How can a change in the terms of trade affect the balance of payments ?
How can a change in the balance of trade affect the terms of payments ?
The terms of trade is the index of export prices divided by index of import prices (*100)
The current account balance of payments is primarily composed of this balance of trade (but also includes investment incomes and transfers)
How terms of trade affects the balance of trade (current account)
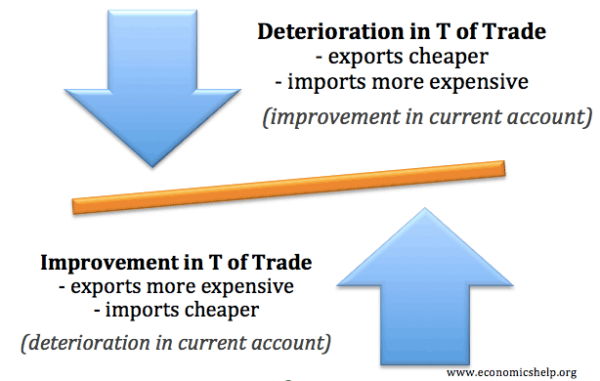
An improvement in the terms of trade means that export prices are increasing faster than import price. Therefore, ceteris paribus, a rise in export prices will cause a fall in the quantity exports. Relatively cheaper import prices will increase the quantity of imports.
Therefore, it is likely that with lower exports the current account deficit (+ trade deficit) will get worse, i.e. bigger deficit.
A deterioration in the terms of trade
A deterioration in the terms of trade means import prices rise relative to export prices (higher import prices, cheaper export prices). Assuming demand is relatively elastic, this will tend to improve the current account – as demand for exports will increase and demand for imports fall.
Evaluation – depends on elasticity of demand
The effect of a change in exchange rate relies on the relative elasticity of demand for exports and imports. If demand is relatively elastic then a deterioration in the terms of trade will improve the balance of trade.
- The Marshall Lerner condition states that if demand for exports and imports is relatively elastic PED x + PED m >1 then an increase in terms of trade will worsen the current account (balance of trade)
- if demand for exports and imports is relatively elastic PED x + PED m >1 then a decrease in the terms of trade will improve the current account (balance of trade)
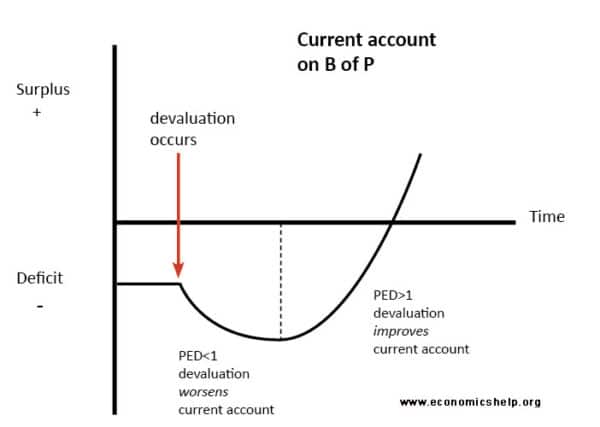
Sometimes elasticity of demand varies over time. In the short term, demand is often inelastic, in the longer term demand becomes more elastic. Therefore, we can often see a J Curve effect, where an improvement in terms of trade worsens current account in the short term but improves in the long term.
How does current account deficit affect the terms of trade?
If a country experiences a deterioration in the balance of trade (value of imports increase faster than the value of exports) then it may impact upon the terms of trade.
A deterioration in the balance of trade means a country is importing more than exporting. Therefore more currency will be leaving a country. This would mean an increase in the supply of pound sterling and lower demand. Therefore, it is likely to cause a devaluation. This would mean cheaper exports and more expensive imports. We say this would be a deterioration in the terms of trade.
Example, in the early 2000s, the US has a large trade deficit, and this has been contributing to a devaluation of the dollar. Therefore there are a deteriorating the terms of trade.
However, other factors may be affecting the terms of trade. For example, it depends on whether there is a strong capital inflow on other aspects of the balance of payments like the trade in services of financial account (capital flows)
Also, other factors can affect exchange rates like confidence, speculation and relative interest rates. Therefore, in the short term, a change in the balance of trade doesn’t necessarily affect the terms of trade although in the long term it probably will.
Related
- What are the terms of trade?
- Effect of devaluation on the terms of trade – a look at the example of the UK in the late 2000s where a devaluation failed to improve terms of trade and current account deficit.

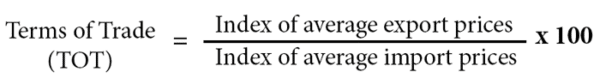
can you please help me to construct a model on the terms of trade to study the relation between the determinants of volume of trade(imports and exports) an the terms of trade. this request if honored will help me in writting my dissertation. thanks
very exellent informative athentic source
i realy enjoy it
A very detailed explanation. I appreciate this a lot.
Very helpfull!!! Just great! 😀
always want to be part of you in sharing ideas in other to get more understanding.
TERMS OF TRADE:- This refers to a ratio of an index of export price to an index of import price.