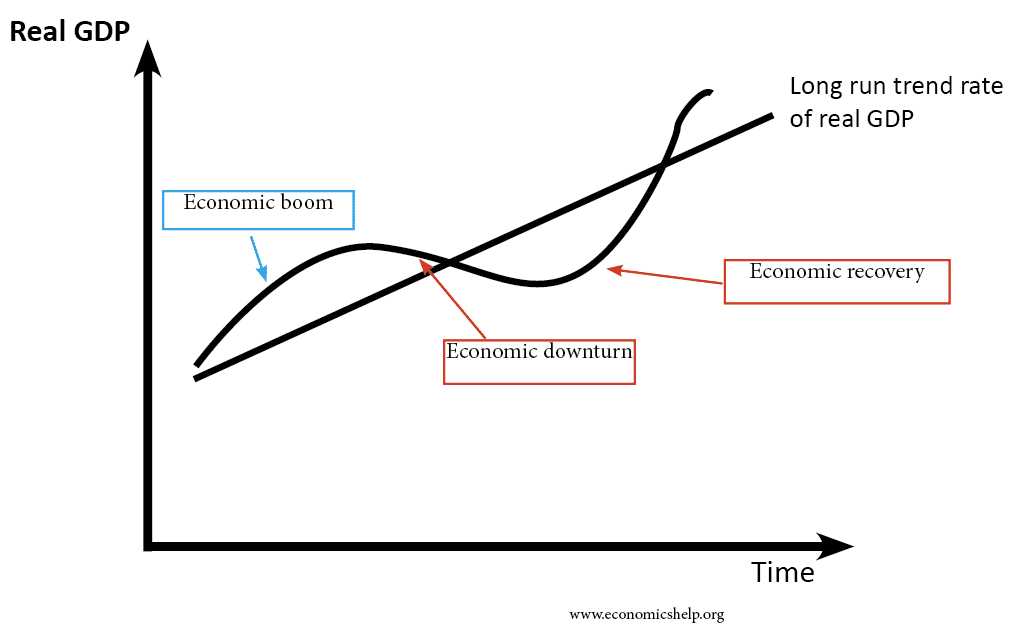
Solution to Stagflation
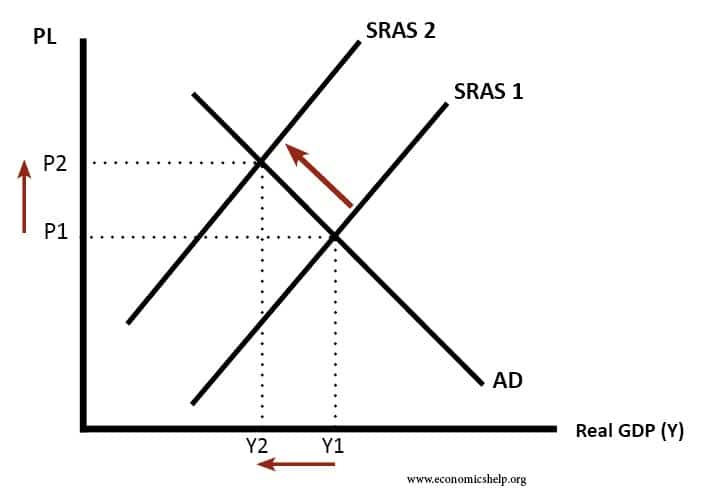
Readers Question: what is the solution for stagflation? Stagflation occurs when there is an increase in inflation and also at the same time an increase in unemployment and lower economic growth. Typically stagflation will be caused by an increase in the cost of production which shifts the SRAS curve to the left. This could be …