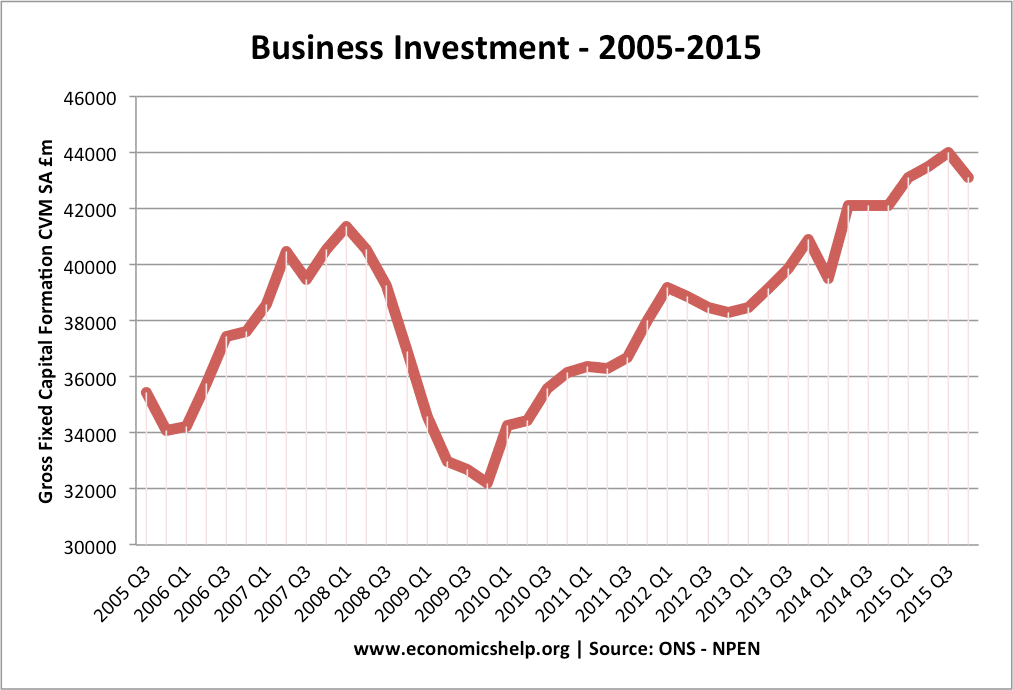
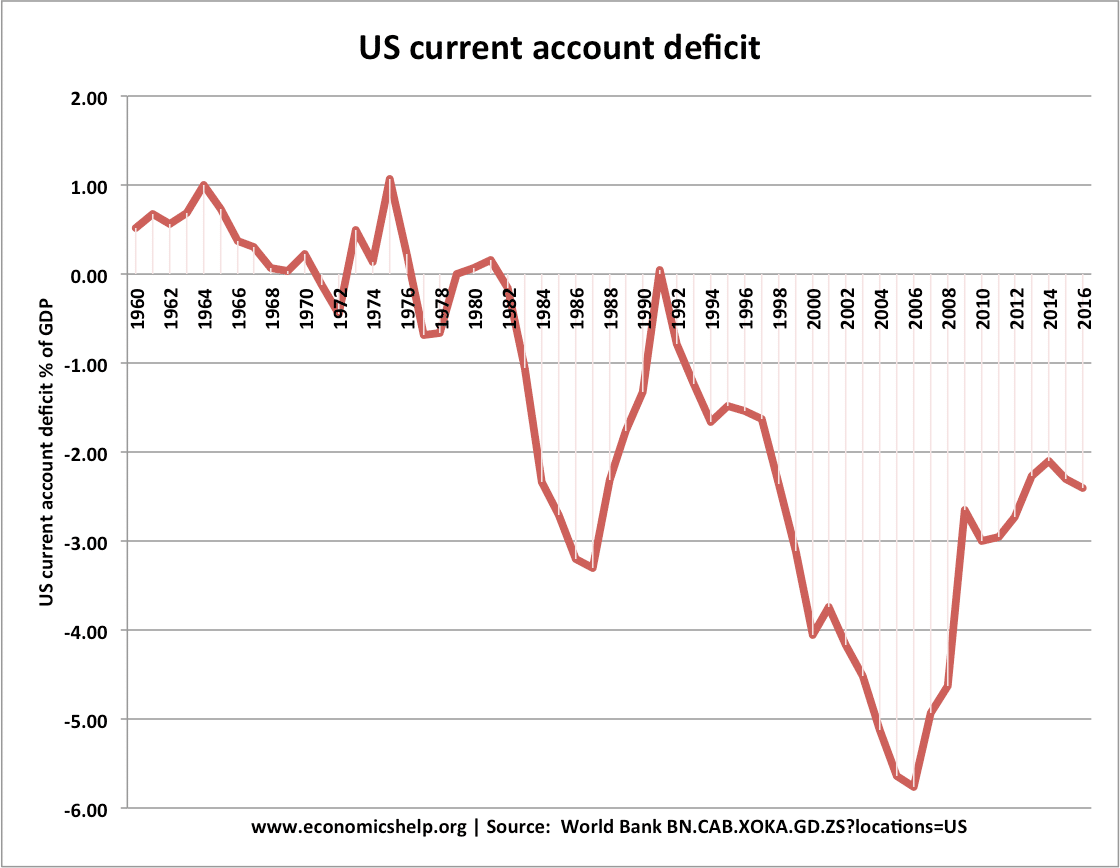
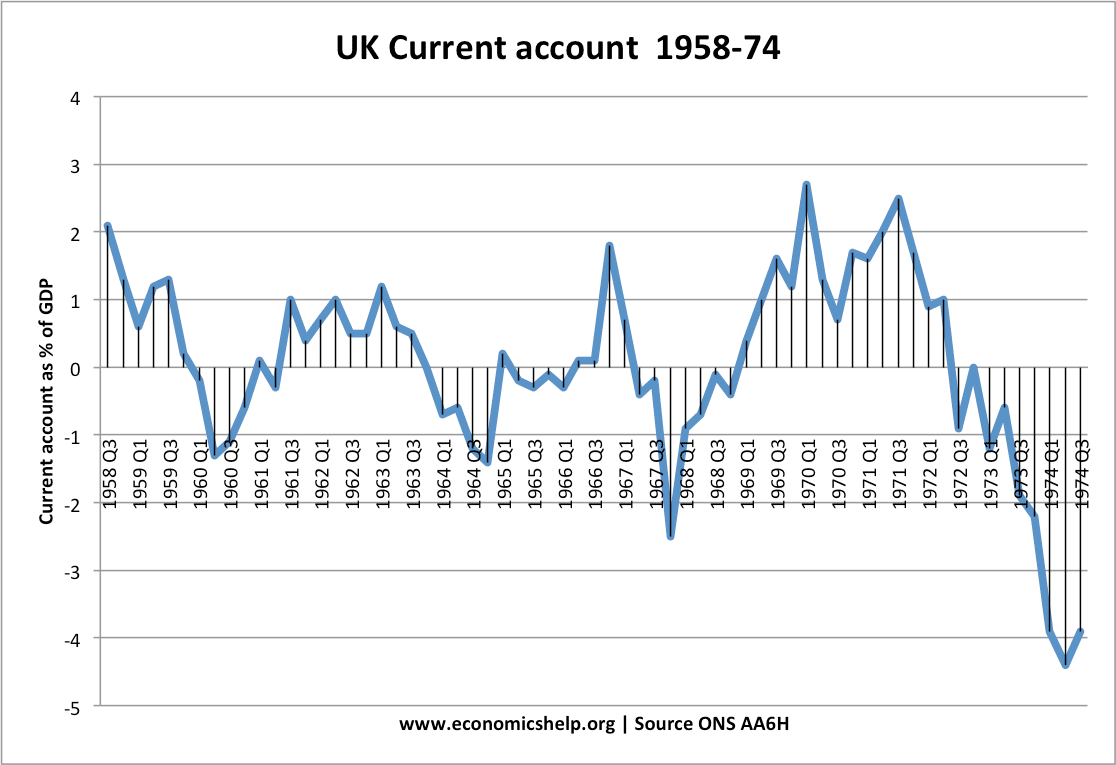
Investment influences the rate of economic growth because it is a component of aggregate demand (AD) and more importantly influences the productive capacity of the economy. (LRAS)
An increase in investment should be a boost to economic growth.
Readers Question: Discuss the importance of investment in increasing economic growth.
Investment means expenditure on capital spending, e.g. buying new machines, building bigger factories, buying robots to enable automation. (in economics investment does not mean saving money in a bank)
Investment is a component of aggregate demand (AD). Therefore, if there is an increase in investment, it will help to boost AD and short-run economic growth.
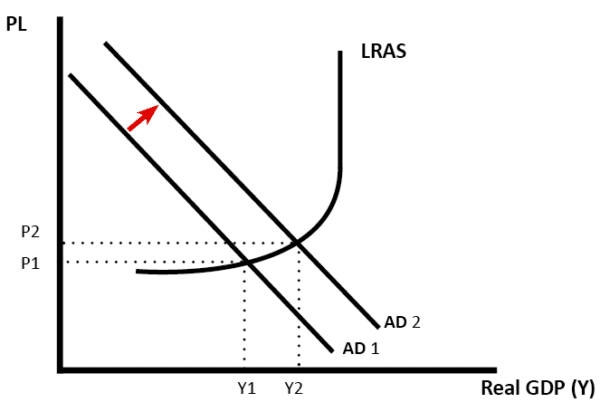
If there is spare capacity, then increased investment and a rise in AD will increase the rate of economic growth.
However, if the economy is close to full capacity, then rising AD will only cause inflation and not an increase in real GDP
However, there are other factors that affect AD apart from investment. For example, if there was a fall in consumer spending or a fall in exports, then a rise in investment may not actually increase AD. Investment is not the biggest component of AD (approx 16%); the biggest component of AD is consumer spending (approx 66%).
Investment and the multiplier effect
If the economy has spare capacity, a rise in investment can also cause a multiplier effect. The initial rise in investment increases economic growth, but if firms gain more sales and profit, they are willing to reinvest this in further investment. Also, households who gain employment from the investment, have more income to spend. Thus an investment of £2 billion could cause a final increase in real GDP of £3 billion. (multiplier effect of 1.5)