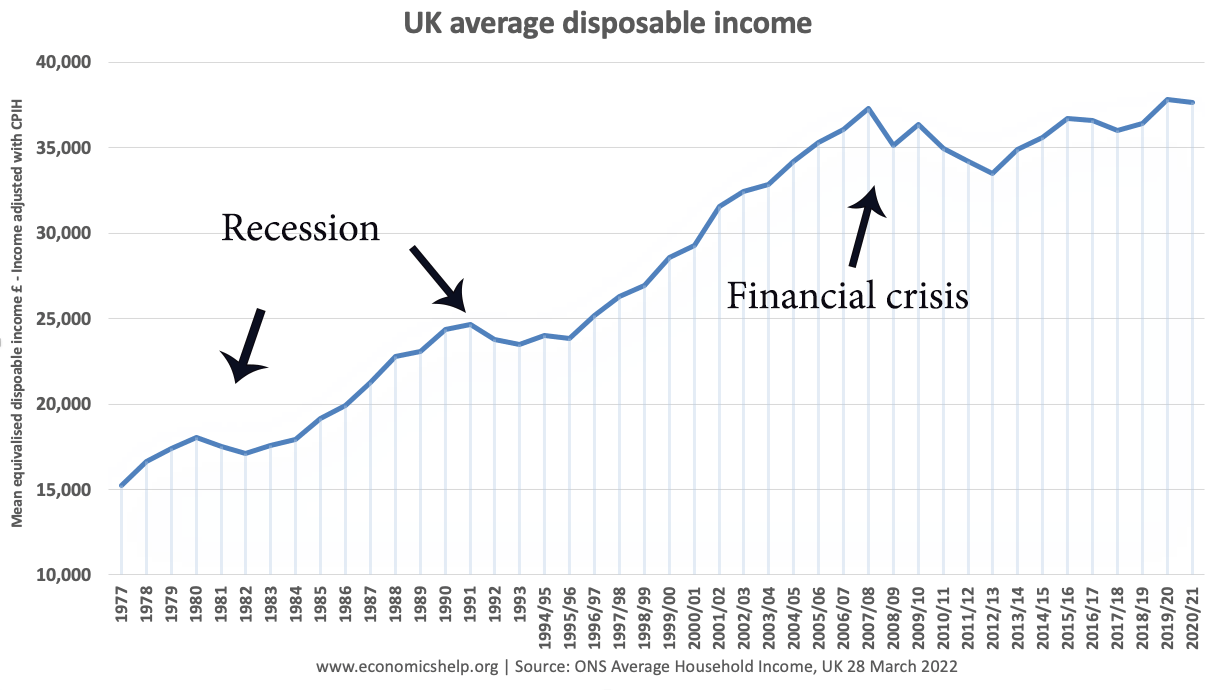
Output Gap Definition
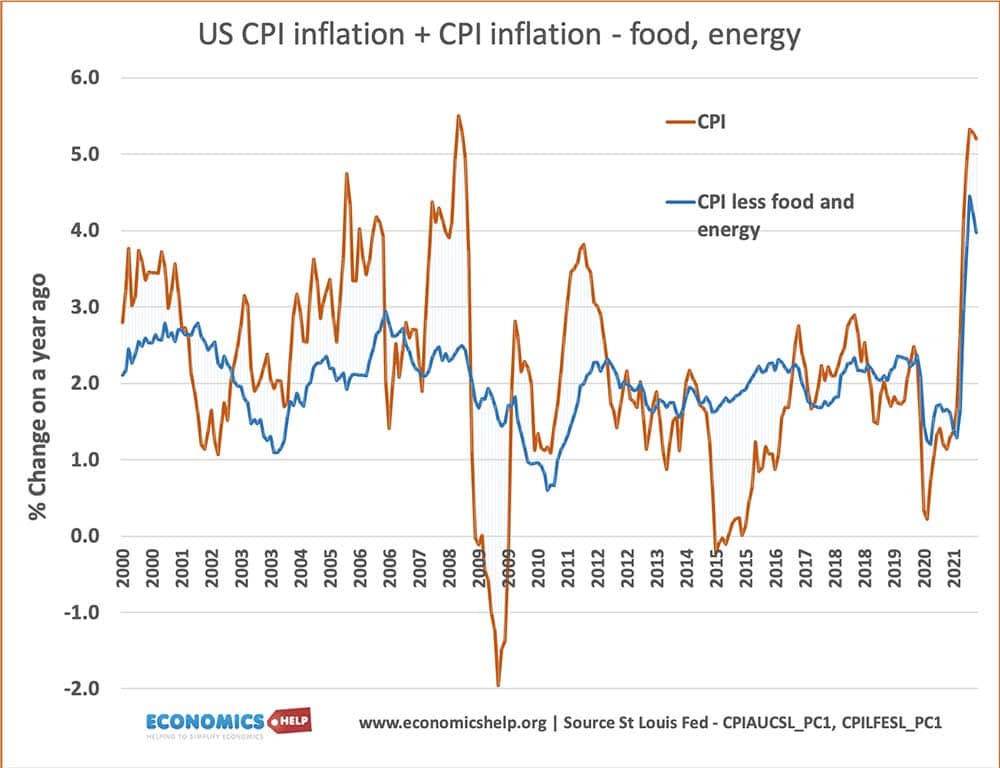
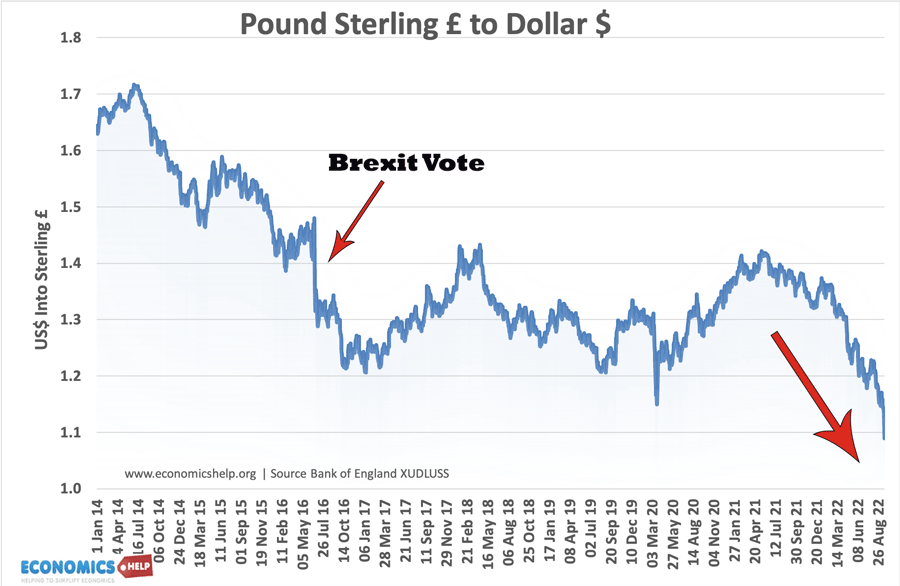
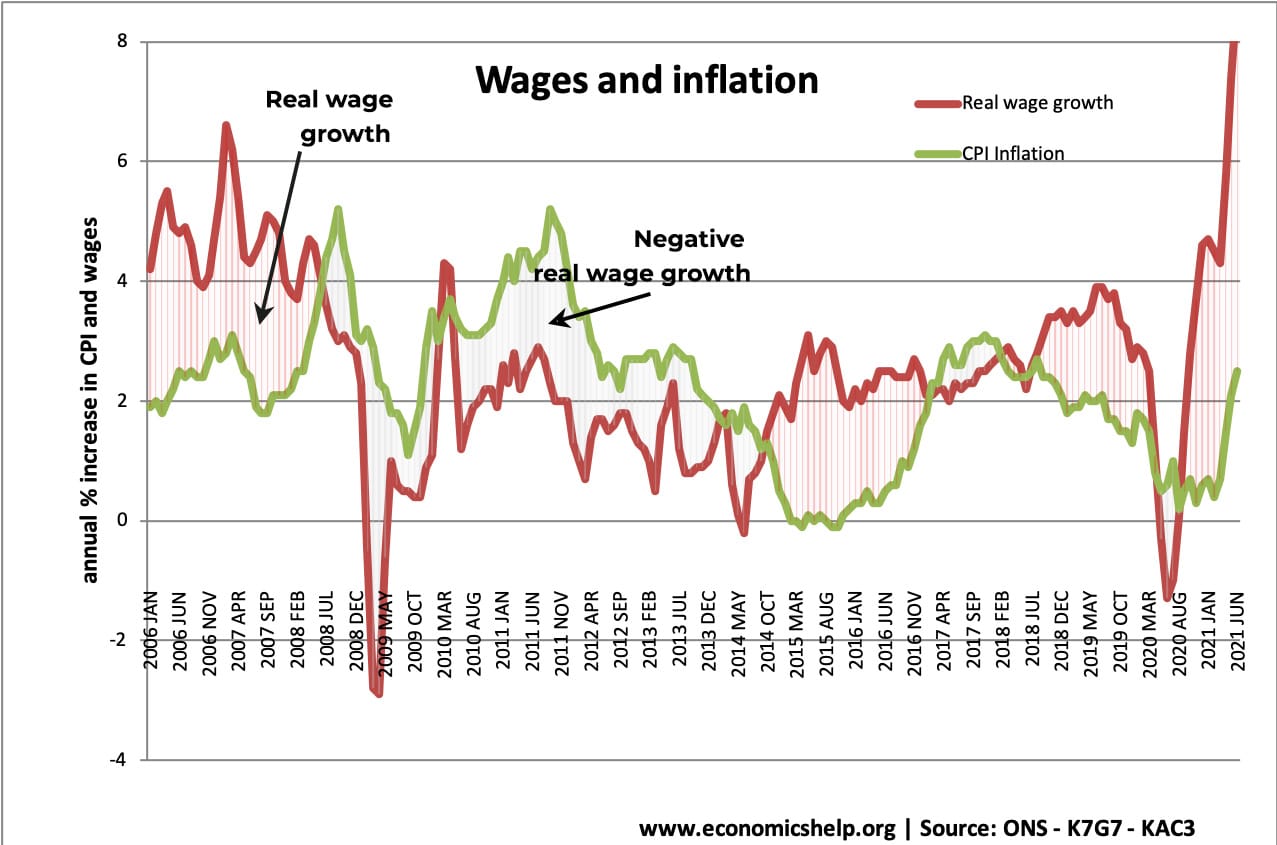
The output gap is a measure of the difference between actual output (Y) and potential output (Yf). A positive output gap means growth is above the trend rate and is inflationary. A negative output gap means an economic downturn with unemployment and spare capacity The output gap = Y- Yf Diagram for Output Gap The …