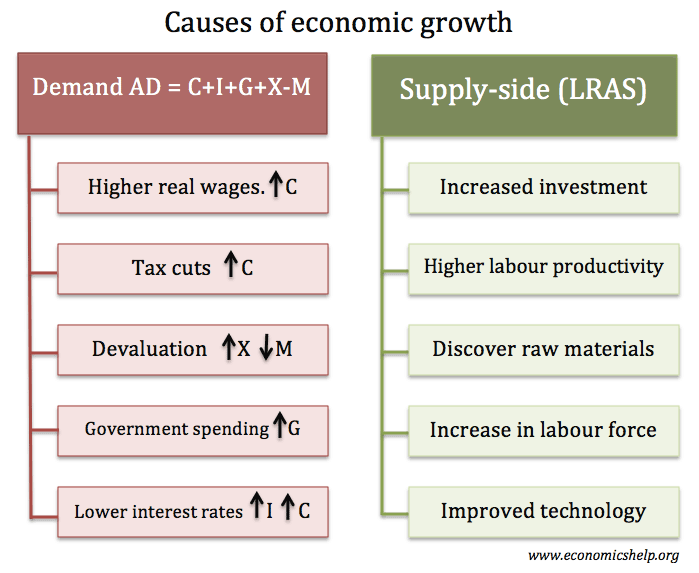
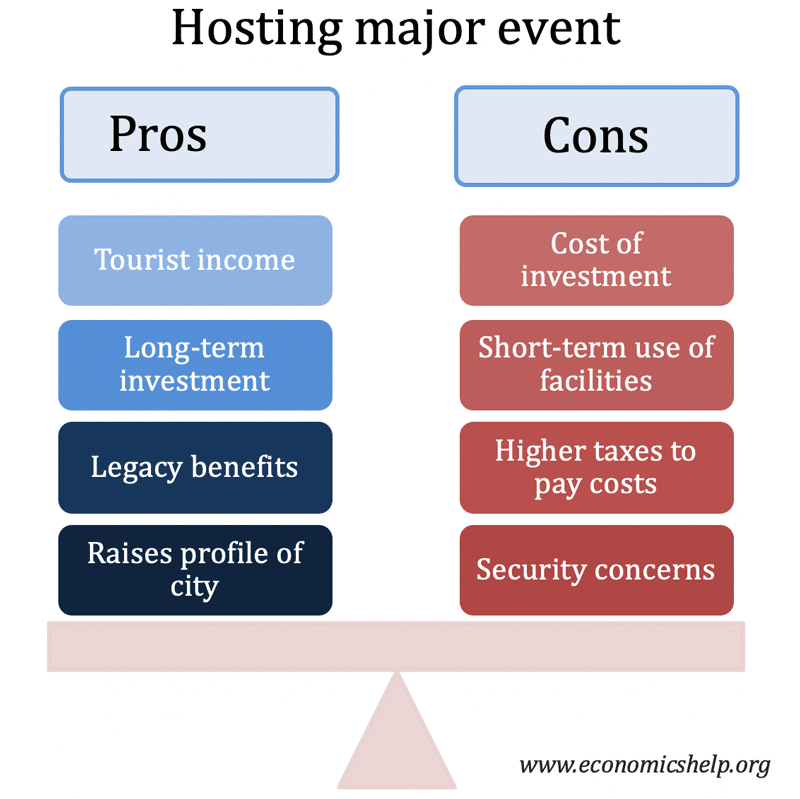
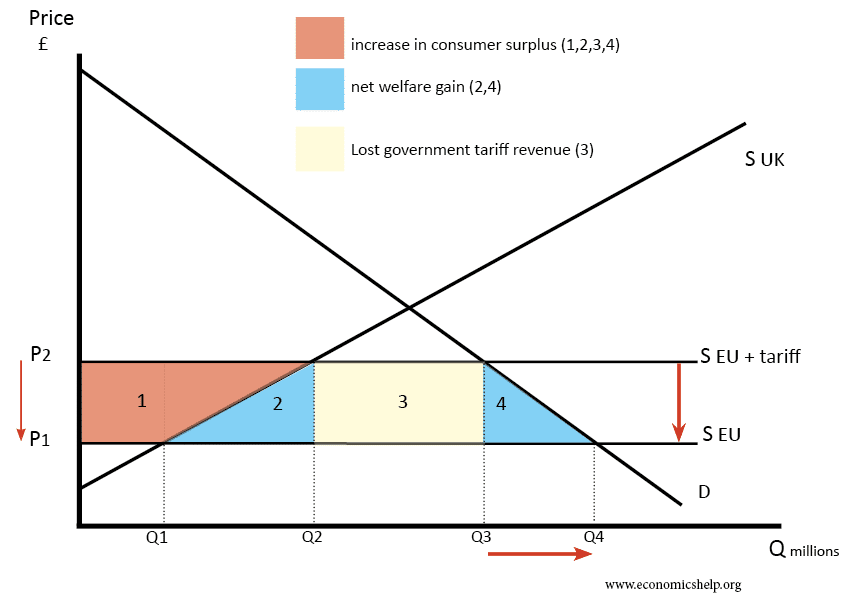
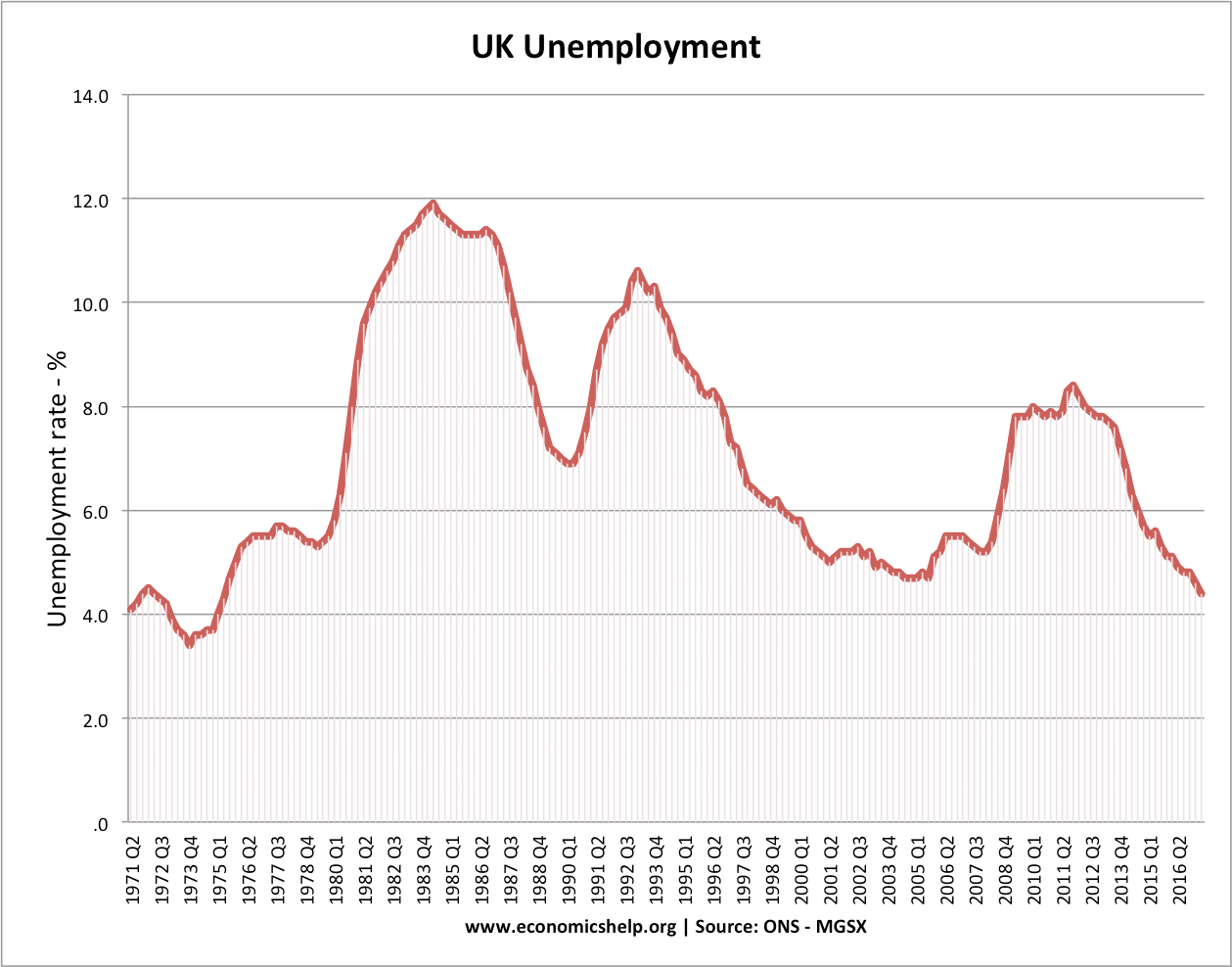
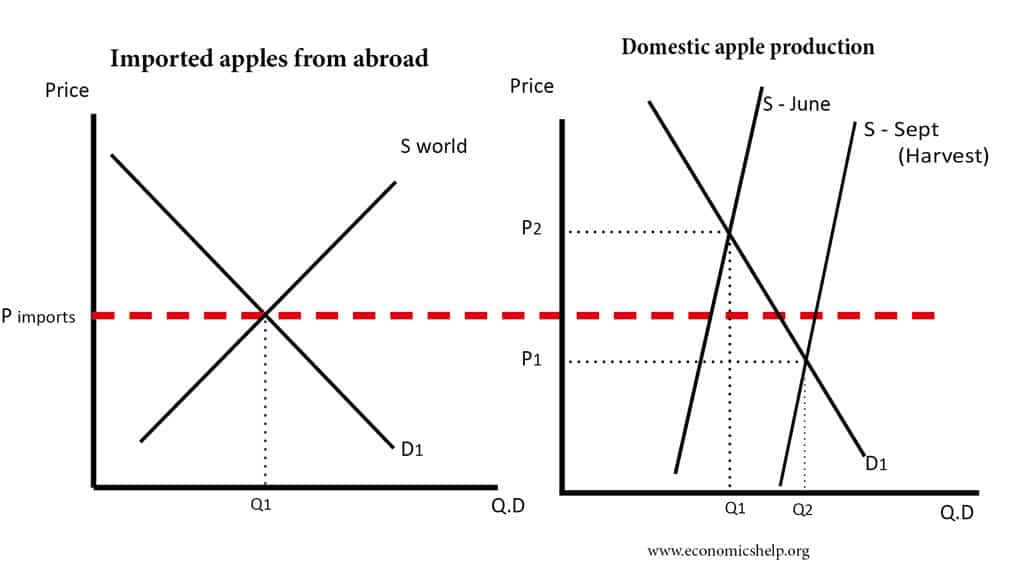
