Effect of Government Subsidies
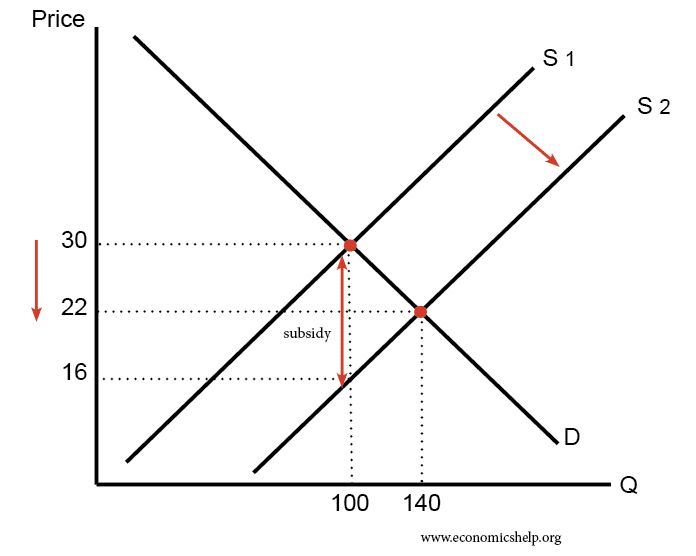
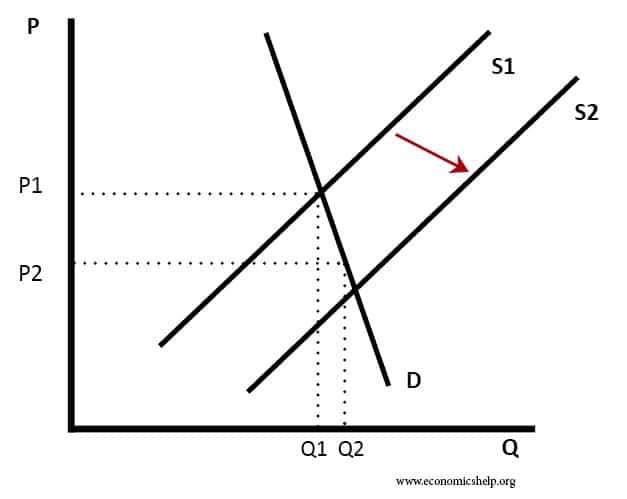
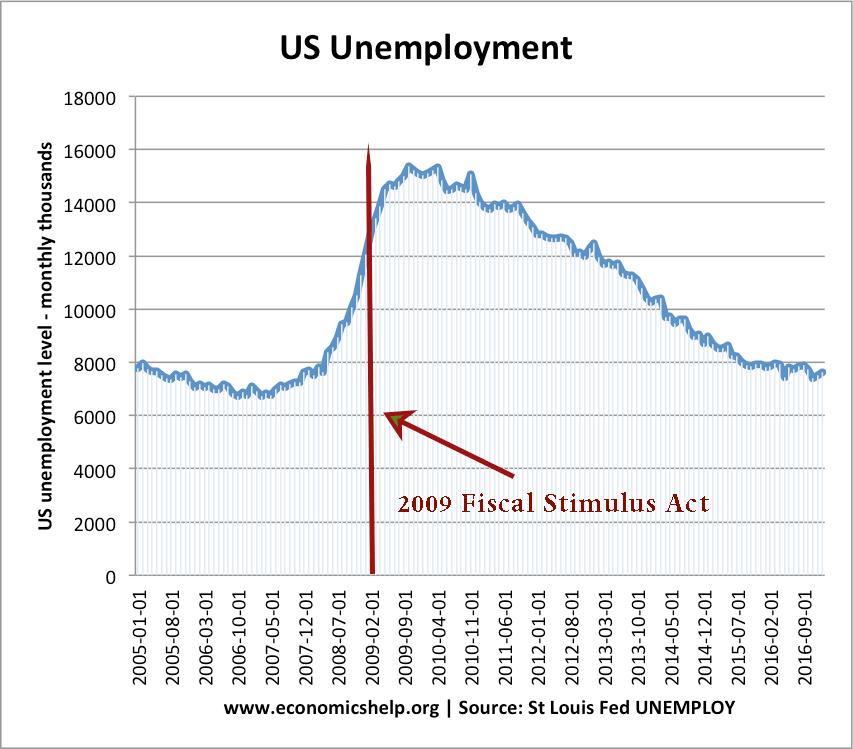
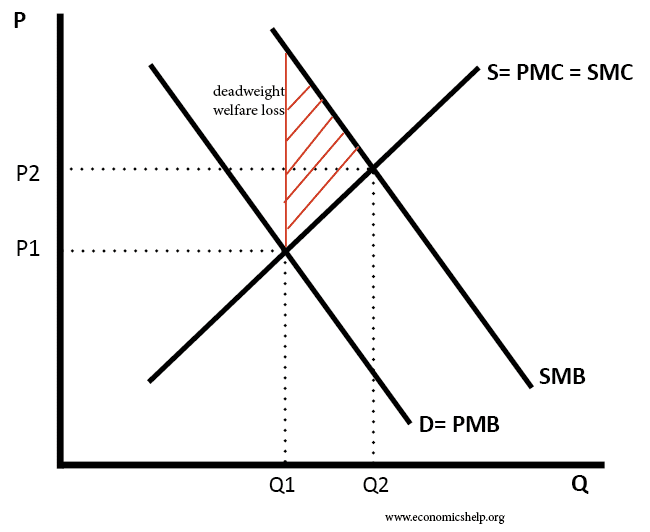
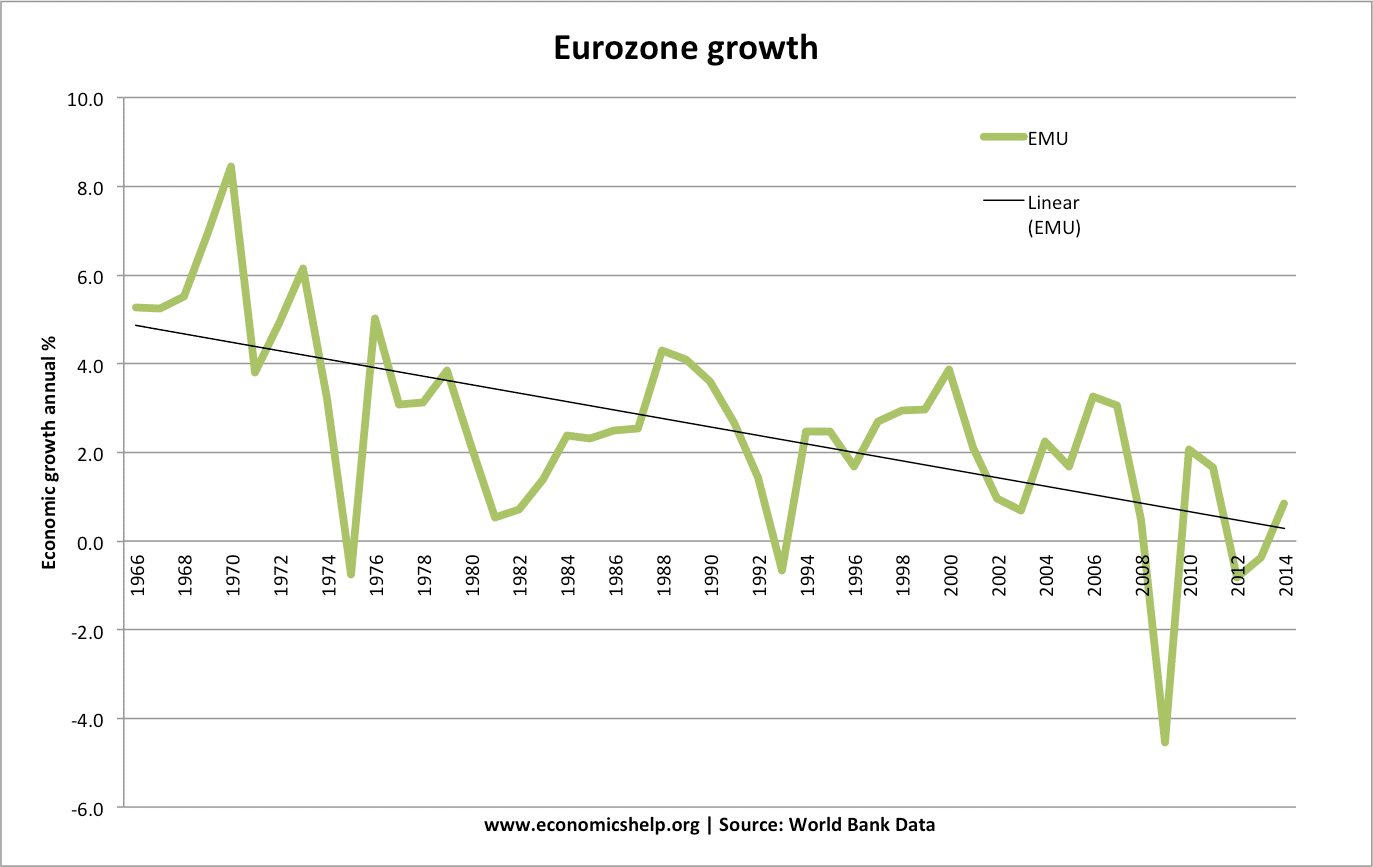
Readers Question: What happens when the government subsidizes a product? A subsidy means the government pays part of the cost. For example, the government may give farmers a subsidy of £10 for every kilo of potatoes. The effect is to shift the supply curve to the right, leading to lower price and higher quantity demanded Diagram …