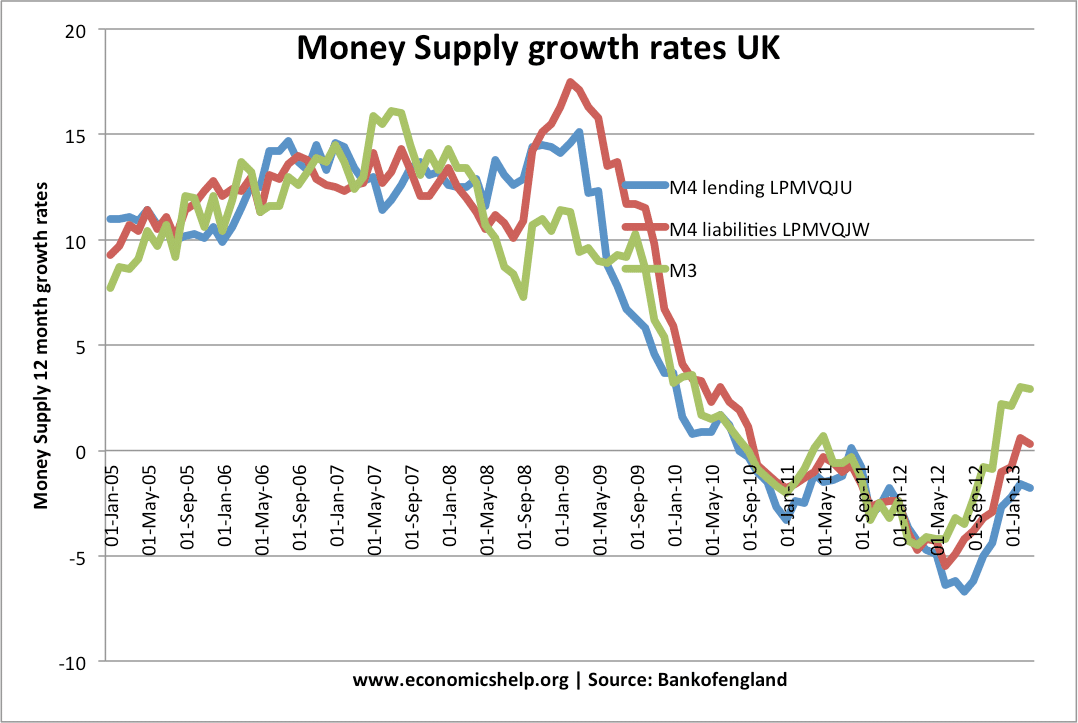
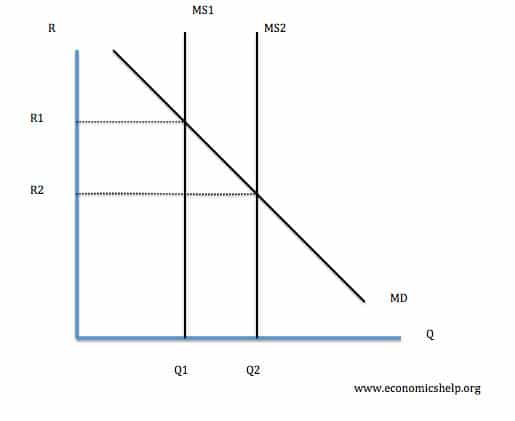
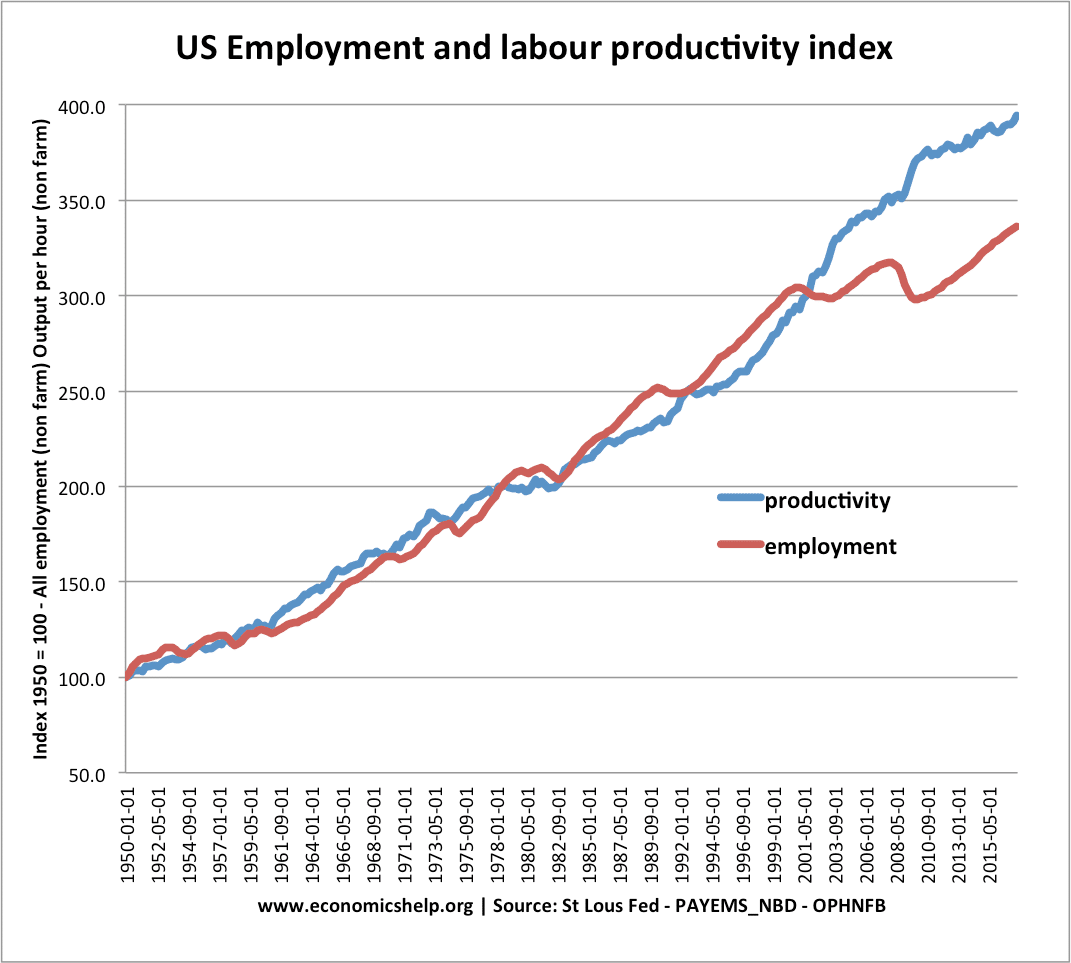
Money Supply, M0, M3, M4 and Inflation
Definition: The money supply measures the total amount of money in the economy at a particular time. It includes actual notes and coins and also any deposits which can be quickly converted into cash. There are different measures of the money supply. Narrow Money e.g. M0 = This is the level of notes and coins …