Definition of Monopoly
- A pure monopoly is defined as a single seller of a product, i.e. 100% of market share.
- In the UK a firm is said to have monopoly power if it has more than 25% of the market share. For example, Tesco @30% market share or Google 90% of search engine traffic.
Monopoly Diagram
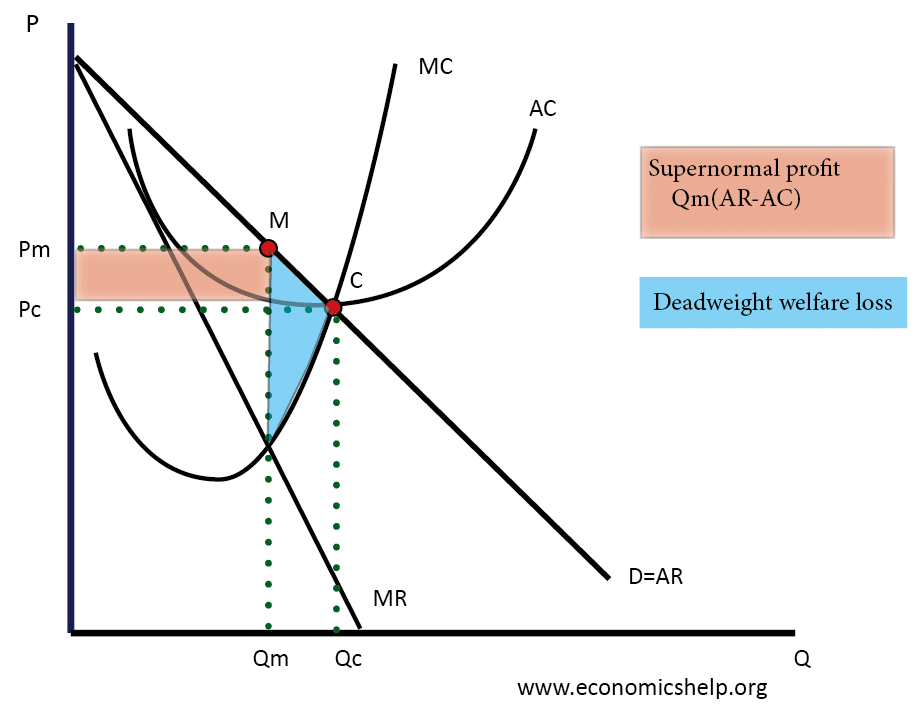
A monopoly maximises profits where MR=MC (at point m). It sets a price of Pm and quantity Qm.
Problems of Monopoly
- Higher prices. Firms with monopoly power can set higher prices (Pm) than in a competitive market (Pc). (Red area is supernormal profit)
- Allocative inefficiency. A monopoly is allocatively inefficient because in monopoly (at Qm) the price is greater than MC. (P > MC). In a competitive market, the price would be lower and more consumers would benefit from buying the good. A monopoly results in dead-weight welfare loss indicated by the blue triangle. (this is net loss of producer and consumer surplus)
- Productive inefficiency A monopoly is productively inefficient because the output does not occur at the lowest point on the AC curve.
- X – Inefficiency. – It is argued that a monopoly has less incentive to cut costs because it doesn’t face competition from other firms.Therefore the AC curve is higher than it should be.
- Supernormal Profit. A monopolist makes Supernormal Profit Qm * (AR – AC ) leading to an unequal distribution of income in society.
- Higher prices to suppliers – A monopoly may use its market power (monopsony power) and pay lower prices to its suppliers. E.g. supermarkets have been criticised for paying low prices to farmers. This is because farmers have little alternative but to supply supermarkets who have dominant buying power.
- Diseconomies of scale – It is possible that if a monopoly gets too big it may experience dis-economies of scale. – higher average costs because it gets too big and difficult to coordinate.
- Lack of incentives. A monopoly faces a lack of competition, and therefore, it may have less incentive to work at product innovation and develop better products.
