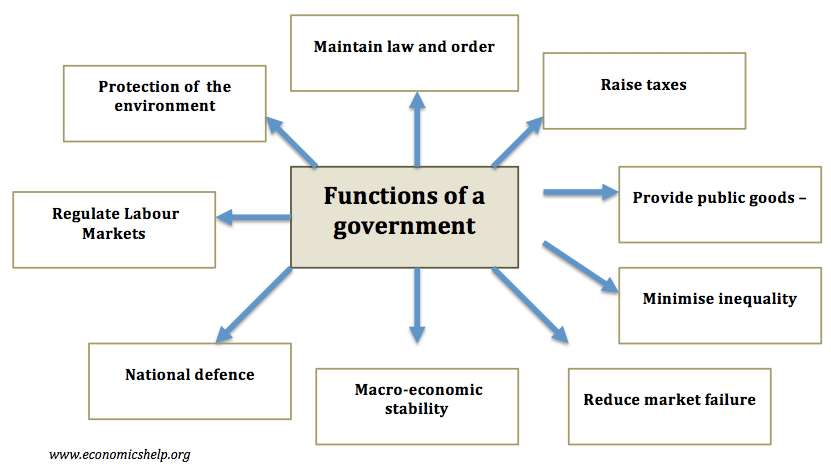
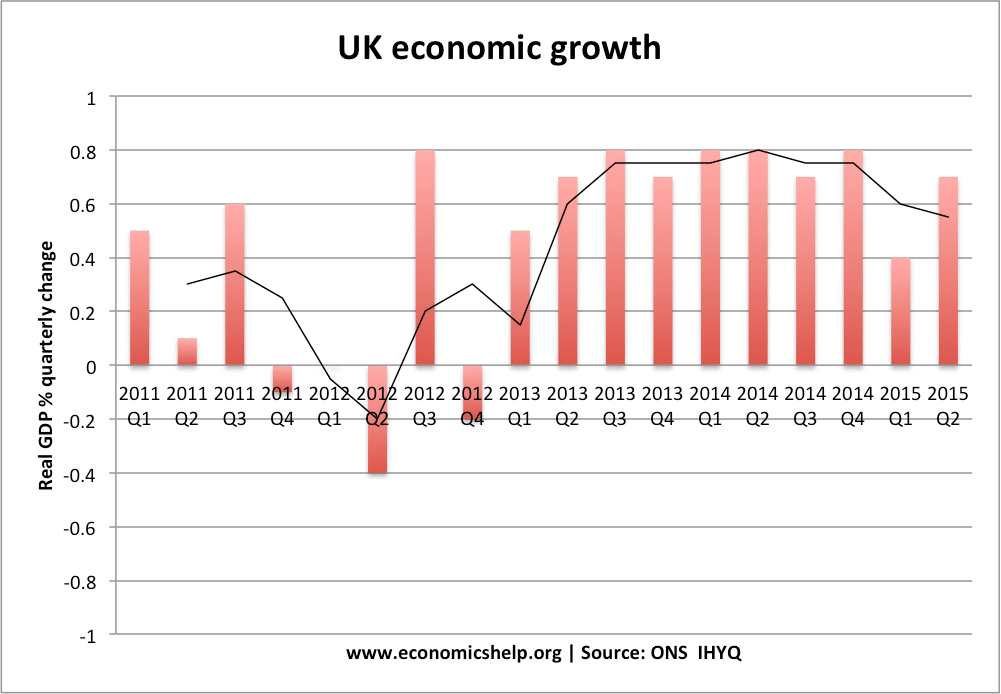
Structural unemployment
Definition: Structural unemployment is caused by a mismatch of skills between the unemployed and available jobs. Structural unemployed is caused by changes in the economy, such as deindustrialisation, which leaves some unemployed workers unable to find work in new industries with different skill requirements. Structural unemployment occurs even during periods of strong economic growth. It …