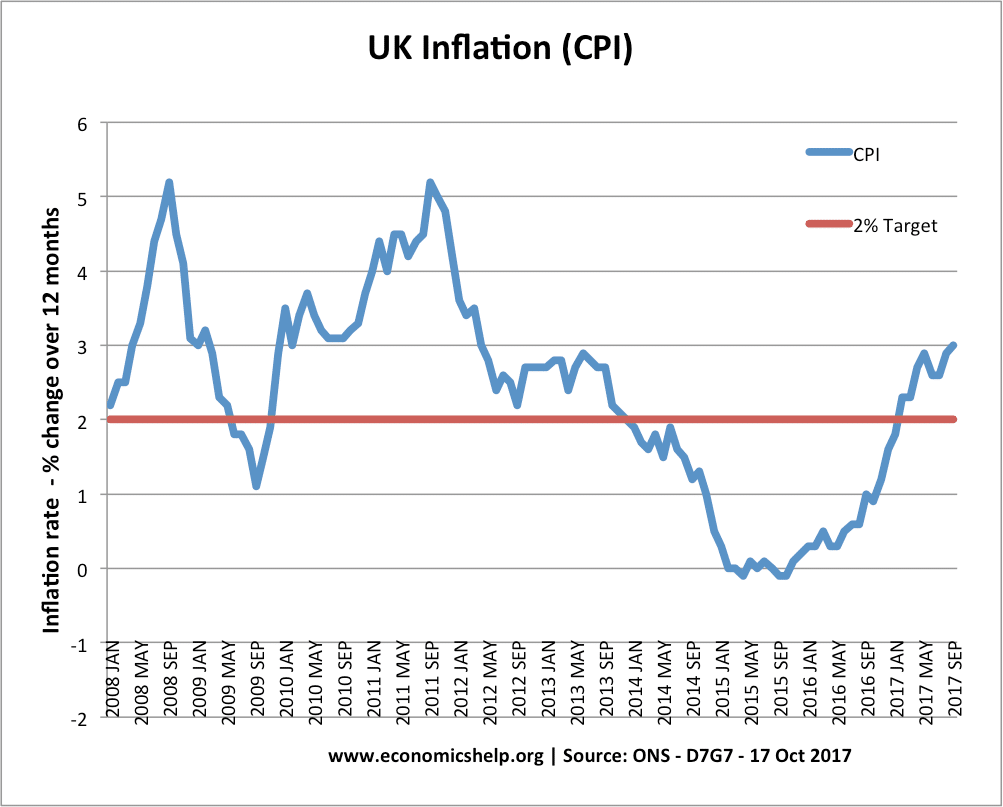
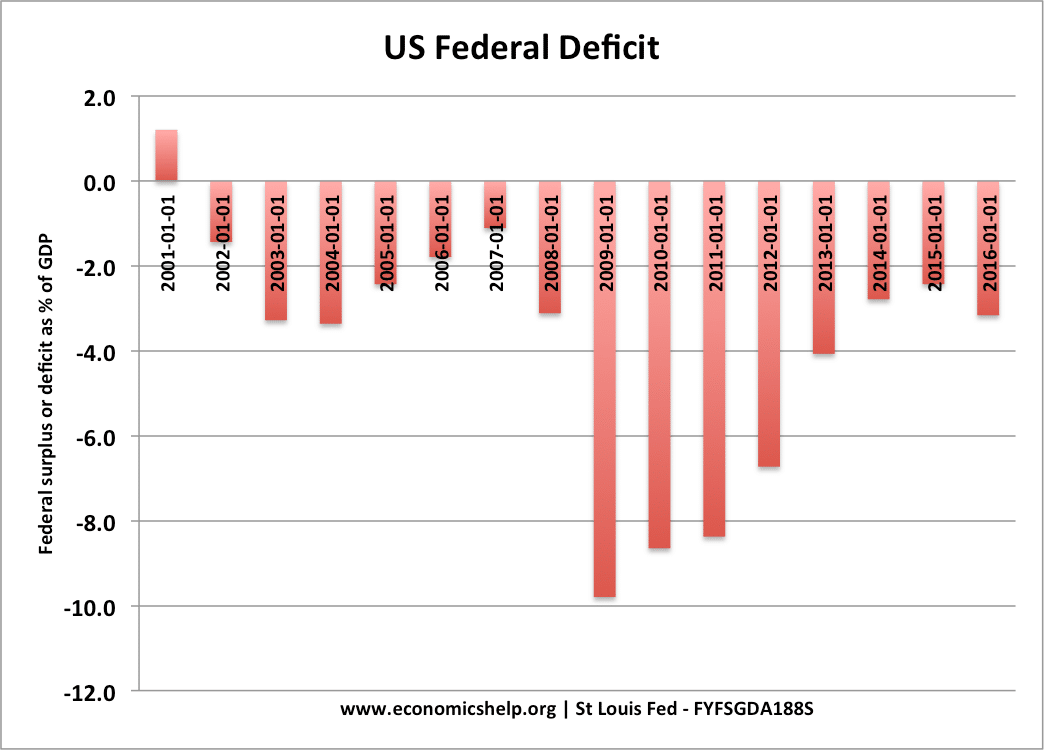
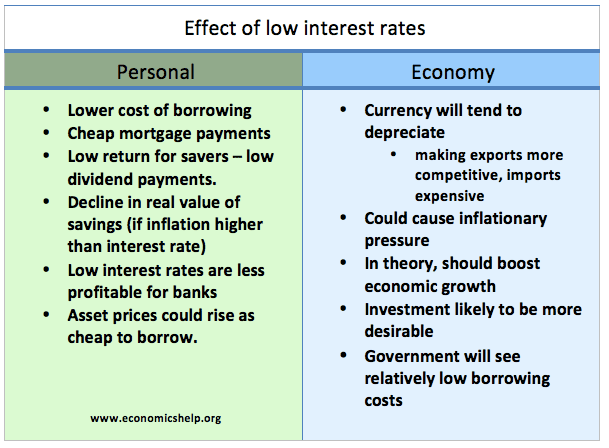
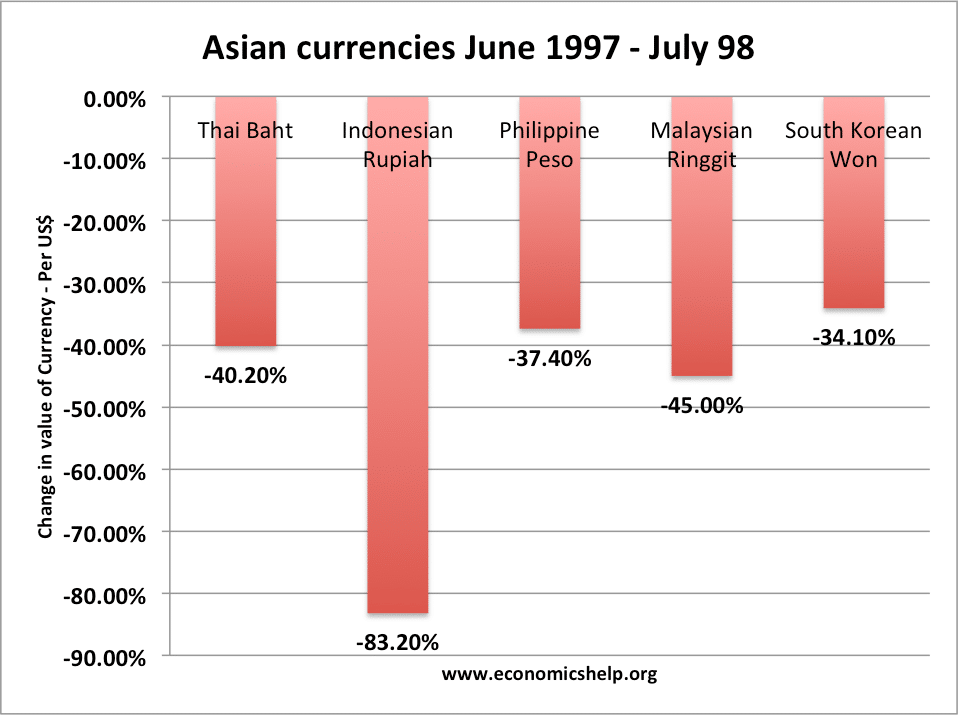
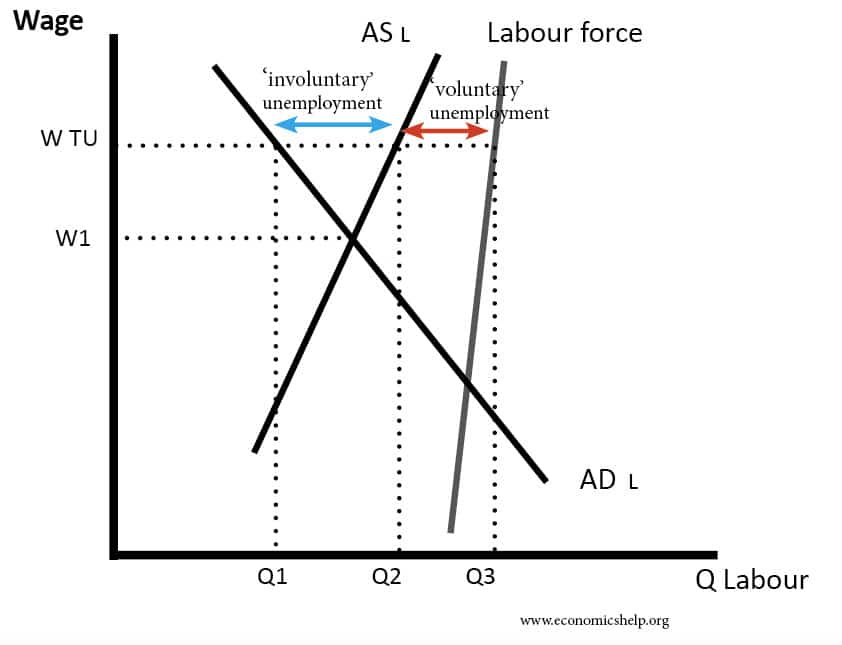
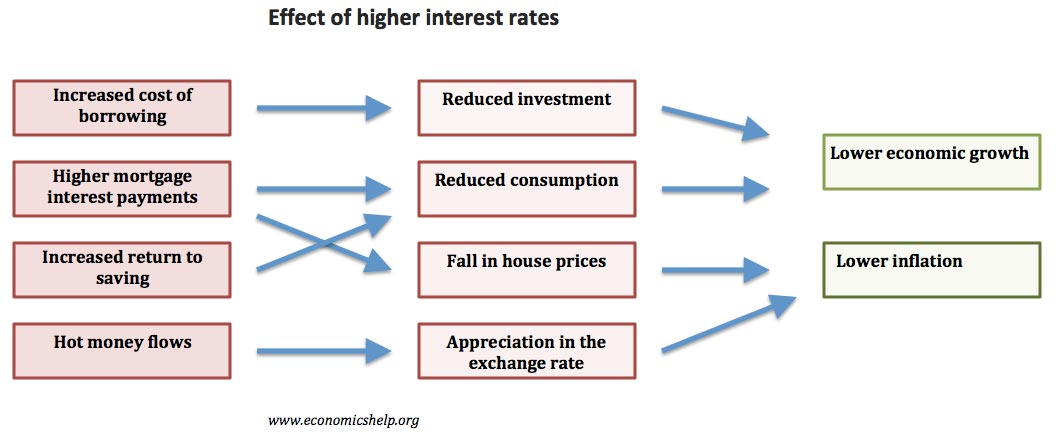
The importance of supply-side policies
Supply side policies are government policies which seek to increase the productivity and efficiency of the economy. They can involve interventionist supply side policies (e.g. government spending on education) or free market supply-side policies (e.g. reduce government legislation) The main macroeconomic objectives of the government include: Higher economic growth Low inflation Low unemployment Equilibrium on …