- Lack of choice. Consumers in a monopoly market face a lack of choice. In some markets – clothing, choice is as important as price
see also: Disadvantages of Monopolies
Advantages of monopoly
1. Economies of scale
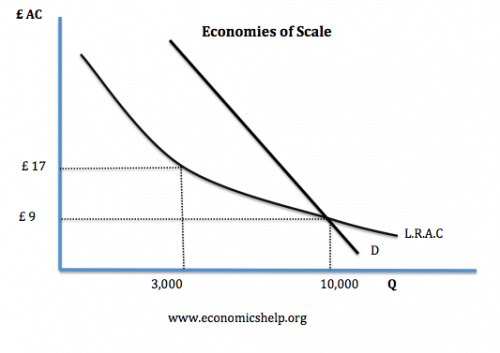
- If there are significant economies of scale, a monopoly can benefit from lower average costs. This can lead to lower prices for consumers.
- In the above example If there were 3 firms producing 3,000 units at an average cost of £17, average costs would be higher than a monopoly producing 10,000 units, and an average cost of £9. Therefore, for natural monopolies and industries with significant economies of scale, monopolies can be more efficient.
2. Research & Development
Monopolies make supernormal profit which can be invested in Research & Development. This is important for industries like medical drugs which require a lot of risky investment. In many industries which require substantial investment – a competitive industry with many small firms would be unsuitable.
3. A firm may gain monopoly power because it is the most efficient
Google gained monopoly power through offering innovative new products. It is hard to argue Google has x-inefficiency because of its monopoly power. You could make a similar case for firms, such as Apple and Amazon. In this case, it is their market dominance which comes from being innovative and meeting a consumer demand.
4. Global competition
A domestic monopoly may face competition from abroad, and therefore what may appear as a monopoly may still face competitive pressures. Also, a monopoly may face competition from related industries, e.g. Eurotunnel has a monopoly on train services from London to Paris, but faces competition from airlines.
see also: Advantages of Monopolies
Evaluation of monopolies
- It depends on the industry in question. For example, a monopoly is needed in a natural monopoly like tap water. However, for restaurants, there are no significant economies of scale and it is important to have a choice. Therefore monopoly would be very inappropriate for restaurants.
- Some industries need a lot of research and development (e.g. building new aeroplanes, research drugs). Therefore, a monopoly may be needed in this industry.
- A government may be able to regulate monopolies to gain benefits of economies of scale, without the disadvantages of higher prices.
How monopolies can develop
- Horizontal Integration. Where two firms join at the same stage of production, e.g. two banks such as TSB and Lloyds
- Vertical Integration. Where a firm gains market power by controlling different stages of the production process. A good example is the oil industry, where the leading firms produce, refine and sell oil.
- Legal Monopoly. E.g. Royal Mail or Patents for producing a drug.
- Internal Expansion of a firm. Firms can increase market share by increasing their sales and possibly benefiting from economies of scale. For example, Google became a monopoly through dominating the search engine market.
- Being the first firm e.g. Microsoft has created monopoly power by being the first firm.
Monopolies also need barriers to entry to protect them from new firms entering the market. Barriers to entry can include – brand loyalty through advertising and economies of scale
Good Monopolies
- Tap Water
- Apple?
Bad Monopolies
- Rockefeller – Standard Oil
- Microsoft in 1980s – keeping out competition by pre-installing Microsoft software packages.
- Facebook? Does Facebook have too much power over our personal data and ability to allow fake news into social media feeds?
Regulation of Monopolies
Governments can regulate monopolies. This, in theory, can enable the best of both worlds. Economies of scale and lower prices. Monopoly regulation can include:
- Price capping RPI-X to limit price increases
- Prevent mergers
- Windfall tax on monopoly profit.
- Investigating abuse of monopoly power, e.g. collusion.
For more details: see: Regulation of monopoly
Related
- Natural monopoly – when the most efficient number of firms in an industry is one.
- Types of market structure

2 thoughts on “Monopoly”
Comments are closed.