What causes price fluctuations for the supplier in an agricultural market such as coffee/tea?
Coffee and tea are agricultural products, and therefore supply can be variable depending on several factors behind the control of producers (weather, disease). Furthermore, because demand and supply are inelastic, any change in supply can cause a significant change in price.
Factors which cause variable supply
1. Weather conditions
For example, an early frost can harm supply (causing a rise in prices). This is a problem for agricultural products like coffee and bananas – plants susceptible to frost.
Good weather can lead to an unexpectedly large increase in supply (which can lead to glut on the market and falling prices.
Also, disease and pests can affect the supply. If potatoes are affected by blight, it can cause potato prices to rise.
2. Inelastic demand
Demand for coffee and tea are relatively price inelastic. If the price of coffee falls, there will be a smaller percentage rise in demand. This is because there are few close substitutes to coffee/tea. Also, coffee/tea accounts for a small percentage of income and therefore a change in price doesn’t make much difference to overall demand.
With inelastic demand, a change in price causes relatively large change in the price.
3. Inelastic supply
In the short term, the supply of coffee and tea is inelastic. If price rises, farmers can’t respond by increasing supply overnight. You have to clear the ground and plant more coffee plants. It will take 3-5 years before new coffee plants start to produce beans. Therefore, there is a big delay in responding to changing prices.
4. Global market
In recent years, the number of countries producing coffee has increased. Traditional producers like Colombia have faced increased competition from new countries seeking to enter the market. More countries make it harder for coffee producers to influence prices through the use of minimum prices and buffer stock schemes.
Diagram showing price of coffee
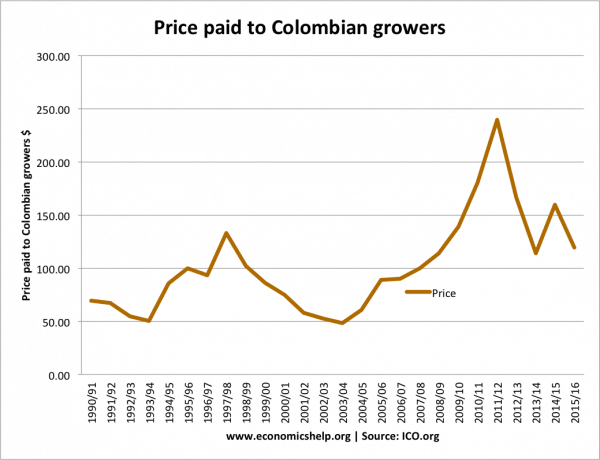
This shows the price paid to Colombian growers for coffee. – in US cents/lb
It shows significant fluctuations in the market price.
Link between supply and price
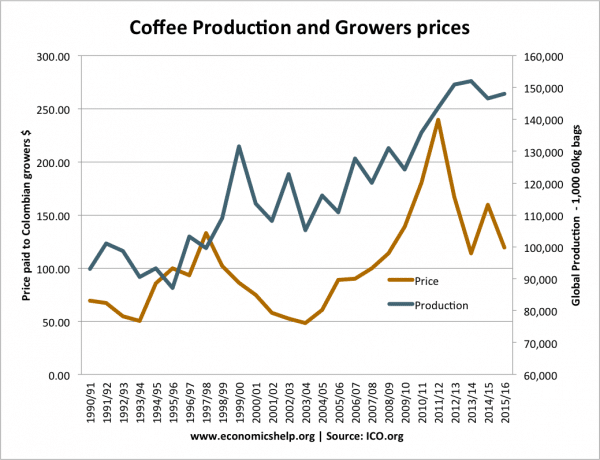
The link between price and production is not always what we would expect.
In theory, we would expect to see a rise in supply causing a fall in price.
- For example, between 1997 to 2000, we see production rise from 90,000 to over 13,000. In this period the price falls from about 130 cents per Pound to 60 cents per Pound.
However, from 2002 to 2010, we see a rise in both price and global production. After 2010, the growth in supply finally leads to a fall in price.
One factor may be that the rise in price 2002, encouraged an increase in supply. When prices started to fall in 2011, the increased planting of coffee plants can’t be reversed so we see the continued increase in supply because of previous years planting.
What could explain a rise in production and rise in price?
There could be a strong rise in global demand. For example, new markets for coffee in China and India; rising incomes in developing countries enable it to become more affordable. In the West, there has been strong growth for coffee as it becomes a more fashionable drink. During the day, coffee has replaced alcohol as a drink of choice for workers and businessmen. If demand rises, then we can see a rise in price, despite rising production.
Coffee retail price and global production
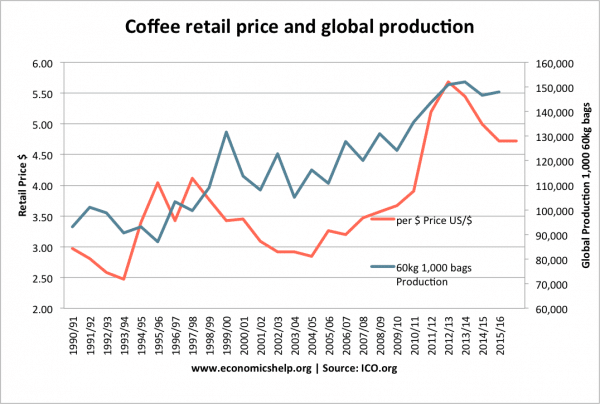
The retail price of coffee mirrors the price paid to suppliers. With a peak in price during 2012.
Why is the price of Starbucks less volatile than the actual price of coffee beans?
If you buy a cappuccino from Starbucks, the price of coffee beans only accounts for a small percentage of the final price. One estimate puts the cost of coffee beans, close to a few cents. Most of the cost is labour costs, rent and other raw materials. Therefore, even if coffee beans double in price, it may only affect the retail price by a few cents.
Source of coffee bean statistics
- International Coffee Organisation
- Consumer price coffee beans the US at St Louis Fed
Related

Dear Tejvan, I love your site. I teach business and economics to kids 10-12 yo and just love how you manage to explain difficult concepts in an accessible way. Congratulations! Any chance you have a similar analysis for chocolate industry? Thank you in advance.
nice data
I like this ur website but if u re explaining some of the factor pls explains it one after the other so that some will understand it better. Thanks
i can also add on, the cob web theory of production also accounts for price changes of agric prdcts; this where when few farmers are inolved in production,prices tend to increase ,thus attracting more farmers to enter the production process in the next season which leads to excess produce on the market thus reduction in prices. which push most of the farmers out of the market,,, the process continues.
dear Tejvan thanks a lot your site is really interesting
Also the seasonality is one of the factors that makes the price of agricultural products to be unstable.
Another thing is perishability of agricultural products like tomatoes
why do primary products cost fluctuate ?
State of the government and government policy. issues of political interest across boarders, exhibited in differentiated embargos, taxes and tax exceptions of particular agro-inputs and ago-products as revenue and tariffs against and in favors of state orientations… Poor and young economies are most likely to have unstable prices as opposed to well managed and stable economies.
What are the methods of controlling price fluctuation of agricultural production
https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/glossary/buffer-stocks/
https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/69/markets/government-price-control/
Thank u , your explanations are really interesting .
But I have a question please help me the “characteristics of agricultural price”.
also to add ,the requirement to process agricultural products before consumption increases the price spread.They are also associated with bulkiness which makes transportation and storage expensive thus the prices may fluctuate in different regions .
I love your site. It really helped understand this concept better. Nice one
Thanks alot you have helped me learn more about economics