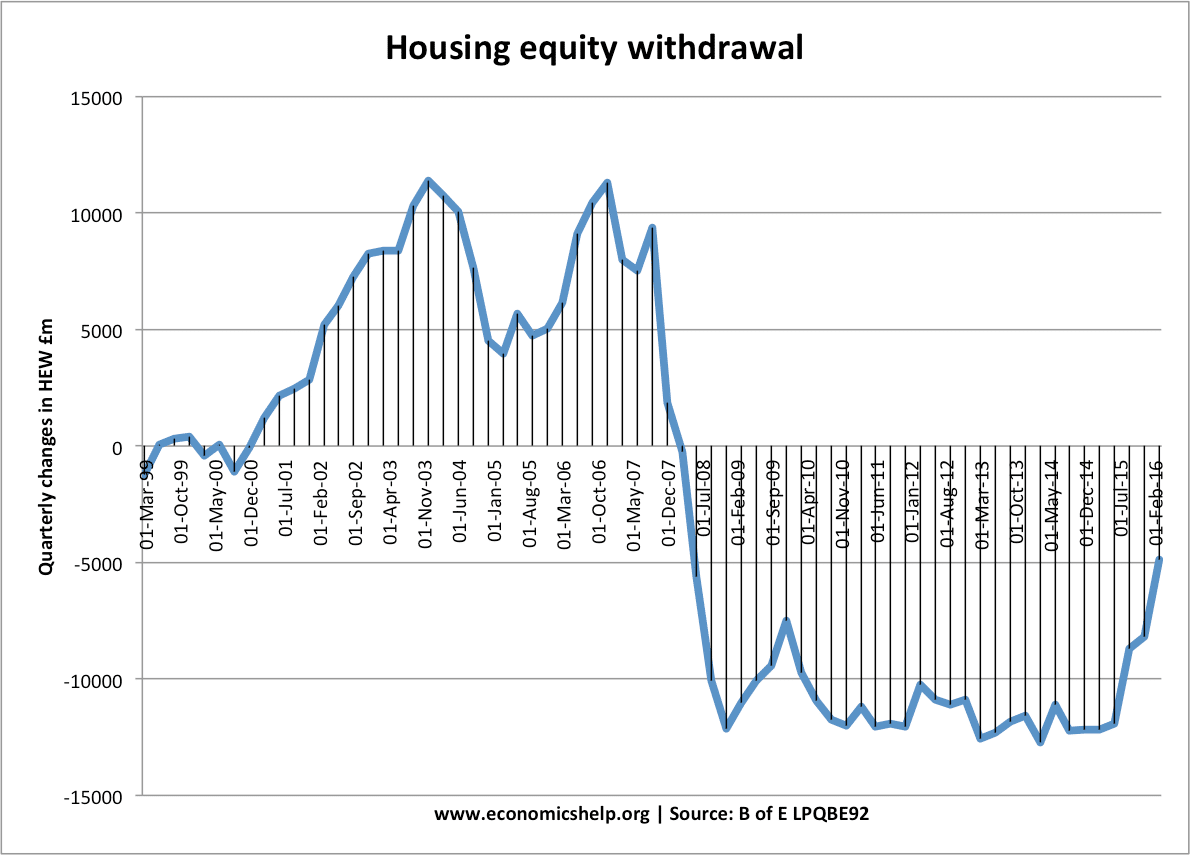
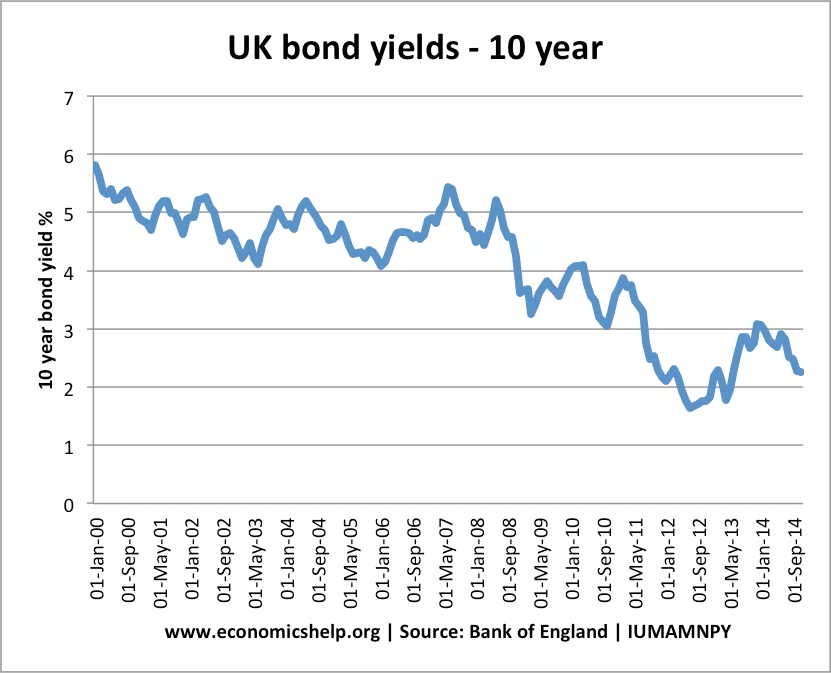
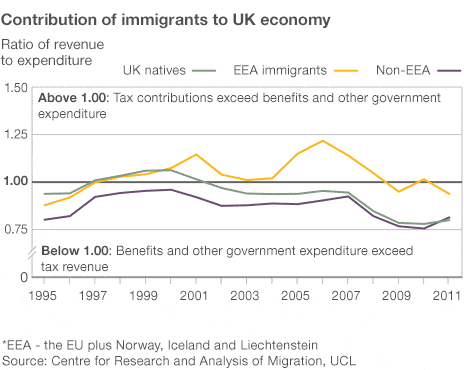
Media bias in the UK
At the 1992 General election, the Conservative Party won a stunning electoral victory – despite being in the middle of a self-imposed recession. Many point to this as an example of how the press can influence national debate and influence elections. The 1991/92 recession was a classic example of a boom and bust. It wasn’t …