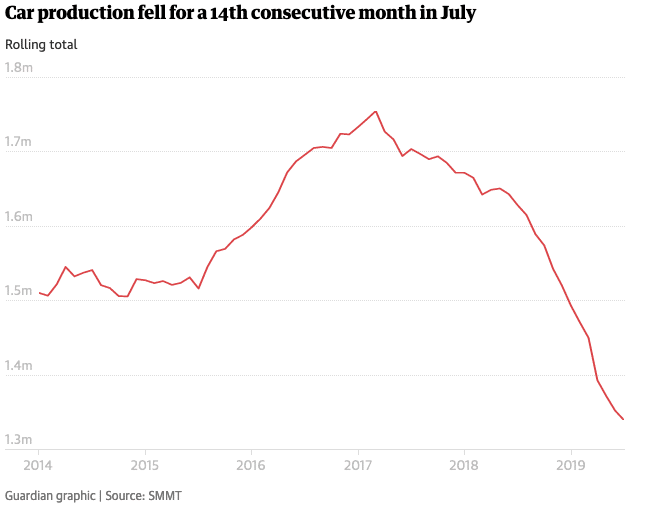
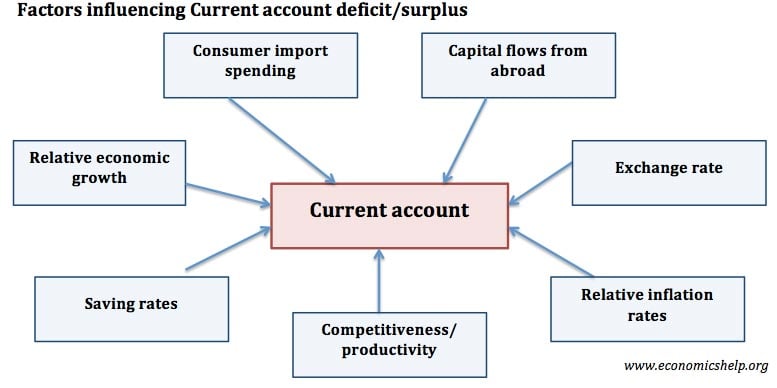
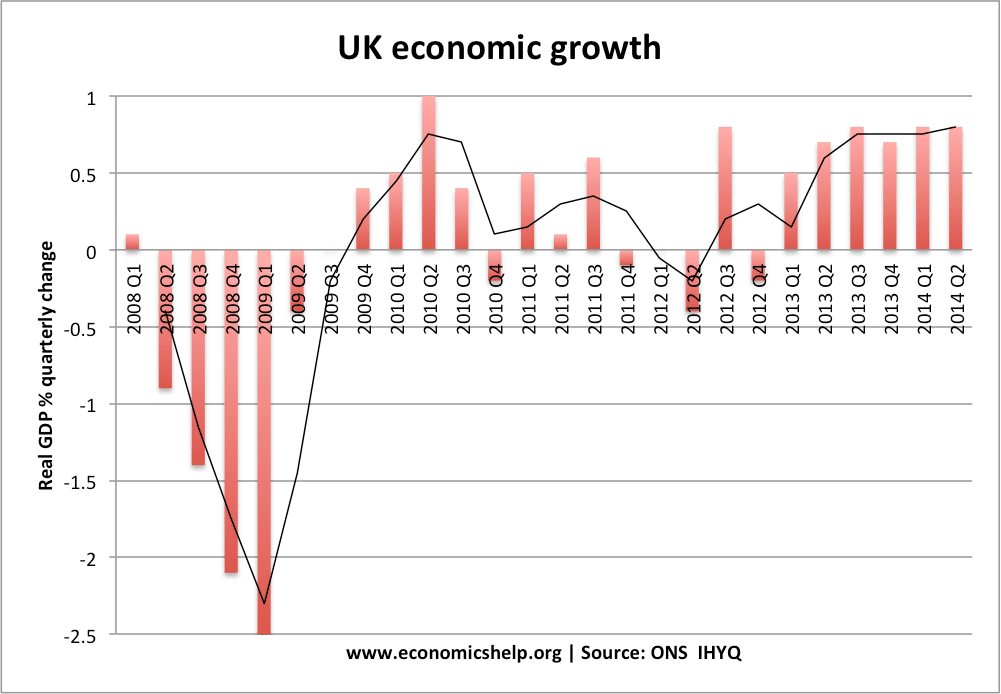
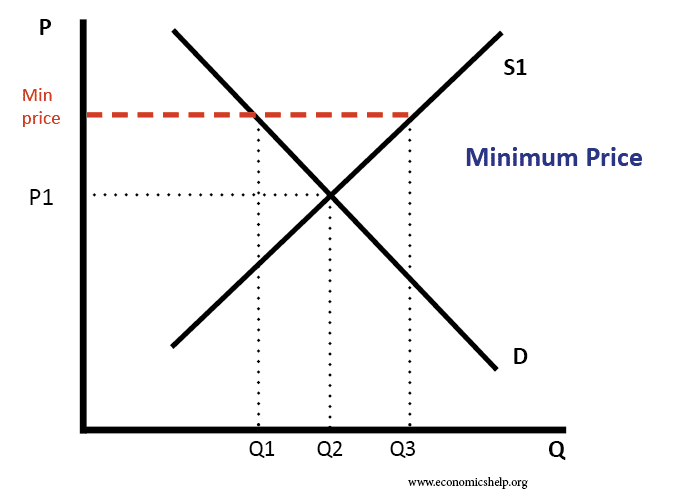
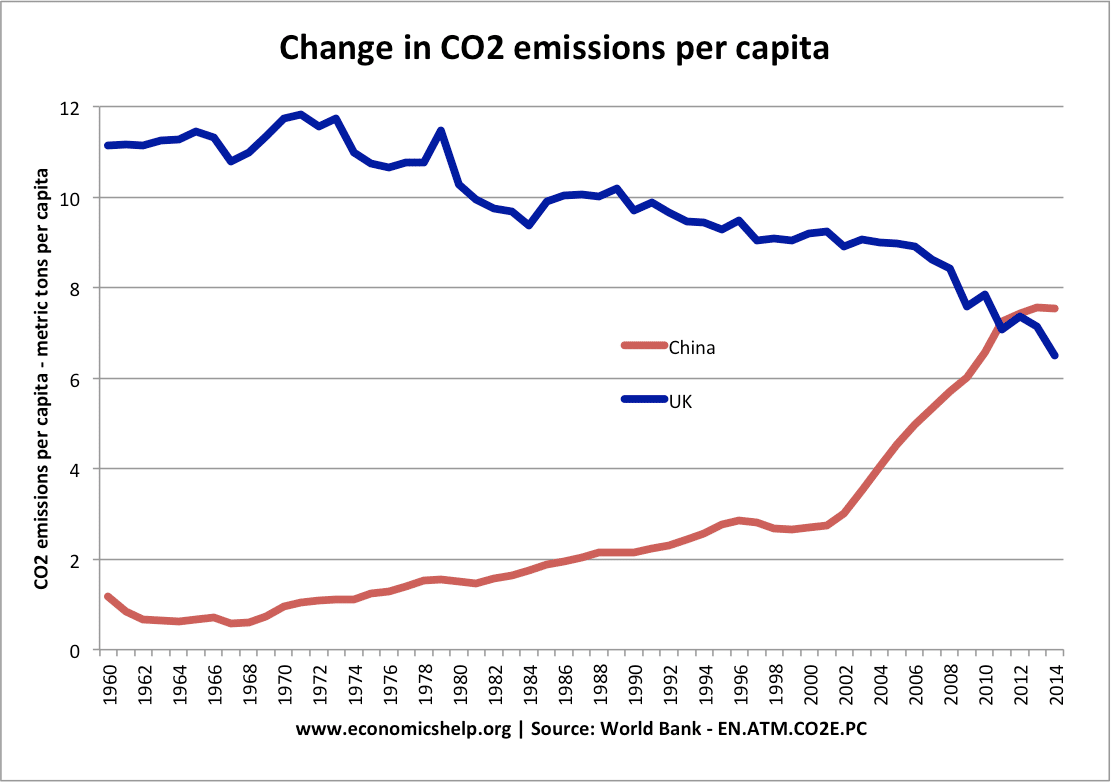
Main Problems of UK Economy 2020
Readers Question: What are the main problems of the current UK economic situation? Low economic growth and in particular stagnant real wage growth Poor productivity growth since 2008 – which affects long-term growth prospects. Uncertainty from Brexit and likely costs to trade from new custom arrangements. Manufacturing sector State of the housing market – expensive …