Readers Question: List and briefly describe the positive and negative attributes of multinational corporations (MNCs).
Multinational corporations are large companies with operations in several countries across the world. For example, Apple, Ford, Coca-Cola, Alphabet (Google) and Microsoft. Their size and turnover can be greater than the total GDP of many developing economies.
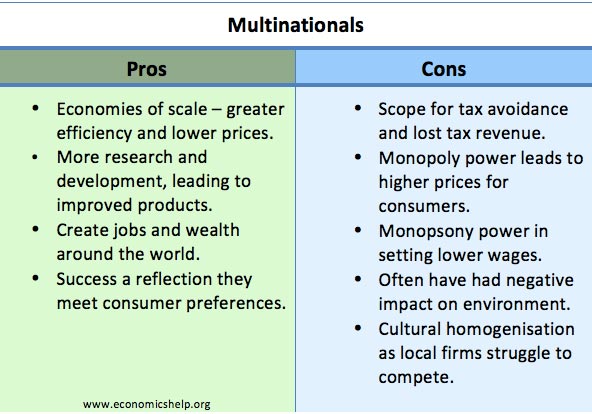
Benefits of Multinational Corporations
- Create wealth and jobs around the world. Inward investment by multinationals creates much needed foreign currency for developing economies. They also create jobs and help raise expectations of what is possible.

- Their size and scale of operation enable them to benefit from economies of scale enabling lower average costs and prices for consumers. This is particularly important in industries with very high fixed costs, such as car manufacture and airlines.
- Large profits can be used for research & development. For example, oil exploration is costly and risky; this could only be undertaken by a large firm with significant profit and resources. It is similar for drug manufacturers who need to take risks in developing new drugs.
- Ensure minimum standards. The success of multinationals is often because consumers like to buy goods and services where they can rely on minimum standards. i.e. if you visit any country you know that the Starbucks coffee shop will give something you are fairly familiar with. It may not be the best coffee in the district, but it won’t be the worst. People like the security of knowing what to expect.
- Products which attain global dominance have a universal appeal. McDonald’s, Coca-Cola, Apple have attained their market share due to meeting consumer preferences.
- Foreign investments. Multinationals engage in Foreign direct investment. This helps create capital flows to poorer/developing economies. It also creates jobs. Although wages may be low by the standards of the developed world – they are better jobs than alternatives and gradually help to raise wages in the developing world.
- Outsourcing of production by multinationals – enables lower prices; this increases disposable incomes of households in the developed world and enables them to buy more goods and services – creating new sources of employment to offset the lost jobs from outsourcing manufacturing jobs.
Criticisms of Multinational Corporations
- Companies are often interested in profit at the expense of the consumer. Multinational companies often have monopoly power which enables them to make an excess profit. For example, Shell made profits of £14bn last year.
- Tax avoidance. Many multinationals set up companies in countries with the lowest tax rate. They funnel profit through the countries with the lowest corporation tax rates – e.g. Bermuda, Ireland, Luxemburg. For example: in 2011, Google had £2.5bn of UK sales, but only paid £3.4 million UK tax. A tax rate of 00.1% despite having a global-wide profit margin of 33%. (tax avoiding companies) This means the multinationals are ‘free-riding on smaller companies who cannot attain the same creative tax accounts.
- Cash reserves – Apple has cash reserves of $216bn, 93% of which is overseas. This represents deadweight welfare loss. It is not being used for investment
- Their market dominance makes it difficult for local small firms to thrive. For example, it is argued that big supermarkets are squeezing the margins of local corner shops leading to less diversity.
- In developing economies, big multinationals can use their economies of scale to push local firms out of business.
- In the pursuit of profit, multinational companies often contribute to pollution and use of non-renewable resources which is putting the environment under threat. For example, some MNCs have been criticised of outsourcing pollution and environmental degradation to developing economies where pollution standards are lower.
- ‘Sweat-shop labour’ MNCs have been criticised for using ‘slave labour’ – workers who are paid a pittance by Western standards.
- Outsourcing to cheaper labour-cost economies has caused loss of jobs in the developed world. This is an issue in the US where many multinationals have outsourced production around the world.
Evaluation
- Some criticisms of MNCs may be due to other issues. For example, the fact MNCs pollute is perhaps a failure of government regulation. Also, small firms can pollute just as much.
- MNCs may pay low wages by western standards but, this is arguably better than the alternatives of not having a job at all. Also, some multinationals have responded to concerns over standards of working conditions and have sought to improve them.
What do you think of Multinational companies? – leave comment below.

This post is very simple to read and appreciate without leaving any details out. Great work!
MNCs are good though they have a aim of taking the benefit of undeveloped countries to better themselves ,,from my point of view,,since even if employment is created we are enticed not to work appropriately to develop our own indigenous local company