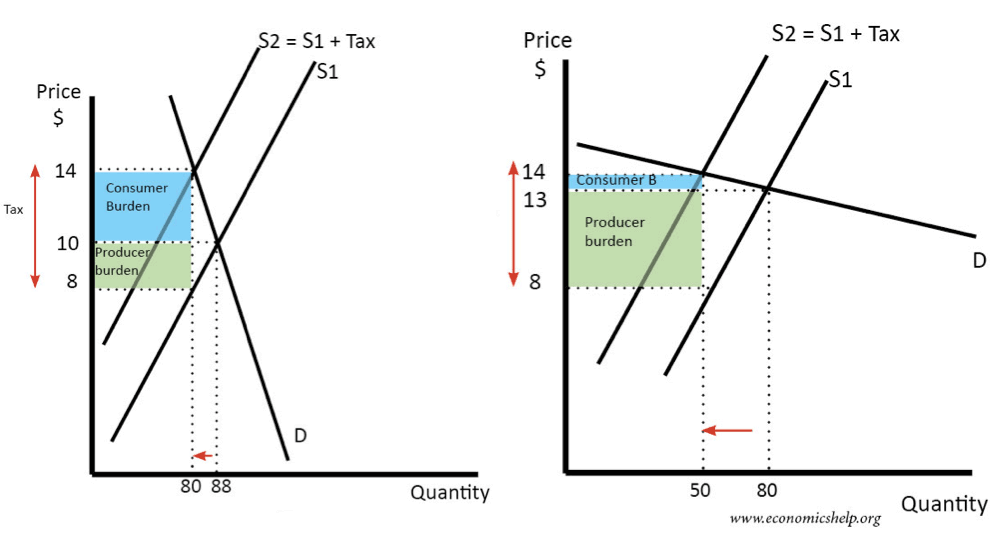
Elasticity in Economics
Elasticity is an important concept in economics. It is used to measure how responsive demand (or supply) is in response to changes in another variable (such as price). Price Elasticity of Demand The most common elasticity is price elasticity of demand. This measures how demand changes in response to a change in price. See: Price …