Asian Financial Crisis 1997
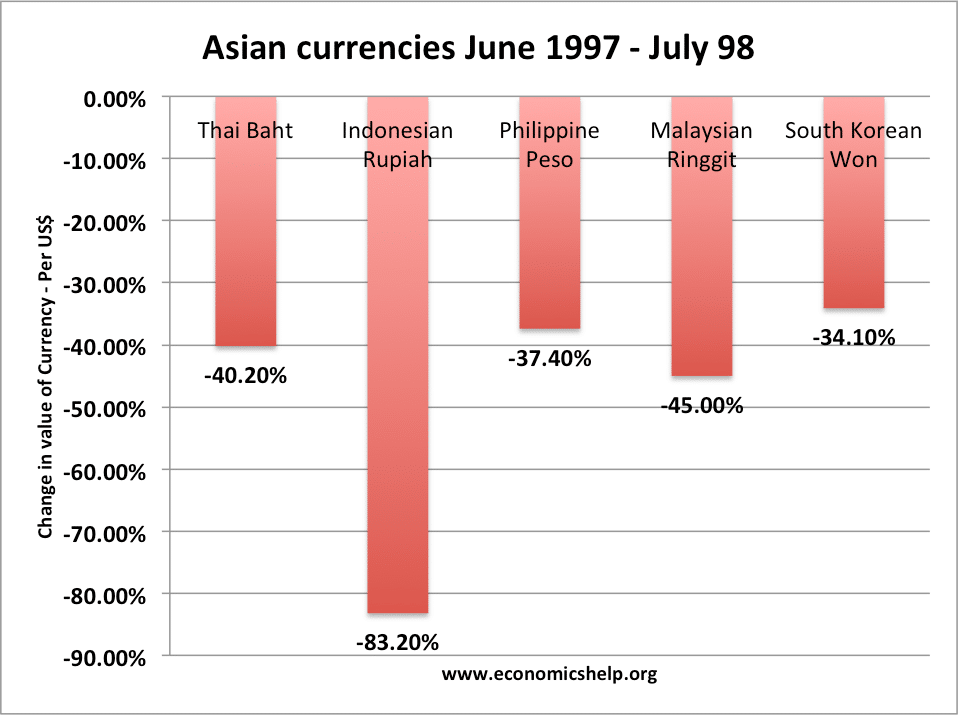
The Asian financial crisis of 1997 refers to a macroeconomic shock experienced by several Asian economies – including Thailand, Philippines, Malaysia, South Korea and Indonesia. Typically countries experienced rapid devaluation and capital outflows as investor confidence turned from over-exuberance to contagious pessimism as the structural imbalances in the economy became more apparent. The crisis of ’97-99 …