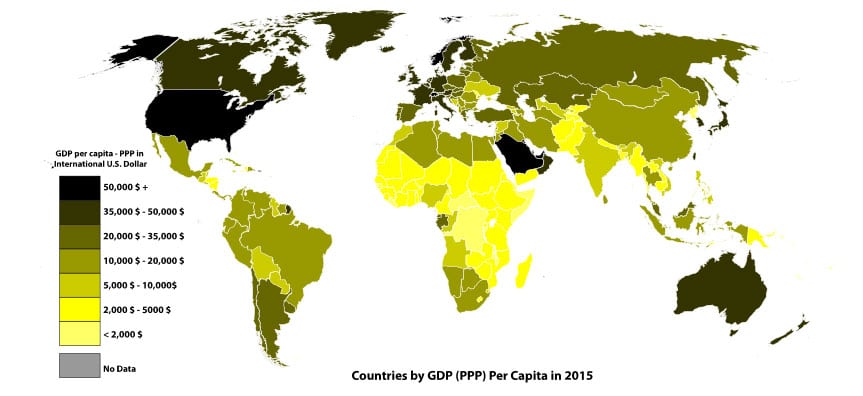
Measures of Global Poverty
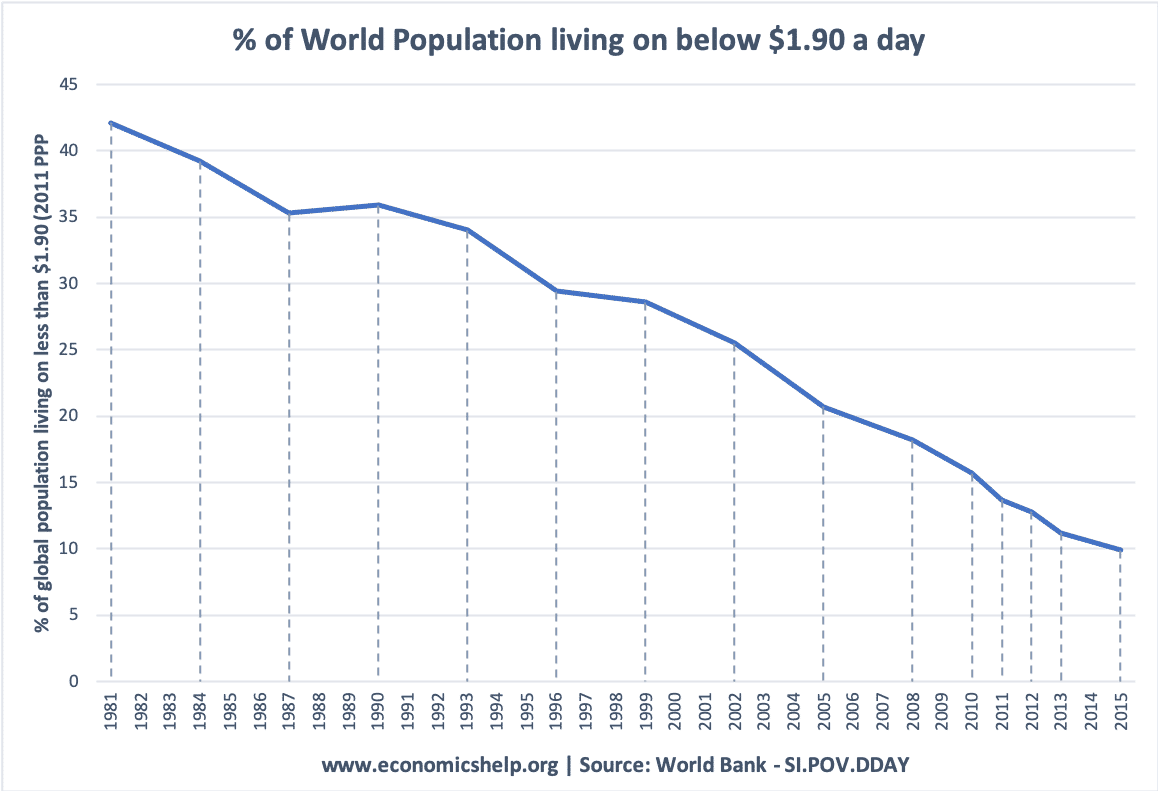
The World Bank publishes several measures of global poverty, which measure poverty by different levels of income. The most common is the percentage of the population who live on less than $1.90 a day. This is a measure of absolute poverty. There are also measures of relative poverty which compare income against the national average. …