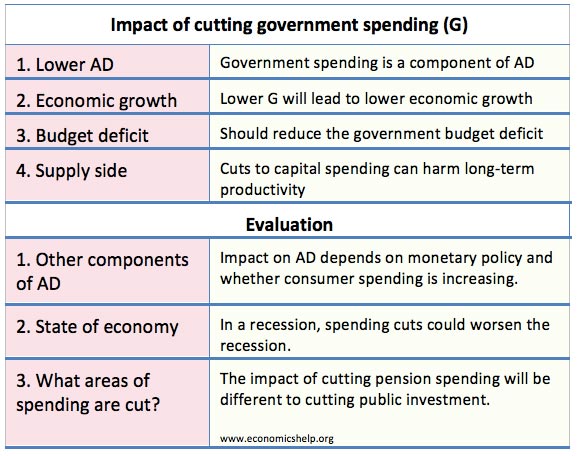
Impact of cutting government spending
Readers Question: Discuss the impact of a decrease in government spending? If the UK government cut government spending, it would have a significant impact on both aggregate demand (AD) and the supply side of the economy – depending on which areas of public spending were cut. Firstly, government spending (G) is a component of Aggregate …