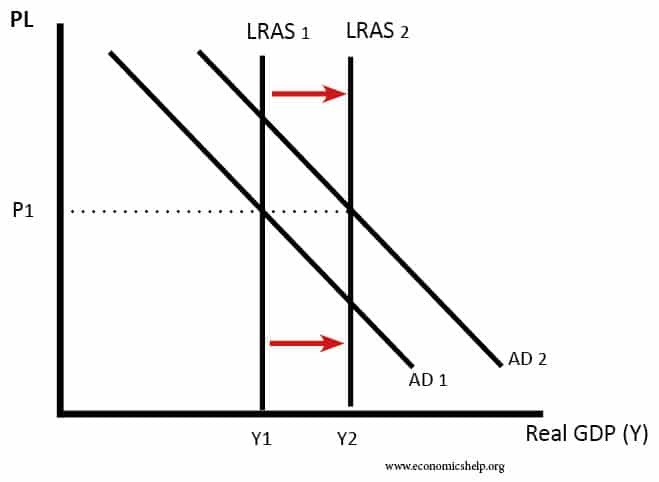
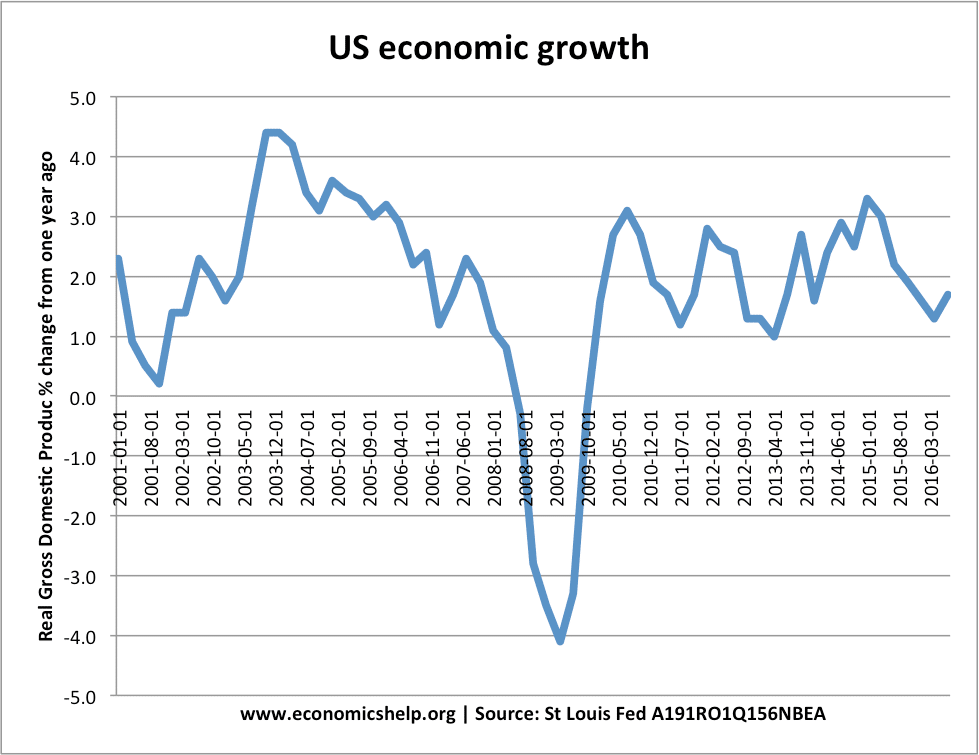
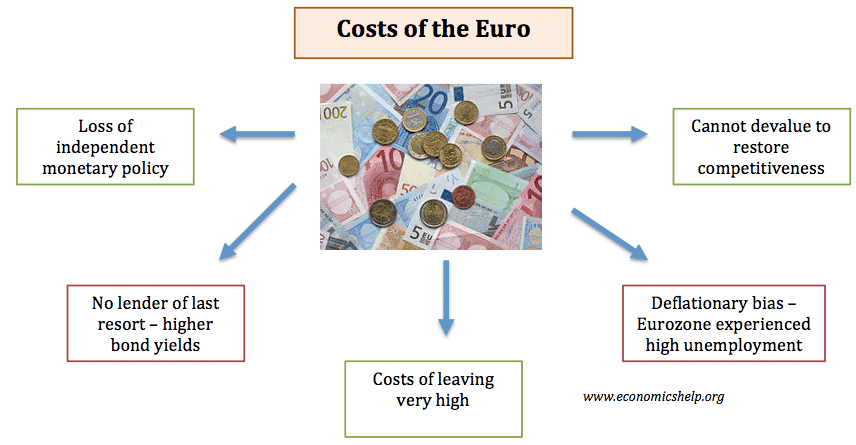
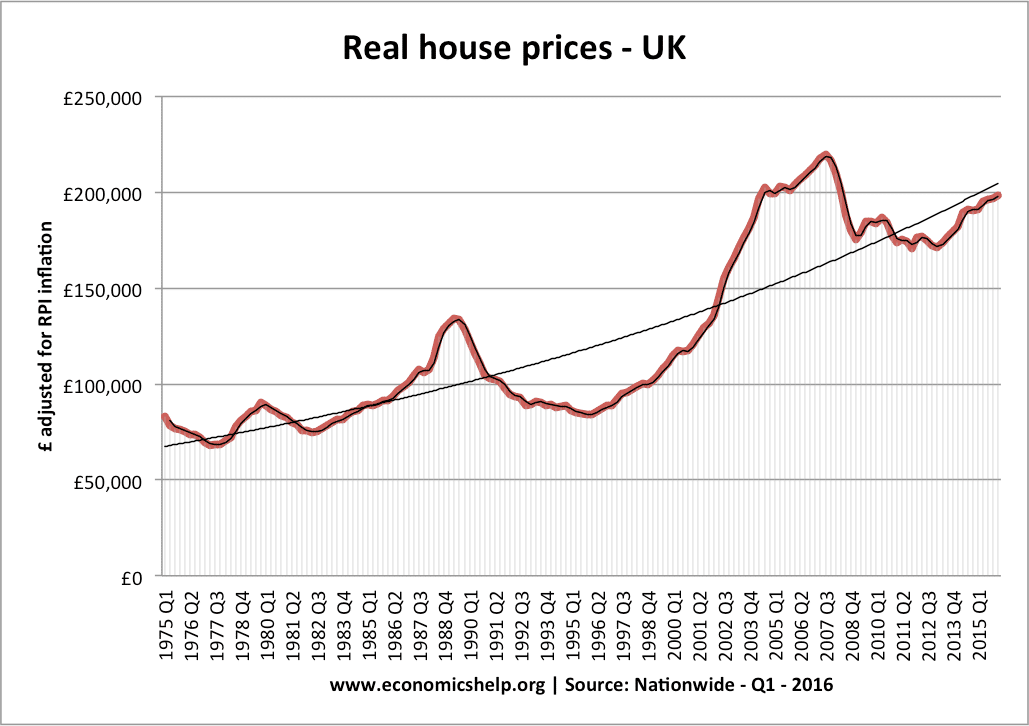
Inelastic supply
Supply is price inelastic if a change in price causes a smaller percentage change in supply. (PES of less than one) Example of inelastic supply – Price of rents falls by 20%; Q.Supply declines by 1%. PES = 0.05 Diagram of inelastic supply In this case, an increase in price from £30 to £40 has …