Sticky wages
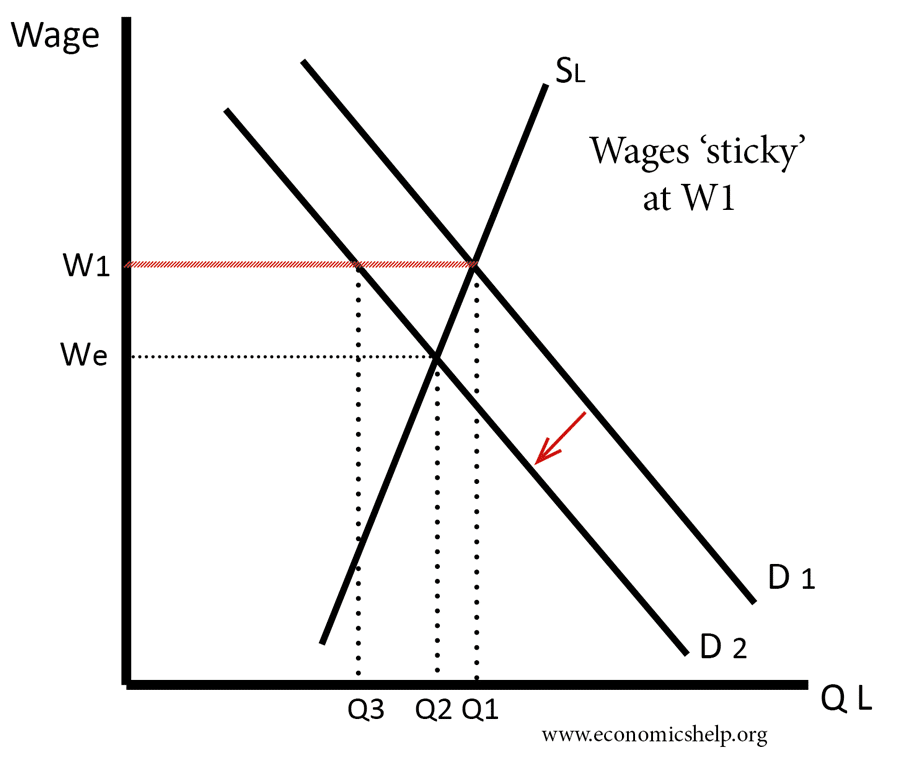
Definition – Sticky wages is a concept to describe how in the real world, wages may be slow to change and get stuck above the equilibrium because workers resist nominal wage cuts. Wages can be ‘sticky’ for numerous reasons including – the role of trade unions, employment contracts, reluctance to accept nominal wage cuts and …