creative destruction is inevitable in an economy and we can’t turn back to a static closed economy. On the upside, if the uncompetitive firms close down, ultimately new jobs will be created in different industries.
- Environmental costs. The transportation of goods and services imposes environmental costs of pollution and carbon emissions, contributing to global warming
Related

I am just trying to better understand the trade wars, the trade rules, the stock market, and the economic factors that impact me as an American. Most of us aren’t taught this from a global standpoint, even though what goes on globally effects the stock markets and our 401ks.
I’m glad you talked about the importance of international trade and why its good to benefit from other countries who have a large number of raw materials to trade. According to my knowledge, international trading helps our economy as much as it helps others. Thank you for the information about how international trade gives people the choices of differentiated products like cars, music, and films.
Indeed international trade has helped create various bridges between producers and consumers across the globe. As a matter of fact, middlemen have made it easy for local producers to easily dispose off their produce. Besides that, globalization of trade has also made it easy for people to get first hand information about the state of the international markets, the world prices and so no. As a Kenyan, i gladly support this website since it helps me in my academics, as an ECONOMICS student at
EGERTON UNIVERSITY, Njoro Main Campus, Nakuru Kenya.
I AM SO PROUD OF ALL THIS YOU SAID ABOUT INTERNATIONAL TRADE.
The policy makers should emphasize on policies promoting exports, maintaining low and stable inflation rates and encourage government expenditure on development projects so as to encourage economic growth in Kenya.
Am grateful about this words you explain about international trade it has given me a good idea in my economic development class.Am student of accounting but manor in economics this topic is very good for our policy Maker to understand for good policies making for us in Liberia.Am student of United Methodist University Monrovia Liberia
Great work. it’s very explicit
Okoli Vincent
International trade had been of great advantage to many nations enable them to use what they have to get what they want in order to achieve meaningful a development
international trade contributes much to the growth of country’s economy because when the country exports much the value of it’s currency increase and also it maintains the good relationship among the trading countries and exchange of creativity and innovation which results into quality products and maximization of customer satisfaction
International trade is the most powerful thing that exists and all of us get benefits from it.
I’m really appreciate with the stated importance and negative impact of the trade.
We are going to make it properly. thanks
One of your charts mentions $2.34tn as being $23,400bn. This is incorrect…
$2.34tn is only $2,340bn
International trade,is very important and they also likely to be imported from low labour cost countries
international trade is very important, because it has help some under developing countries
i really want to know likely the importance of tools in international trade and list the tools also applicable