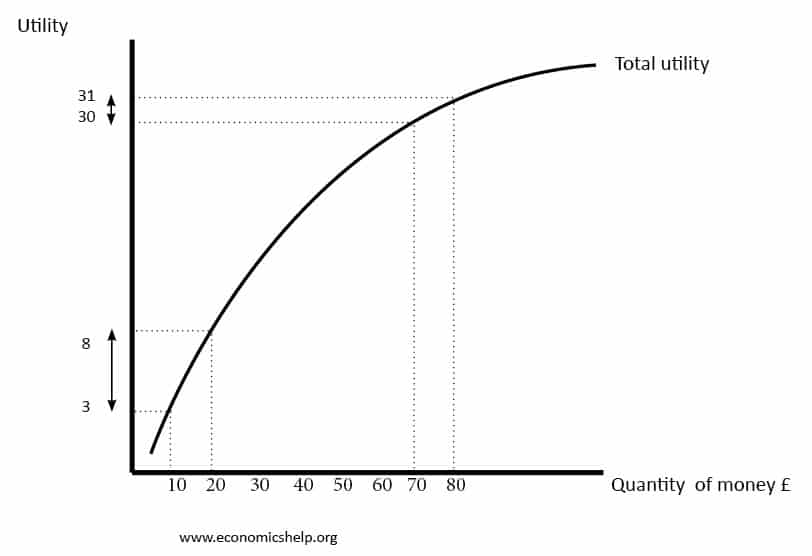
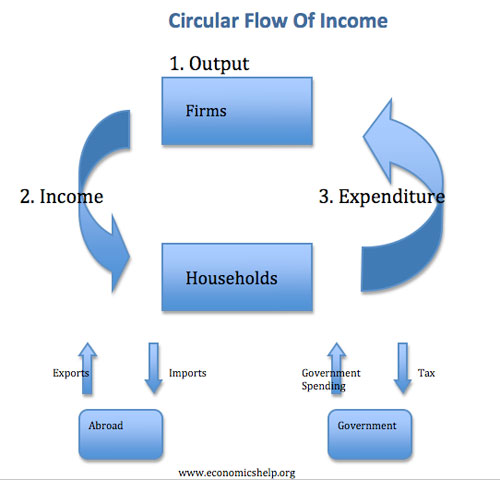
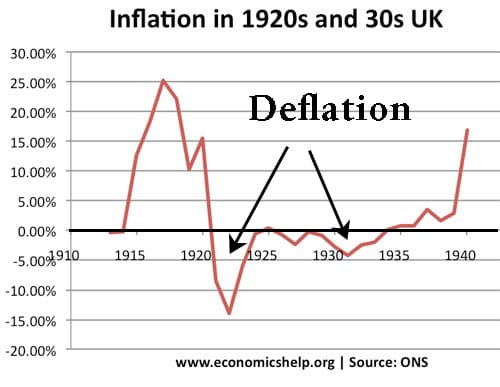
Readers Question: what is the solution for stagflation?
Stagflation occurs when there is an increase in inflation and also at the same time an increase in unemployment and lower economic growth.
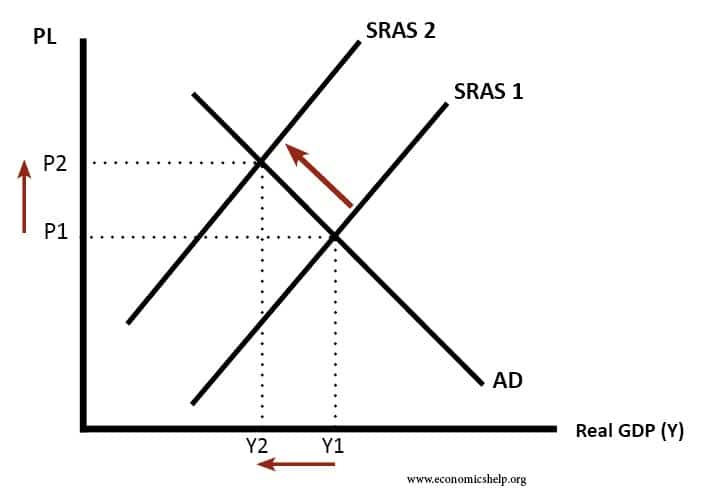
Typically stagflation will be caused by an increase in the cost of production which shifts the SRAS curve to the left. This could be caused by a rise in oil prices.
Diagram of Stagflation
The diagram shows that the stagflation causes the price level to rise from P1 to P2. Output falls from Y1 to Y2
How to solve stagflation?
It is not easy. For example, the Central Bank could use Monetary policy to try and reduce inflation. Higher Interest rates increase the cost of borrowing and this will reduce aggregate demand (AD). This will be effective for reducing inflation, but, it will cause a bigger fall in GDP. Therefore, the Central Bank may be reluctant to target inflation when growth is already low.
In 2008/09, The Bank of England tolerated cost-push inflation of 5% because they were concerned about UK economic growth.