Indifference curves and budget lines
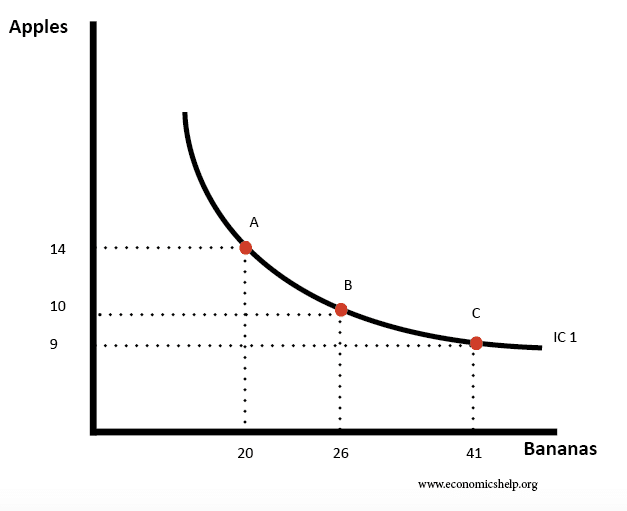
An indifference curve is a line showing all the combinations of two goods which give a consumer equal utility. In other words, the consumer would be indifferent to these different combinations. Example of choice of goods which give consumers the same utility Table plotted as indifference curve Diminishing marginal utility The indifference curve is convex …