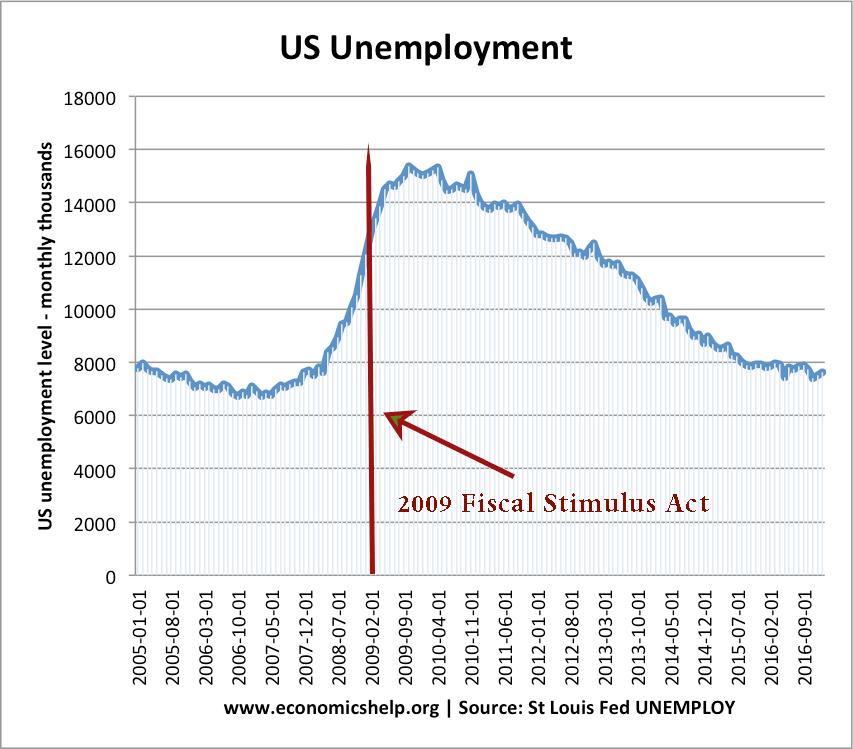
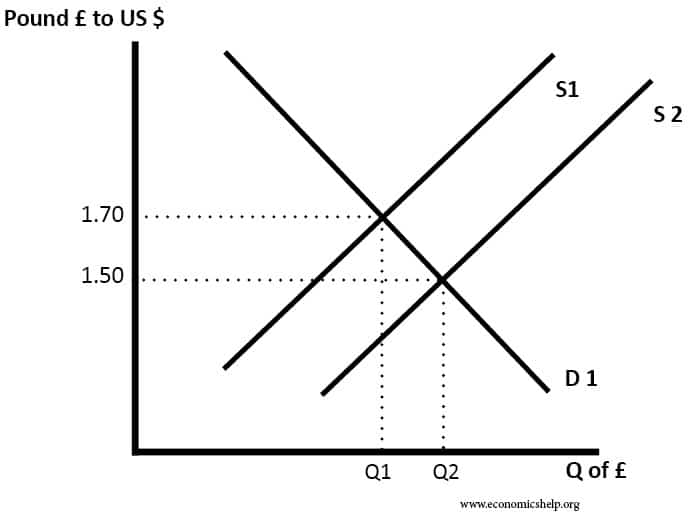
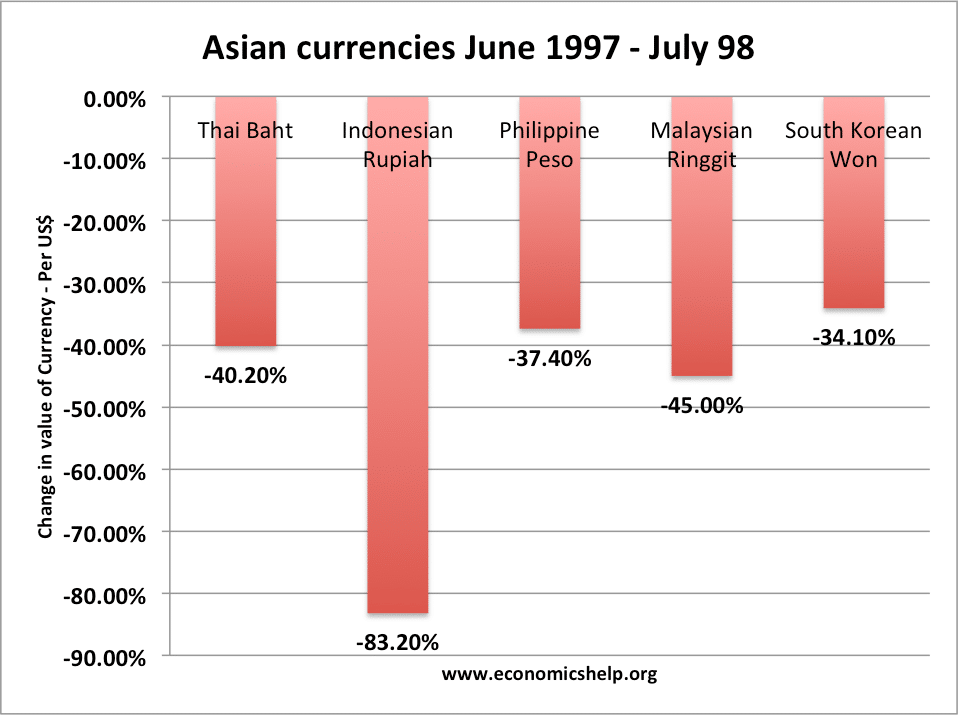
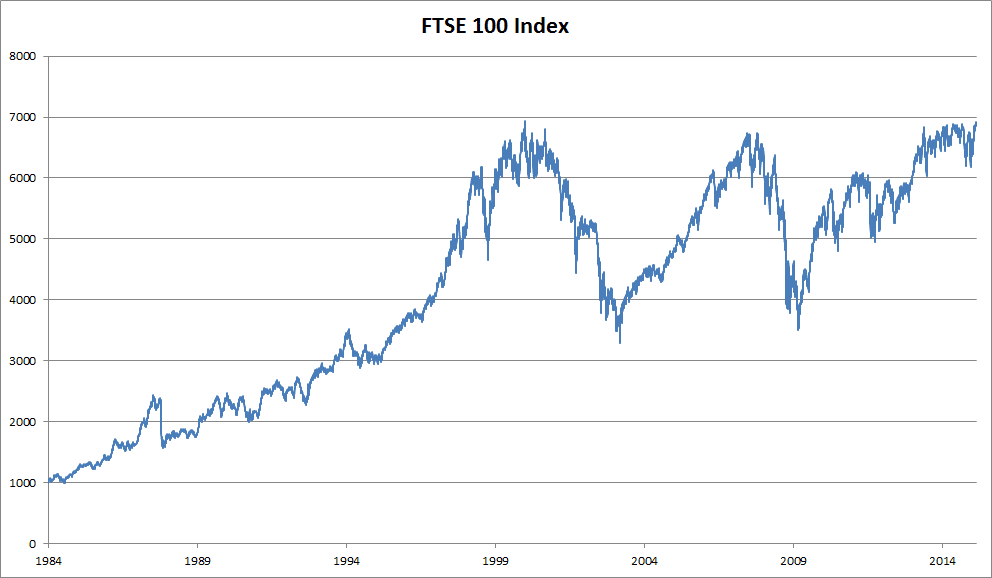
Solutions to national debt
Readers Question: Please is there any solution to national/public debt? National (public sector) debt is the outstanding level of debt owed by the government to the private sector. It is the accumulation of annual budget deficits. Do we need a solution? Firstly, it is worth evaluating whether we need an actual ‘solution.’ National debt has …