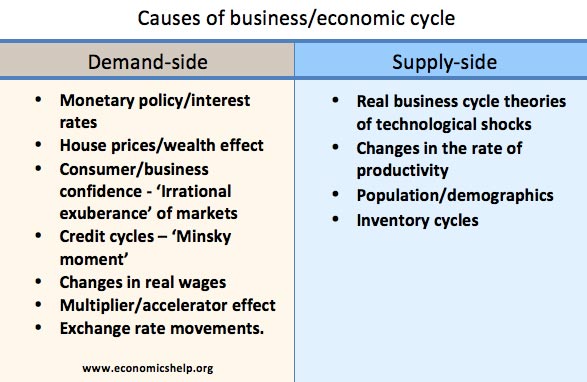
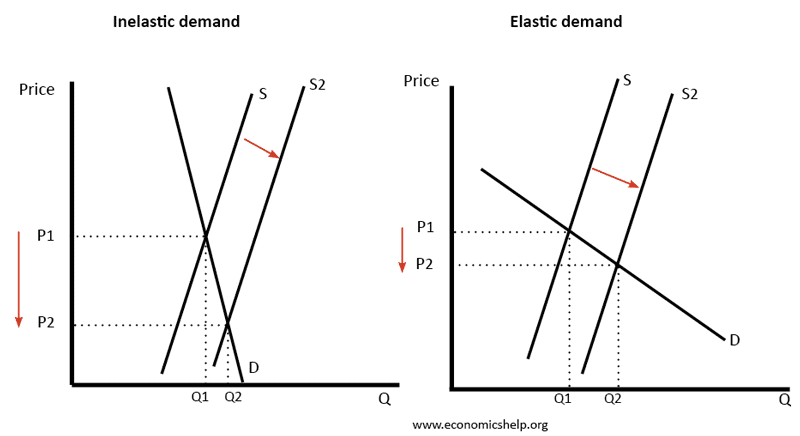
Positive Externalities
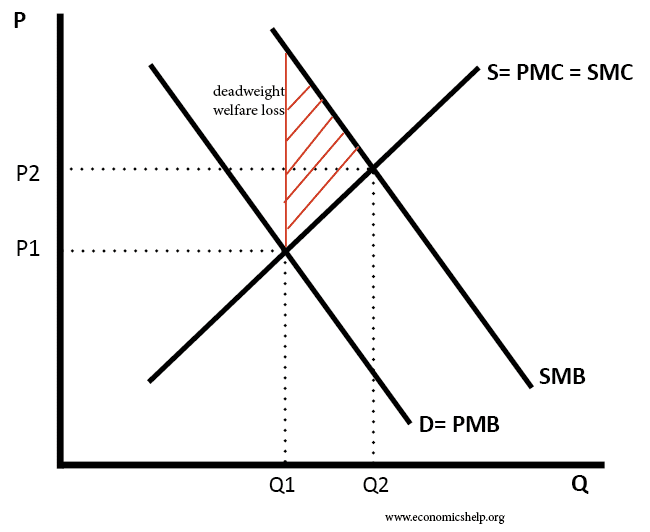
Definition of Positive Externality: This occurs when the consumption or production of a good causes a benefit to a third party. For example: When you consume education you get a private benefit. But there are also benefits to the rest of society. E.g you are able to educate other people and therefore they benefit as …