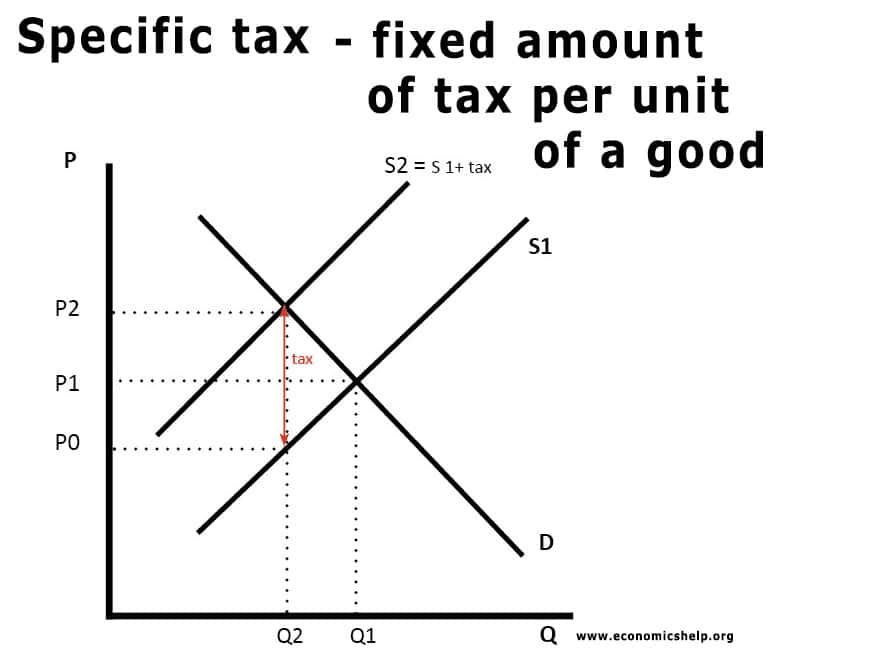
Shut down price
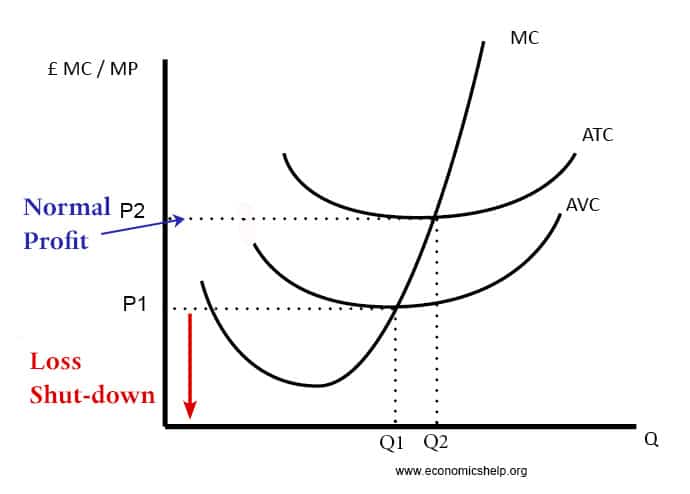
The shut down price are the conditions and price where a firm will decide to stop producing. It occurs where AR <AVC The shut down price is said to occur, where price (average revenue AR) is less than average variable costs (AVC). At this price (AR<AVC), the firm is making an operating loss. The total …