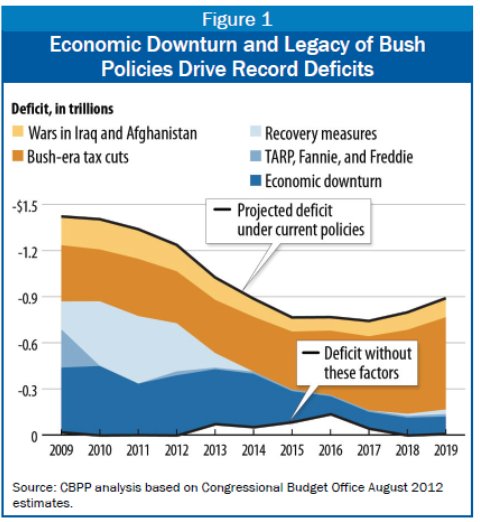
This graph illustrates some of the different causes of the US budget deficit.
Source: CBO estimates 2012 | via Krugman
This shows how the deficit has been affected by certain issues.
Cyclical factors
- Cyclical spending and lost tax revenues due to recession.
- Expansionary fiscal policy (economic recovery measures)
- Financial intervention to bailout banks and financial institutes.
Structural Factors
- Bush tax cuts
- Cost of wars (unexpected spending)
The particular graph doesn’t show other factors affecting the budget deficit, such as growth in health care spending, the cost of social security and factors related to an ageing population. But, it is interesting to see $0.9 trillion of the 2009 deficit (roughly 75%) was caused by cyclical factors.
Impact of Premature Fiscal Tightening
The other interesting prediction is the impact on economic of premature fiscal tightening (the so called fiscal cliff). CBO estimates suggest, if the fiscal cliff occurs (spending cuts and tax rises come into effect) then the US economy will see a recession with negative growth of -0.5% in 2013. However, if this fiscal tightening is avoided then the CBO predict economic growth of 1.7% in 2013 (link)
That is quite a different scenario, and given how much the budget deficit is caused by cyclical factors, something to be avoided.
Causes of US Budget Deficit
- After the budget surplus of the Clinton years, there were significant tax cuts. The first tax cut was to prevent ‘too large a budget surplus’. The second was intended as a temporary economic stimulus measures after 9/11. By making these temporary tax cuts permanent, it has contributed to the underlying deficit. (Tax cuts account for around $2.8 trillion of the $11.7 trillion discrepancy. The big income tax cut of 2001 accounts for about $1.2 trillion in revenue foregone over the decade (1)
- Growth in health care spending. The fastest growing area of US government spending is on health care spending. Unlike European health care systems, there is less control over costs because there is a different principle of payments (insurance companies pick up the bill). (There has also been a growth in the private sector spending on health care. See: global health care costs)
- Ageing population. One reason for the budget surplus of the Clinton years was the fact that the ‘babyboomer’ generation was getting towards the end of their working life – a time when people tend to make the biggest net contribution to tax revenues. As this age group retires, they move from being net contributors to net receivers – no longer paying income tax, but becoming entitled to pensions and health care. According to Concord, Population aging accounts for 64% of the cost growth of Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid through 2035.
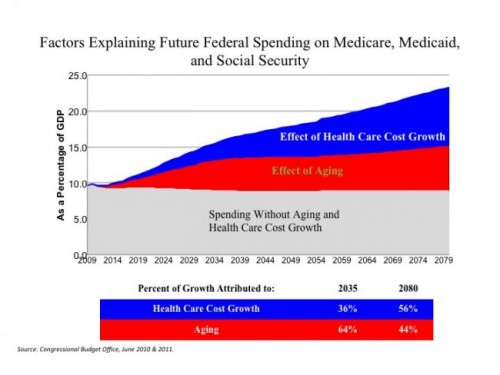 source: Concord US Structural deficit
source: Concord US Structural deficit - Temporary fiscal measures to boost growth. The US pursued an economic recovery package of lower taxes to boost economic growth. This is being gradually withdrawn, but it led to a temporary increase in the budget deficit.
- Cyclical Factors. As mentioned above, the recession had a deep impact on both spending (e.g. unemployment insurance) and tax revenues, which fell sharply. This graph from St Louis Fed helps illustrate the impact on tax revenues following the recession of 2008
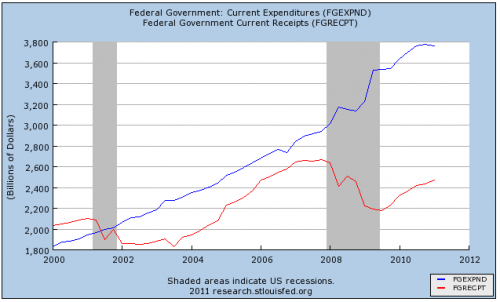
source: Business insider – cause of US deficit
