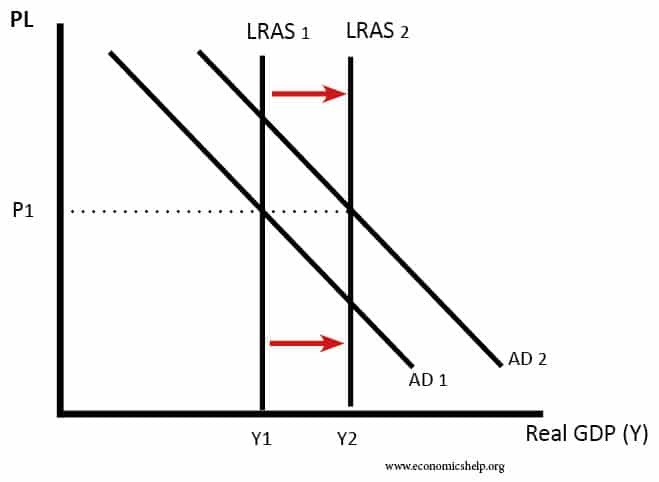
Should we tax robots?
Automation and AI have been called the fourth industrial revolution. Robots replacing the jobs of human labour will increase efficiency and enables higher economic growth But, others are concerned that rapid automation can create unequal outcomes, with some losing their job and struggling to gain new forms of employment. A robot tax would, in theory, …